Themed collection Ionic liquids: from fundamental properties to practical applications

Fundamental properties and practical applications of ionic liquids: concluding remarks
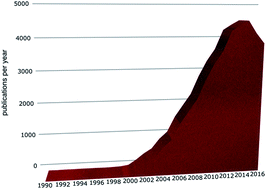
The Faraday Discussion on Ionic Liquids: From Fundamental Properties to Practical Applications took place in Cambridge in September 2017. A summary of the conference and a vision for the future of ionic liquids are presented.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 587-601
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD90090B
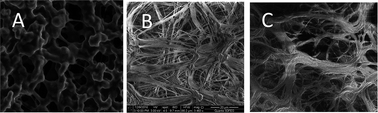
Selective separation of furfural and hydroxymethylfurfural from an aqueous solution using a supported hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent liquid membrane
For the first time, 12 different supported deep eutectic solvent (DES) liquid membranes were prepared and characterized.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 77-92
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00152E
Brønsted acidity in deep eutectic solvents and ionic liquids
Relative pH values are calculated using an indicator dye and a glass electrode, and they are found to provide consistent results.

Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 365-377
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00153C
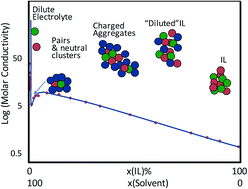
New dimensions in salt–solvent mixtures: a 4th evolution of ionic liquids
The important properties and applications of molecular liquid mixtures with ionic liquids and low melting organic salts are discussed.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 9-28
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00189D
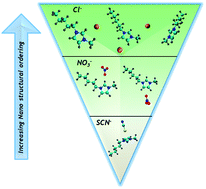
Design principles from multiscale simulations to predict nanostructure in self-assembling ionic liquids
Nanoscale MD simulations with the Effective Fragment Potential are performed on aqueous mixtures of dialkylimidazolium ILs paired with three anions, producing insights on ionic domain structure. Ionic domain structure is correlated to nanoscale structure as determined by SAXS.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 159-181
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00154A
Structure and lifetimes in ionic liquids and their mixtures
With the aid of molecular dynamics simulations, we study the structure and dynamics of different ionic liquid systems.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 219-245
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00166E
Biredox ionic liquids: new opportunities toward high performance supercapacitors
Nowadays, commercial supercapacitors are based on purely capacitive storage, and porous carbons are used as electrodes.

Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 393-404
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00174F
Molecular scale structure and dynamics at an ionic liquid/electrode interface
The structural arrangement and dynamics of ions near the IL/electrode interface during charging and discharging was studied by a combination of time resolved X-ray reflectivity and impedance spectroscopy.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 141-157
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00171A
Exploring the bulk-phase structure of ionic liquid mixtures using small-angle neutron scattering
Small-angle neutron scattering experiments, supported by molecular dynamics simulations, have been performed on a range of compositions of the [C2mim]1−x[C12mim]x[Tf2N] ionic liquid mixture system.
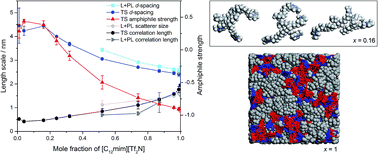
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 265-289
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00167C
Determining the composition of the vacuum–liquid interface in ionic-liquid mixtures
The vacuum–liquid interfaces of a number of ionic-liquid mixtures have been investigated using a combination of RAS-LIF, selected surface tension measurements, and molecular dynamics simulations.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 497-522
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00175D
Exfoliation of graphene and fluorographene in molecular and ionic liquids
We use molecular dynamics simulations to study the exfoliation of graphene and fluorographene in molecular and ionic liquids using computer experiments in which one layer of the 2D nanomaterial is peeled, in vacuum or with solvent present.
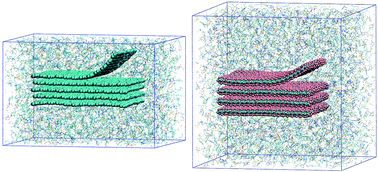
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 61-75
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00169J
Nano-mechanics of ionic liquids at dielectric and metallic interfaces
Using a dynamic surface force apparatus, we investigate the nano-mechanics and the nano-rheology of an ionic liquid at dielectric and metallic solid surfaces.
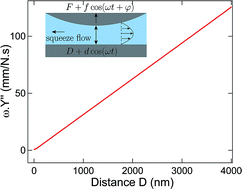
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 443-457
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00149E
Atomic charges of sulfur in ionic liquids: experiments and calculations
A wide variety of experimental and computational methods are used to probe sulfur atomic charges in ionic liquids.
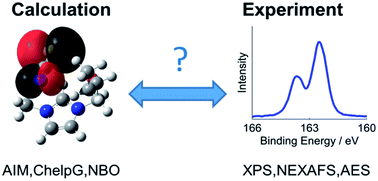
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 183-201
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00155J
Time-resolved SERS study of the oxygen reduction reaction in ionic liquid electrolytes for non-aqueous lithium–oxygen cells
We use the Raman active bands of O2˙− to probe its changing Lewis basicity through its interaction with various ionic liquid electrolytes at the electrode surface.
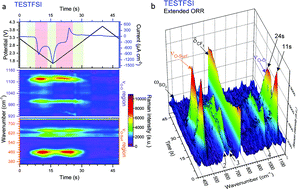
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 379-392
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00170C
Interfacial structure and structural forces in mixtures of ionic liquid with a polar solvent
Oscillatory and monotonic decay in mixtures of salt and solvent at interfaces with varying surface charge.
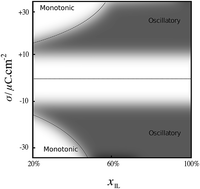
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 427-442
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00168A
Interactions and stabilisation of acetone, sulfur dioxide and water with 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate [OMIM][BF4] at low temperatures
After heating the acetone under the porous [OMIM][BF4] to 120 K, the acetone diffuses into pores lined with octyl chains (destabilised acetone) and pores lined with ions (stabilised acetone).
![Graphical abstract: Interactions and stabilisation of acetone, sulfur dioxide and water with 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate [OMIM][BF4] at low temperatures](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C7FD00146K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2018)
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 475-495
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00146K
Low-temperature and high-pressure phases of a room-temperature ionic liquid and polyiodides: 1-methyl-3-propylimidazolium iodide
Experimental results are summarized on the P–T–m diagram. In pure [C3mim][I], amorphous phase appeared both at low-temperature and high-pressure. Stoichiometric [C3mim][I3] promotes crystallization, while non-stoichiometric [C3mim][I3.66] indicates anomalies.
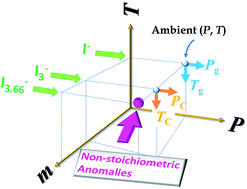
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 49-60
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00172J
Applying neutron diffraction with isotopic substitution to the structure and proton-transport pathways in protic imidazolium bis{(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl}imide ionic liquids
Neutron diffraction with isotopic substitution has been applied to examine the potential for complex-ion formation in protic imidazolium bis{(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl}imide ionic liquids.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 247-263
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00143F
Low cost ionic liquid–water mixtures for effective extraction of carbohydrate and lipid from algae
Here we show that biomass derived from Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis can be pretreated with low cost choline amino acid based ionic liquids to effectively yield lipids and sugars.
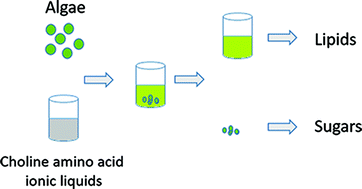
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 93-112
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00158D
ILs through the looking glass: electrostatics and structure probed using charge-inverted ionic liquid pairs
Ionic liquids combining potassium cations with 1-alkyl-3-methylcyclopentadienyl anions, K[CnC1Cp] (n = 4 and 6) have been synthesized.
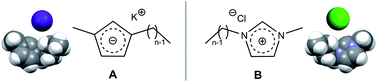
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 203-218
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00139H
The Au(111)/IL interfacial nanostructure in the presence of precursors and its influence on the electrodeposition process
Ionic liquids have attracted significant interest as electrolytes for the electrodeposition of metals and semiconductors, but the details of the deposition processes are not yet well understood.
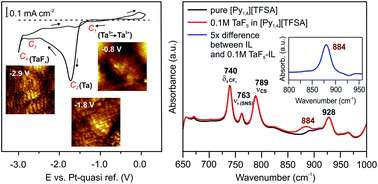
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 459-473
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00165G
How ionic species structure influences phase structure and transitions from protic ionic liquids to liquid crystals to crystals
Phase behaviour of n-alkylammonium (C6 to C16) nitrates and formates was characterised using synchrotron small angle and wide angle X-ray scattering, differential scanning calorimetry, cross polarised optical microscopy and FTIR.
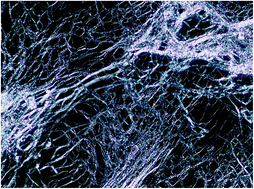
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 29-48
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00148G
Effects of the ether oxygen atom in alkyl side chains on the physical properties of piperidinium ionic liquids
Various types of piperidinium ionic liquids equipped with an oxygen atom-containing alkyl side chain on the positively charged nitrogen atom were systematically synthesized and their physical properties investigated.
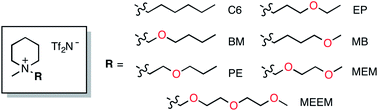
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 523-534
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00142H
Amphoteric water as acid and base for protic ionic liquids and their electrochemical activity when used as fuel cell electrolytes
Amphoteric water was mixed with equimolar amounts of a super-strong acid, trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (TfOH), and a super-strong base, 1,8-diazabicyclo-[5.4.0]-7-undecene (DBU) to explore the properties as fuel cell electrolytes.

Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 353-364
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00132K
Impact of SCILL catalysts for the S–S coupling of thiols to disulfides
SCILL catalysts are active and selective for the S–S coupling of thiols to the corresponding disulfides showing a significantly increased stability.
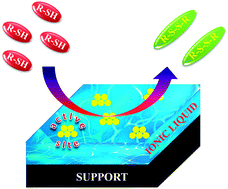
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 535-547
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00159B
Anomalous electroless deposition of less noble metals on Cu in ionic liquids and its application towards battery electrodes
Electroless deposition can be triggered by the difference in the redox potentials between two metals in an electrolyte.
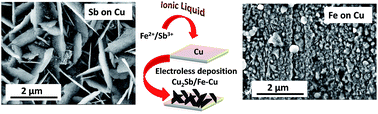
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 339-351
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00121E
Ionic liquids at interfaces: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 549-586
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD90094E
Structure and dynamics of ionic liquids: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 291-337
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD90092A
Electrochemistry: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 405-426
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD90093G
Phase behaviour and thermodynamics: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,206, 113-139
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD90091K
About this collection
We are delighted to share with you a selection of the papers which will be presented at our Faraday Discussion on Ionic liquids: from fundamental properties to practical applications taking place in Cambridge, United Kingdom in September 2017. More information about the event may be found here: http://rsc.li/ionicliquids-fd2017. Additional articles will be added to the collection as they are published. The final versions of all the articles presented and a record of the live discussions will be published after the event.
ILs have been the focus of intense research over the last 20 years because of their remarkable potential for applications coupled to favourable environmental properties. ILs are also a medium whereby the nature of the complex interactions (Coulombic, van der Waals and hydrogen bonding) provides a liquid whose structure and properties can be tuned by the choice of the cation and anion wherein reactions are likely to be distinct in terms of activity and selectivity profiles compared with common molecular solvents.
Over the last three years, there has been an increase in the range of ionic liquids (ILs) utilised and significant advances in our understanding of the fundamental aspects of these materials. Therefore, the time is apt for Faraday Discussions to provide a foundation for future fundamental challenges and theories which need to be developed to move the subject area forward.