Themed collection Advances in Passive Sampling of Contaminants

Advancing passive sampling of contaminants in environmental science
Guest editors Philipp Mayer, Frank Wania and Charles Wong introduce the Passive sampling themed issue of Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 366-368
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EM90004A
Measurement of environmental pollutants using passive sampling devices – an updated commentary on the current state of the art
State-of-the-art of passive sampling techniques for environmental monitoring; future applications and directions for research.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 369-373
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00585B
A review of passive sampling systems for ambient air mercury measurements
Application of passive sampling methods for measurement of Hg concentrations and deposition is useful for understanding sources and trends.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 374-392
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00501A
Monitoring for contaminants of emerging concern in drinking water using POCIS passive samplers
Contaminants of emerging concern (CEC) have been detected in drinking water world-wide.
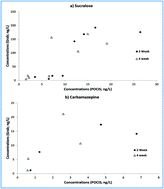
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 473-481
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00508A
Cluster analysis of passive air sampling data based on the relative composition of persistent organic pollutants
Cluster analyses of POP data distinguish sampling sites influenced by local sources from those with regional or continental POP fingerprints.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 453-463
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00605K
Remedy performance monitoring at contaminated sediment sites using profiling solid phase microextraction (SPME) polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) fibers
A demonstration of solid phase microextraction techniques using polydimethylsiloxane fibers to assess in situ contaminated sediment remedy performance at three sites.
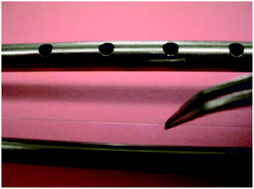
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 445-452
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00695F
Quantitative passive soil vapor sampling for VOCs- part 2: laboratory experiments
Passive diffusive samplers for VOC concentration monitoring can also be used under conditions similar to soil vapor sampling applications.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 491-500
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00128H
Quantitative passive soil vapor sampling for VOCs- part 3: field experiments
Passive soil vapor sampling can now be used to quantify concentrations of VOC vapors, no longer just the relative mass.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 501-510
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00653K
Outdoor passive air monitoring of semi volatile organic compounds (SVOCs): a critical evaluation of performance and limitations of polyurethane foam (PUF) disks
A polyurethane foam passive air sampler shows large inter-compound variability in sampling performance for semivolatile organic compounds in the outdoor environment.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 433-444
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00644A
Quantitative passive soil vapor sampling for VOCs- part 1: theory
Passive soil vapor sampling has been used for VOC assessment for decades, but the ability to determine concentrations from the mass of an analyte sorbed by the sampler has not been well established, until now.
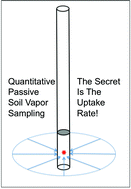
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 482-490
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00652B
Evaluation of DGT as a long-term water quality monitoring tool in natural waters; uranium as a case study
DGT can be used as a long-term water quality environmental monitoring tool, however extensive DBL measurements are recommended.
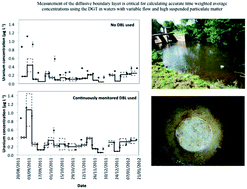
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 393-403
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00574G
Silicone passive equilibrium samplers as ‘chemometers’ in eels and sediments of a Swedish lake
The potential of passive equilibrium sampling to study the thermodynamic controls on persistent organic chemicals in the environment is illustrated for bioaccumulation of HCB and PCBs in a Swedish lake.
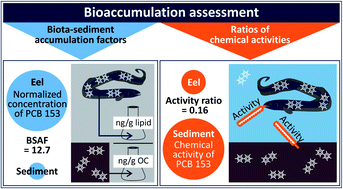
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 464-472
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00589E
Testing flow-through air samplers for use in near-field vapour drift studies by measuring pyrimethanil in air after spraying
Field evaluation of flow-through samplers indicates their viability as a wind-driven alternative to high-volume samplers in pesticide vapour drift studies.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 422-432
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00498H
Field calibration of low density polyethylene passive samplers for gaseous POPs
A field calibration study of low density polyethylene for measuring atmospheric concentrations of persistent organic pollutants was performed in East Providence (RI), USA.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 414-421
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00493G
Neutral polyfluoroalkyl substances in the global Atmosphere
Active and passive air sampling confirms ubiquitous presence of fluorinated telomer alcohols, sulfonamides, and sulfonamidoethanols in the global atmosphere.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014,16, 404-413
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00499F
About this collection
This themed collection, guest edited by Philipp Mayer, Frank Wania and Charles S. Wong showcases some of the latest developments in passive sampling research – which has now progressed well beyond measuring aqueous concentrations of legacy contaminants. The contributions in this collection contain a wide range of different passive sampling approaches which were applied to water, air, soil vapours, sediments and even fish tissue. Improved sampler designs and materials are being developed and tested, contributing to the increasing popularity of passive sampling. The apparent simplicity of passive sampling is at the core of its true potential and betrays a wealth of opportunity for future research and monitoring.