Themed collection Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology Recent HOT Articles

First report of components responsible for odor sensation from a vertical flow constructed wetland treating combined sewer overflow
A VF CW exhibited low-level production of the components responsible for odor sensation and were similar whether or not VF was operational. VOCs are the only component related to some odor sensation and were higher in the morning.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 2013-2019
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00303A
Uranium rejection with nanofiltration membranes and the influence of environmentally relevant mono- and divalent cations at various pH
Major groundwater cations can influence the U(IV) rejection of membranes. Water chemistry modeling, membrane characterization, uranium rejection, and membrane selectivity are investigated, with results showing optimal treatment operation at pH 7.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 2075-2086
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00324A
Enhanced combined sewer overflow treatment by rapid magnetic flocculation–magnetic sedimentation: efficiency and mechanism
Rapid magnetic flocculation required a reaction time of only 2 minutes to achieve the ideal pollutant removal efficiency.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 1586-1594
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00242C
Cation–π-induced mixed-matrix nanocomposite for the detection and removal of Hg2+ and azinphos-methyl towards environment remediation
Organic-cation modified MWCNTs-based nanocomposite derived membrane to reduce environmental pollution.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 1595-1609
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00114A
ZnCl2 activated mesoporous carbon from rice straw: optimization of its synthetic process and its application as a highly efficient adsorbent for amoxicillin
An optimized and efficient zinc chloride-based activation of rice straw yielded highly mesoporous carbons with an exceptional ability to adsorb the antibiotic amoxicillin. The maximum adsorption capacity was found to be as high as 1308 mg g−1.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 1389-1405
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00171K
Bioelectrochemically enhanced autotrophic Feammox for ammonium removal via the Fe(II)/Fe(III) cycle
The electrochemically assisted autotrophic Feammox achieves a faster rate of ammonium oxidation through iron cycling with an optimal applied voltage of 0.6 V.
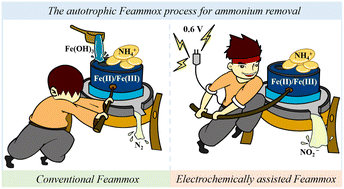
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 1355-1364
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00074A
Effect of chain length, electrolyte composition and aerosolization on the removal of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances during electrochemical oxidation
We utilized a BDD anode in a two-electrode system to investigate the degradation of a suite of PFASs in aqueous matrices.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 1377-1388
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00886J
Geochemistry, health risk assessment and statistical source identification of dissolved trace elements in surface water of the Chishui River, China
As the most famous wine industry area in China, the concentration of dissolved trace elements (DTEs) in surface water of the Chishui River has attracted attention.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 1122-1134
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00740E
Towards the cost-effective design of stormwater infiltration trenches: a hybrid model integrating cost–benefit analysis and an analytical stochastic approach
This study proposes a hybrid analytical model integrating two cost–benefit analysis approaches and an analytical stochastic approach for the proper design of infiltration trenches.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 1108-1121
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00963G
Formation of nitro(so) by-products of concern during the treatment of phenolic compounds by the hydroxylamine-enhanced Fe(II)/peroxymonosulfate process
The transformation pathway of hydroxylamine and the formation mechanism of nitro(so) by-products during the treatment of phenols using the Fe(II)/peroxymonosulfate/hydroxylamine system are elaborated.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 902-911
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00903C
Identification and quantification of diffuse groundwater pollution in a mineralised watershed
Locating and quantifying sources of metals in a mineralised catchment, using tracer injection and synoptic sampling.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 668-676
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00194F
A combined experimental and computational approach to unravel degradation mechanisms in electrochemical wastewater treatment
Understanding electrochemical oxidation mechanisms through a combined experimental and computational approach.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 652-667
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00784G
Reactions of hypobromous acid with dimethyl selenide, dimethyl diselenide and other organic selenium compounds: kinetics and product formation
We studied reactions between a variety of organic forms of the essential element selenium (Se) and the oxidant hypobromous acid (HOBr). The studied Se compounds, especially selenomethionine, had a high reactivity with HOBr.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 620-630
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00787A
Water recycling public toilets based on onsite electrochemical wastewater treatment
14-month performance study of an anaerobic bioreactor combined with electrochemical oxidation and integrated into a self-contained public bathroom under daily use in Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu, India).
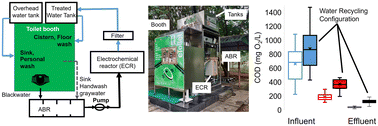
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 157-167
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00454F
Integrated fabrication of CMC@UiO-66–NH2@PEI composite adsorbents for efficient batch and dynamic phosphate capture
A separable bio-adsorbent was created through a straightforward cross-linking process, leading to effective capture of phosphate in both static and dynamic aqueous systems.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 168-181
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00685A
A stochastic approach for assessing the chronic environmental risk generated by wet-weather events from integrated urban wastewater systems
Environmental chronic risk generated by wet-weather discharges compared to final effluent was stochastically assessed, also from a climate-change perspective, stressing their growing contribution for many (micro-)pollutants.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 3174-3190
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00143A
Towards urban drainage sediment accumulation monitoring using temperature sensors
An innovative technique based on temperature measurements promises to better understand and manage sediments in urban drainage systems.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 3200-3212
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00820C
Predicted aquatic exposure effects from a national urban stormwater study
Episodic stormwater discharges expose aquatic ecosystems to extensive contaminant mixtures. Cumulative acute risks to multiple aquatic trophic levels are estimated based on contaminant mixtures documented in a US stormwater reconnaissance.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 3191-3199
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00933A
Role of height and position in the vertical distribution pattern of urban surface-deposited sediments and associated heavy metals
Urban surface-deposited sediments (USDs) with different spatial positions and heights are a mixture of various pollutants with complex sources and are widely distributed in urban environments.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 3146-3157
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00813K
Antimicrobial peptide-functionalized polyhydroxyalkanoate bio-beads as a bactericidal material for water disinfection
Introduce BDH as a new class of environmentally-friendly antimicrobial biomaterial for water disinfection.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2880-2890
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00396E
rGO induced enhanced antifouling properties in electrospun PVA–rGO nanocomposite membranes
Remediation of water contaminated by oils, using advanced materials and membrane based processes.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2891-2902
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00406F
Unlocking the effect of Zn2+ on crystal structure, optical properties, and photocatalytic degradation of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) of Bi2WO6
The effect of Zn2+ on the crystal structure, optical properties, and photocatalytic activity for degradation of perfluoroalkyl substances of Bi2WO6 was studied.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2866-2879
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00430A
Legionella pneumophila occurrence in reduced-occupancy buildings in 11 cities during the COVID-19 pandemic
Legionella pneumophila was quantified during the COVID-19 pandemic in 26 buildings in three countries to identify factors that influenced positivity.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2847-2865
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00278K
Efficient treatment of landfill leachate membrane bioreactor effluent through sequential coagulation–flocculation and electrooxidation
This study investigated the performance of sequential chemical coagulation–electrooxidation (EO) processes in treating leachate membrane bioreactor (MBR) effluent.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2253-2262
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00290J
Successful prediction for coagulant dosage and effluent turbidity of a coagulation process in a drinking water treatment plant based on the Elman neural network and random forest models
The uncertainty of the changes in the quality of raw water, and the long lag in the process of coagulation introduce significant difficulties in eliminating turbidity during the treatment of drinking water.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2263-2274
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00181D
The removal of Cd(II) by the UV/permanganate process: role of continuously in situ formed MnO2 and reactive species
Cd(II) could be removed completely by the UV/permanganate process, in which the continuously formed nano-sized MnO2 played the critical roles in its abatement.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2031-2040
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00345K
Effect of the organic carbon to nutrient (N and P) ratio on the biological performance of a microalgal–bacterial membrane photobioreactor
The MB-MPBR can achieve effluent COD, N and P discharge standards in one single step.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2021-2030
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00117B
The degradation of ciprofloxacin in the UV/NH2Cl process: kinetics, mechanism, pathways and DBP formation
In this work, UV/NH2Cl was utilized to remove ciprofloxacin (CIP) from water and the formation of disinfection by-products (DBPs) following disinfection was investigated to determine its applicability and safety.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2041-2052
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00166K
Emerging investigator series: enhancing the degradation of ciprofloxacin in water using Oxone activated by urchin-like cubic and hollow-structured cobalt@N-doped carbon prepared by etching-engineering: a comparative study with mechanistic and eco-toxic assessments
Enhancing the degradation of ciprofloxacin in water using Oxone activated by urchin-like cubic and hollow-structured cobalt@N-doped carbon.
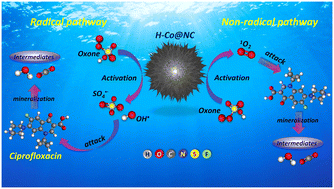
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1992-2007
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00009E
Nanobubbles can modulate microbial communities and sedimentary ecosystem during the treatment of pond water
Nanobubbles are applied in diverse water-treatment technologies.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1804-1812
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00257H
Treatment of wastewater from the thermal desorption of oil-contaminated soil: performance and sorption mechanism of pyrolytic modified sawdust
Waste biomass sawdust was modified into adsorbent by pyrolysis. The properties of modified sawdust and the mechanism of oil removal were discussed. The modified sawdust was first used to remove emulsified oil from thermal desorption wastewater.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1599-1609
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00918H
Treatment of nitrate-contaminated groundwater using microbially enhanced permeable reactive barrier technology
We present a preliminary design for a microbial-enhanced permeable reactive barrier technology for the treatment of nitrate contaminated groundwater.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1610-1619
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00019B
Co-adsorption of tetracycline and Cu(II) onto a novel amino-functionalized biochar: adsorption behavior and mechanism
In this work, a novel amino-functionalized biochar (NS-700) was prepared successfully by pretreating biomass with (NH4)2S2O8, and could be used for the simultaneous and efficient removal of tetracycline (TC) and Cu(II).
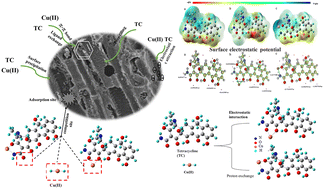
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1577-1586
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00985D
Probing into the mechanisms of disinfection by-product formation from natural organic matter and model compounds after UV/chlorine treatment
Compared to regulated DBPs such as TCM and TCAA, the significant formation of chloral hydrate and nitrogenous DBPs associated with UV/chlorine treatment needs close scrutiny when considering this process being applied in practice.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1587-1598
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00065F
Amino acid-driven adsorption of emerging contaminants in water by modified graphene oxide nanosheets
Amino acid modified graphene nanosheets adsorb emerging contaminants from tap water outperforming unmodified precursors and activated carbon for carbamazepine, bisphenol A and benzophenone 4. Structure–adsorption relationships are unraveled.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1030-1040
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00871H
Combined sewer overflows: relating event duration monitoring data to wastewater systems' capacity in England
Water pollution caused by the frequent use of combined sewer overflows (CSOs) has been attracting increased media and political coverage in England as in other places in the world.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 707-722
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00637E
Pyrolysis transports, and transforms, PFAS from biosolids to py-liquid
Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in wastewater solids have resulted in bans on land application of biosolids, causing utilities to explore thermal treatment options.
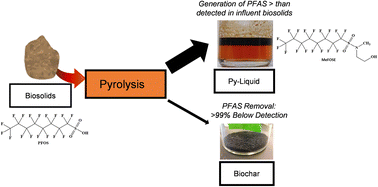
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 386-395
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00677D
Novel protein nanofibril–carbon hybrid adsorbent efficiently removes As(III), As(V) and other toxic elements from synthetic and natural waters in batch and rapid small-scale column tests
Novel adsorbents produced from β-lactoglobulin, a low-cost milk protein, have shown a high affinity to inorganic As(III) and As(V).

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 375-385
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00502F
The role of ammonia oxidizing microorganisms in biofiltration for the removal of trace organic compounds in secondary wastewater effluent
Although nitrifying microorganisms play an important role in TOrC biotransformation, ammonia-rich environments appear to hinder important cometabolic processes, whereas low-dose monochloramine has minimal impact on biofilter performance.
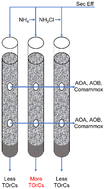
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2994-3006
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00662F
Spatiotemporal profiling of chemicals of emerging concern in a megacity: a case study of Lagos, Nigeria
This is the first study reporting the use of pharmaceutical and illicit drugs by profiling wastewater in Lagos, Nigeria.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2917-2939
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00034B
Sludge-based biochar with lanthanum modification for phosphate recovery from wastewater streams
Sludge based biochar granules were prepared and modified with lanthanum for effective phosphate recovery from wastewater and anaerobic digestion liquid.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2873-2883
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00624C
Piezoelectric catalytic performance of BaTiO3 for sulfamethoxazole degradation
During the piezoelectric catalytic process, highly reactive species might be generated and contribute to the effective degradation of the target organic pollutants.
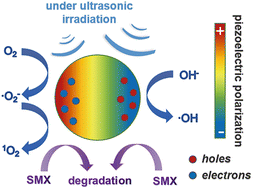
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 3007-3018
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00314G
Kinetics, products and pathways for the removal of pentachlorophenol (PCP) by sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-nZVI)
Sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-nZVI) was applied in the treatment of pentachlorophenol (PCP)-polluted water to explore the reaction pathways and the effects of water chemistry on PCP adsorption and transformation.
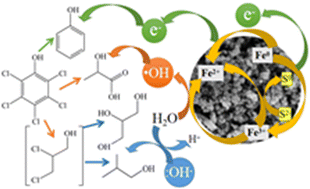
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2567-2579
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00440B
Cationic dye removal using surface treated activated carbon as an adsorbent
The use of treated activated carbon (AC) is investigated to eliminate cationic dye malachite green (MG) using modelled dye solution.
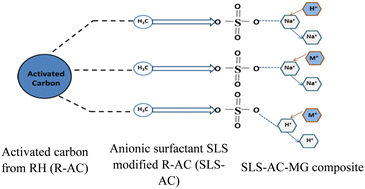
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2545-2566
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00460G
QSDsan: an integrated platform for quantitative sustainable design of sanitation and resource recovery systems
QSDsan is an open-source platform that integrates the design, simulation, and sustainability characterization of sanitation and resource recovery systems.
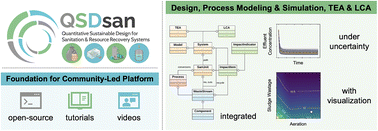
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2289-2303
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00455K
Enhanced electro-peroxymonosulfate activation using a carbon nanotube filter with a functionalized polyelectrolyte
An innovative electroactive membrane was designed with polyelectrolyte modification for electro-PMS activation and degradation of refractory organic contaminants in a flow-through filtration model.
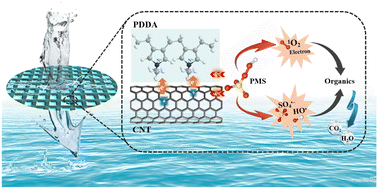
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2314-2325
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00398H
Effects of dissolved oxygen on water quality and biofilms in the raw water distribution pipeline for a reserved water source
Higher initial DO concentrations could enhance the nitrification reaction and purification process of the raw water.
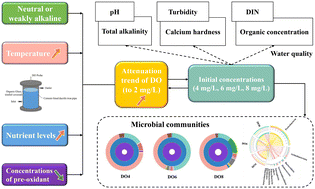
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2277-2288
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00184E
Degradation of sulfapyridine antibiotics by chlorination in a pilot-scale water distribution system: kinetics, THMs, and DFT studies
Sulfonamides (SAs) have been proved to damage organisms if the contact time last over the long term.
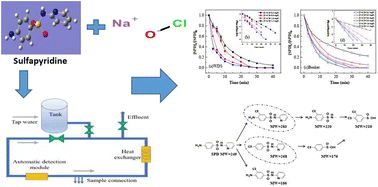
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2207-2215
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00198E
Inactivation mechanisms of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica by free residual chlorine
The sub-cellular mechanisms by which residual free chlorine (FC) inactivates E. coli O157:H7 and S. enterica in the absence of organic matter was investigated.
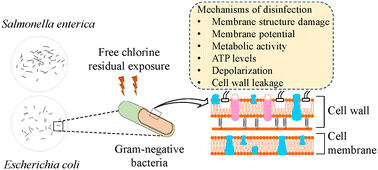
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2006-2018
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00382A
Preparation of an rGO and iron oxide nanoparticle-incorporated polyvinyl acetate based membrane for the removal of Pb2+ from anticorrosive paint industrial wastewater
rGO–Fe2O3 NPs incorporated PVAc based mixed matrix membrane for efficient removal of Pb2+ from anti-corrosive paint industrial wastewater.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1895-1909
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00172A
Mechanism of galvanic reduction of selenate oxyanions and surface immobilization by nano zero-valent iron aggregates under anaerobic conditions: towards high electron efficiency
Elucidation of the galvanic mechanism of selenate reduction by nZVI leads to >99.95% removal and record electron efficiency by suppressing H2 evolution via in situ Se doping.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1910-1922
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00321J
Integrated experimental and modeling evaluation of removal efficiency and energy consumption for an autotrophic denitrifying biocathode
A mathematical model for autotrophic biocathodic denitrification of groundwater has been developed. The model predictions captured current demand and energy consumption related to reduction of N-forms.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1466-1477
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00165A
The development of a rapid monitoring method for radiocesium in seawater in the Fukushima region
A new monitoring method has been developed for the rapid assessment of low levels of 137-Cs and its effective concentration and quantification in Fukushima seawater, directly using KCuHCF slurry ink with a 137-Cs recovery exceeding 99% within 30 min.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1547-1560
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00211F
Recovery of anaerobic ammonium oxidation via hydrazine following sulfate inhibition
The presence of sulfate in sewage treatment has obvious impacts on biological nitrogen removal.
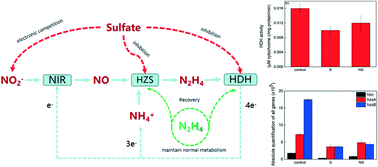
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1458-1465
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00041E
Removal of 293 organic compounds in 15 WWTPs studied with non-targeted suspect screening
The influence of WWTP treatment standard on contaminant breakthrough is explored for 293 compounds.
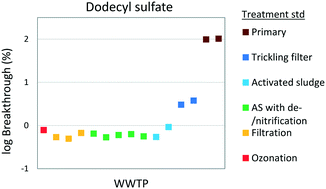
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1423-1433
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00088A
Emerging investigator series: meta-analyses on SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA levels in wastewater and their correlations to epidemiological indicators
Recent applications of wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) have demonstrated its ability to track the spread and dynamics of COVID-19 at the community level.
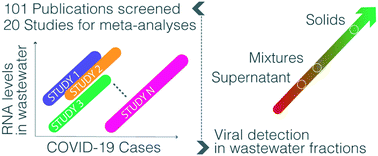
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1391-1407
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00084A
Elimination of micropollutants by the solar/chlorine process: contribution of reactive species and formation risk of NDMA
Role of reactive species in the solar/chlorine process for elimination of diuron and risk of NDMA formation.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1252-1260
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00965F
Drivers of variability in disinfection by-product formation potential in a chain of thermally stratified drinking water reservoirs
Increasing hydraulic residence time (HRT) along a chain of interconnected reservoirs enhances the formation potential of carbonaceous disinfection by-products (DBPs) and reduces the formation potential of nitrogenous DBPs, particularly N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA).

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 968-980
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00788B
Emerging investigator series: a comparison of strong and weak-acid functionalized carbon electrodes in capacitive deionization
Strong-acid functionalized cathode is pH stable and sulfonic groups are stable to charge–discharge cycling.
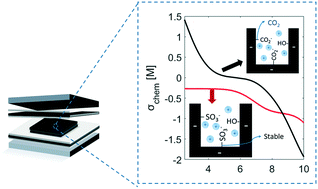
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 949-956
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00967B
Succession of founding microbiota in an anaerobic baffled bioreactor treating low-temperature raw domestic wastewater
Spatiotemporal development of anaerobic seed sludge in a new ABR after transfer from a long-running ABR treating low-temperature domestic wastewater.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 792-806
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00014H
Simultaneous prediction of trihalomethanes, haloacetic acids, haloacetonitriles and haloacetamides using simulated distribution system tests
This study analysed the spatial and temporal occurrence of 29 disinfection by-products (DBPs) formed by chlorination and chloramination.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 742-756
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00824B
SARS-CoV-2 RNA is enriched by orders of magnitude in primary settled solids relative to liquid wastewater at publicly owned treatment works
We compared SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentrations in primary settled solids and raw wastewater samples matched in date to investigate the relationship between the two matrices.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 757-770
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00826A
Glycerol-driven denitratation: process kinetics, microbial ecology, and operational controls
This study implicated stoichiometric limitation of influent organic carbon, unique microbial community enrichment, and differential nitrate and nitrite reduction kinetics as determinant factors in glycerol-driven denitratation.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 729-741
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00700A
Comparison of disinfection in intermittently mixed (6 am–6 pm) and continuously mixed high rate algal ponds treating domestic wastewater in winter
Daytime-only and continuously mixed HRAPs had equivalent disinfection performance, compliant with reuse guidelines. Daytime-only mixing reduces energy demand and capital cost of wastewater treatment, promoting adoption of HRAPs in rural communities.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 771-780
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00691F
Modelling of a CH4-producing microbial electrosynthesis system for energy recovery and wastewater treatment
Electrode kinetics, gaseous CO2 dissolution, mass transfer, and equilibrium of pH buffer and bicarbonate are considered to illustrate the bioelectrochemical behaviors of an MES.
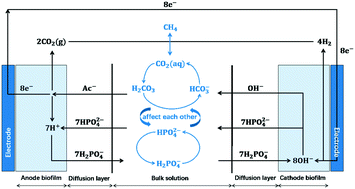
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 781-791
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00725D
Simple and selective method for simultaneous removal of mercury(II) and recovery of silver(I) from aqueous media by organic ligand 4,4′-azo-1,2,4-triazole
Based on coordination chemistry, the removal of Hg2+ and the recovery of Ag+ are achieved simultaneously by selecting the 4,4′-azo-1,2,4-triazole (Atrz) as an organic ligand only through simple mixing, agitation and filtration.
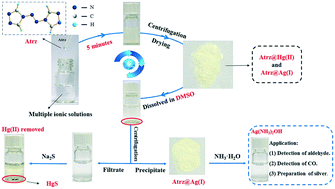
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 534-542
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00651G
Reactivities of hydrated electrons with organic compounds in aqueous-phase advanced reduction processes
Novel linear free energy relationships were determined between experimentally measured rate constants of solvated electrons and theoretically calculated one electron reduction potential for the elucidation of reductive reaction mechanisms.
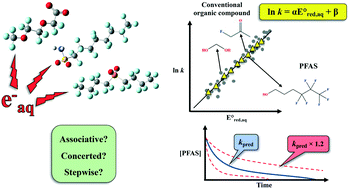
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 543-574
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00897H
Application of plasma for the removal of pharmaceuticals in synthetic urine
Application of plasma oxidation for removal of pharmaceuticals in urine was assessed and compared to a traditional advanced oxidation process.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 523-533
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00863C
Fate of influent microbial populations during medium chain carboxylic acid recovery from brewery and pre-fermented food waste streams
Waste streams continuously introduce active and inactive microbial populations that can influence assembly of microbial communities in chain elongation systems.
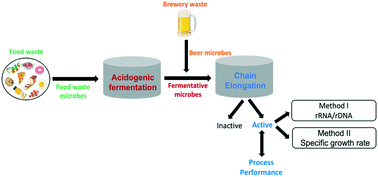
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 257-269
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00656H
Exploring the carbon and nitrogen removal capacity of a membrane aerated biofilm reactor for low-strength municipal wastewater treatment
Sustainable HRT of 3–4 h achieved for MABR effluent with carbon and nitrogen meeting the discharge standard of level I class A in China for synthetic municipal wastewater treatment.
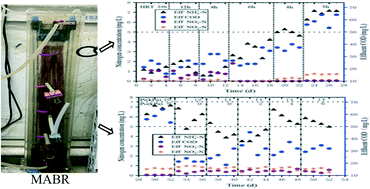
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 280-289
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00724F
About this collection
Here is a collection of recent Environmental Science: Water, Research & Technology articles which have been classified as ‘HOT articles’ due to receiving particularly high scores at peer review.