Themed collection Geochemistry

Environmental significance of trace elements in the Athabasca Bituminous Sands: facts and misconceptions
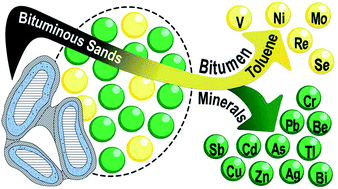
The distribution of trace elements (TEs) in the bituminous sands is dichotomous: V, Ni, Mo, Se and Re are found predominantly in the bitumen fraction, and all other TEs in the mineral fraction.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1279-1302
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00049K
Mechanism and applications of bidirectional extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella
Electrochemically active microorganisms (EAMs) play an important role in the fields of environment and energy.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1863-1877
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00224A
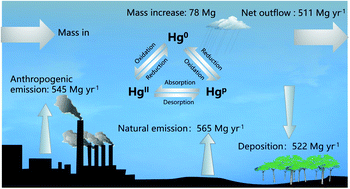
Mercury pollution in China: implications on the implementation of the Minamata Convention
This paper summarizes the atmospheric release of Hg, distribution of air Hg concentration, human exposure to MeHg and health impacts caused by Hg pollution in China.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 634-648
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00039C
Development of a sampling protocol for collecting leaf surface material for multiphase chemistry studies
We describe a robust and flexible protocol to collect water-soluble chemicals from leaf surfaces for atmosphere-biosphere interaction studies.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1008-1021
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00065J
Potential effects of soil petroleum contamination on decomposition of Artemisia annua plant litter
Artemisia annua litter produced in soil contaminated with 15 and 30 g kg−1 of petroleum exhibited significantly lower decomposition rates than that from uncontaminated soil.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1022-1030
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00096J
An uneven distribution of strontium in the coccolithophore Scyphosphaera apsteinii revealed by nanoscale X-ray fluorescence tomography
Coccolithophores are biogeochemically and ecologically important phytoplankton that produce calcium carbonate scales, or coccoliths. Here, we show that one species of coccolithophore grows coccoliths with uneven distribution of Sr, in contrast to current fractionation model theory.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 966-974
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00509G
Atmospheric mercury uptake and accumulation in forests dependent on climatic factors
The uptake of total gaseous mercury (TGM) by Korean forest foliage is mainly affected by local wind speed, boosting its passage and absorption. Mercury levels and isotopic signatures in litter and topsoil fluctuate, particularly in areas with high wind speed, temperature, and low elevation.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 519-529
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00454F
Elevated levels of environmental radioactivity in fluvial sediment: origin and health risk assessment
To study the geogenic processes of naturally occurring radioactive materials' distribution, a transboundary Himalayan river (Punarbhaba) is chosen due to its trivial anthropogenic impacts.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 555-581
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00455D
Emerging investigator series: impacts of land use on dissolved organic matter quality in agricultural watersheds: a molecular perspective
In aquatic systems, dissolved organic matter (DOM) has important ecological and biogeochemical functions, where the molecular composition of DOM has larger-scale implications for climate change and global carbon cycles.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 247-258
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00506B
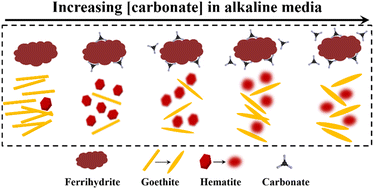
Effects of carbonate on ferrihydrite transformation in alkaline media
This study indicates that in alkaline media, carbonate slightly inhibits ferrihydrite transformation and suppresses goethite formation, but promotes hematite formation, which has important implications for elemental biogeochemical cycles.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 288-297
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00469D
Contrasted redox-dependent structural control on Fe isotope fractionation during its adsorption onto and assimilation by heterotrophic soil bacteria
Despite the importance of structural control on metal stable isotope fractionation in inorganic and abiotic systems, the link between metal structural changes and related isotopic fractionation during reactions with organic surfaces and live cells remains poorly established.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 344-356
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00332A
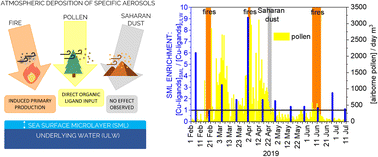
How do certain atmospheric aerosols affect Cu-binding organic ligands in the oligotrophic coastal sea surface microlayer?
We showed that oligotrophic coastal marine areas are susceptible to the deposition of pollen and aerosols from open-fire biomass burning, which alter Cu-binding organic ligands in the sea surface microlayer.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 119-135
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00415E
Contact with soil impacts ferrihydrite and lepidocrocite transformations during redox cycling in a paddy soil
We studied the transformation of 57Fe-labelled ferrihydrite and lepidocrocite mixed with a flooded paddy soil by using 57Fe-Mössbauer spectroscopy.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1945-1961
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00314K
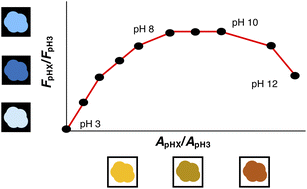
Evaluating the pH-dependence of DOM absorbance, fluorescence, and photochemical production of singlet oxygen
The protonation state of dissolved organic matter (DOM) impacts its structure and function in natural and engineered environmental systems, including DOM's ability to absorb light and form photochemically produced reactive intermediates (PPRI).
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1974-1985
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00316G
Resistance profiles of microbial communities in maize rhizospheres to the introduction of exogenous antibiotics to agricultural systems with a high arsenic geological background
The soil environment in regions with a high arsenic geological background may have enabled microbial adaptation, through co-selection mechanisms, to withstand the introduction of exogenous antibiotics.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1224-1237
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00149K
Prehistoric and technogenic loads of Hg in raised and blanket peats from the lower Amur River basin, eastern Asia
Prehistoric and modern records of Hg in peats from the lower Amur River basin, eastern Asia, were investigated.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1193-1203
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00008G
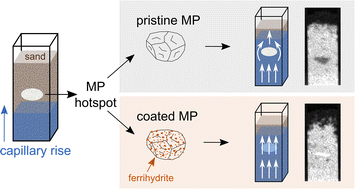
Ferrihydrite coating reduces microplastic induced soil water repellency
Addition of microplastics (MP) to soil has the potential to increase soil water repellency. Absorption of soil abundant substances on MP surfaces has the potential to overcome MP inherent hydrophobicity.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1094-1101
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00077J
Biogeochemical and hydrologic synergy control mercury fate in an arid land river-reservoir system
Methylmercury formed in anoxic reservoirs associates with organic-rich particles and is exported downstream.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 912-928
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00032J
Indexical and statistical approaches to investigate the integrated origins of elements in the sediment of Teesta River, Bangladesh: sediment quality and ecological risk assessment
This study investigates ecological consequences from the combined provenance (natural and manmade) of fifteen metal(oid)s (Na, Al, K, Ti, Cr, Mn, Co, Zn, As, Rb, Sb, Cs, Ba, Th, and U) from a major Indo-Bangla transboundary river (Teesta).

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 832-849
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00475E
Arsenic in Lake Geneva (Switzerland, France): long term monitoring, and redox and methylation speciation in an As unpolluted, oligo-mesotrophic lake
The formation and dynamic partitioning of As species in the water column of a large oligo-mesotrophic lake is driven by biological processes.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 850-869
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00431C
Fate and recovery of nitrogen applied as slow release brown coal-urea in field microcosms: 15N tracer study
The over-use of synthetic nitrogen (N) fertilisers for crop production can cause environmental pollution through leaching and gaseous losses, resulting in low N use efficiency (NUE).

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 648-658
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00482H
Laboratory growth capacity of an invasive cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa) on organic substrates from surface waters of permafrost peatlands
Under global warming, invasive cyanobacteria, can migrate northward and colonize lakes in permafrost-affected territories. This study tests the potential growth of M. aeruginosa onto various organic-rich solutions of those regions.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 659-669
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00456A
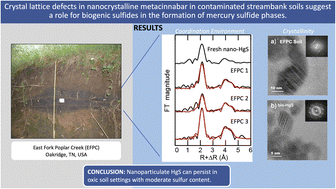
Crystal lattice defects in nanocrystalline metacinnabar in contaminated streambank soils suggest a role for biogenic sulfides in the formation of mercury sulfide phases
At mercury (Hg)-contaminated sites, streambank erosion can act as a main mobilizer of Hg into nearby waterbodies.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 445-460
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00549A
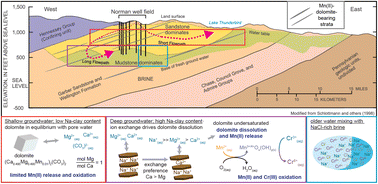
Dissolution of Mn-bearing dolomite drives elevated Cr(VI) occurrence in a Permian redbed aquifer
Cr(III) oxidation and Cr(VI) occurrence corresponds to regions of cation-exchange induced Mn-carbonate dissolution.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2419-2436
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00395C
Sorption–desorption of some transition metals, boron and sulphur in a multi-ionic system onto phyto-biochars prepared at two pyrolysis temperatures
Batch sorption–desorption of Zn, Cu, Fe, Mn, B and S onto phyto-biochars prepared from lantana, pine needles and wheat straw by pyrolysis at 300 °C and 450 °C were studied in a multi-ionic system.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2378-2397
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00212D
Controls on the photochemical production of hydrogen peroxide in Lake Erie
Photochemical production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) may not the dominant source of H2O2 in Lake Erie, where toxin-forming harmful algal blooms follow high concentrations of H2O2.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2108-2118
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00327A
Ferrihydrite transformations in flooded paddy soils: rates, pathways, and product spatial distributions
The rate and pathway of ferrihydrite transformation in soil depends on the properties of the soil pore water and diffusion processes.
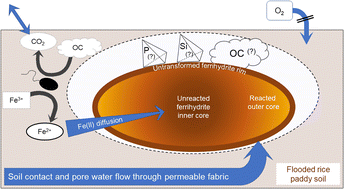
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1867-1882
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00290F
Changes in light absorption and composition of chromophoric marine-dissolved organic matter across a microbial bloom
Marine chromophoric dissolved organic matter (m-CDOM) mediates many vital photochemical processes in the surface ocean.
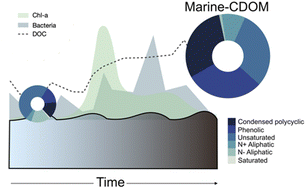
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1923-1933
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00150K
Heteroaggregation of PS microplastic with ferrihydrite leads to rapid removal of microplastic particles from the water column
Heteroaggregation of microplastic and ferrihydrite leads to sedimentation and therefore removal of microplastic from the water column.
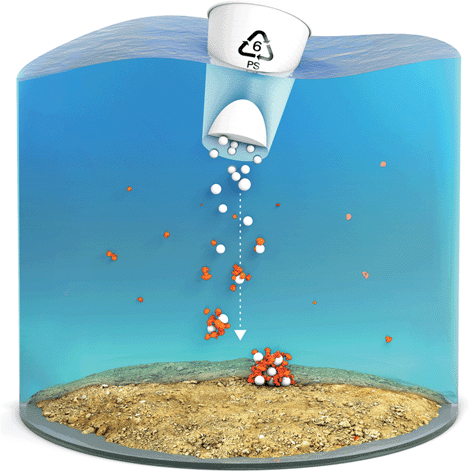
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1782-1789
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00207H
Impact of beaver ponds on biogeochemistry of organic carbon and nitrogen along a fire-impacted stream
Beaver ponds act as biological "hotspots" with unique geochemistry and microbiomes in fire-impacted systems.
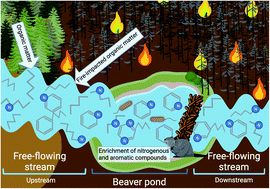
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1661-1677
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00184E
Influence of microorganisms on uranium release from mining-impacted lake sediments under various oxygenation conditions
Microbial processes can be involved in the remobilization of uranium (U) from reduced sediments under O2 reoxidation events such as water table fluctuations.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1830-1843
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00104G
Effects of aluminum incorporation on the schwertmannite structure and surface properties
Aluminum in schwertmannite structure increases the proportion of covalent bonding with adsorbed arsenates.
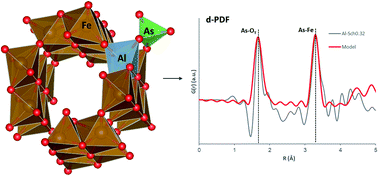
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1383-1391
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00029F
Hydrobiogechemical interactions in the hyporheic zone of a sulfate-impacted, freshwater stream and riparian wetland ecosystem
Biogeochemical cycling of S, Fe, and C in the hyporheic zone is influenced by dynamic hydrologic conditions.
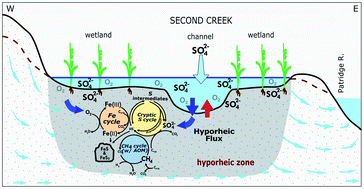
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1360-1382
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00024E
Thallium adsorption onto phyllosilicate minerals
We studied the extent and mode of thallium adsorption onto several phyllosilicate minerals. Thallium, in analogy to cesium, strongly adsorbs onto micaceous phyllosilicates in soils and sediments via complexation in siloxane cavities.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1343-1359
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00028H
Response of sediment phosphorus partitioning to lanthanum-modified clay amendment and porewater chemistry in a small eutrophic lake
Porewater geochemistry in a lanthanum-remediated lake reveal that phosphorus mobility depends on the interplay between carbon and iron.
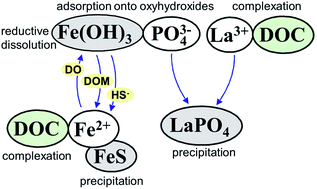
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1494-1507
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00544H
Two decades of changing anthropogenic mercury emissions in Australia: inventory development, trends, and atmospheric implications
Australian anthropogenic emissions of mercury have decreased by a factor of two since 2000, with implications for atmospheric mercury concentrations and deposition to the Australian continent.
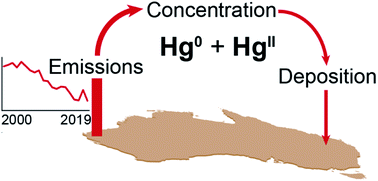
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1474-1493
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00019A
Relationship between surface dissolved iron inventories and net community production during a marine heatwave in the subarctic northeast Pacific
Marine heatwave conditions diminished (micro)macronutrient vertical transport, reducing (micro)macronutrient inventories and net community production when external nutrient sources were absent.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1460-1473
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00021K
Impact of abiotic and biogeochemical processes on halogen concentrations (Cl, Br, F, I) in mineral soil along a climatic gradient
Halogens in soil are closely linked to abiotic processes, biota and pedogenesis, and thus to the availability of water; vertical halogen depth patterns become less pronounced with increasing dryness.
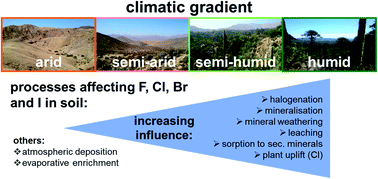
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1330-1342
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00015F
Organic carbon, and major and trace elements reside in labile low-molecular form in the ground ice of permafrost peatlands: a case study of colloids in peat ice of Western Siberia
The low molecular weight fraction of peat porewater is enriched in DOC, anions, oxyanions, alkalis and some trace metals. An increase in the active layer depth can liberate a large amount of labile metals and nutrients from the peat.
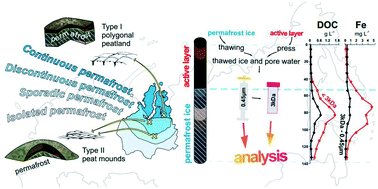
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1443-1459
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00547B
Selenium distribution and speciation in waters of pristine alpine lakes from central-western Pyrenees (France–Spain)
The distribution and chemical speciation of micronutrient selenium is reported for the first time in twenty alpine lakes (Pyrenees, France–Spain).
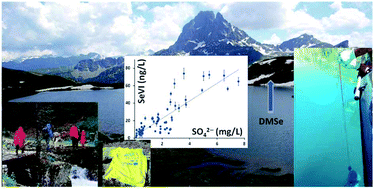
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1430-1442
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00430A
Demystifying mercury geochemistry in contaminated soil–groundwater systems with complementary mercury stable isotope, concentration, and speciation analyses
A holistic multi-analyses (led by Hg stable isotope analysis), multi-media, multi-site approach to improving contaminated site Hg geochemistry, particularly process tracing.
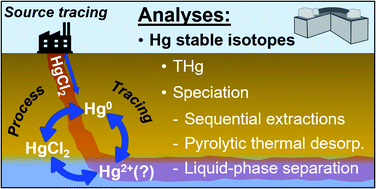
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1406-1429
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00368B
Direct observation of humic acid-promoted hydrolysis of phytate through stabilizing a conserved catalytic domain in phytase
HA promotes enzymatic hydrolysis of phytate as shown by the increase in nucleation of Pi-bearing particles, which is achieved by conformation change to stabilize a catalytic domain resulting from noncovalent phytase–HA interaction.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1082-1093
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00065B
Metal (hydr)oxide surface precipitates and their effects on potassium sorption
Surface precipitation has been shown to occur on rapid time scales in clay and metal oxide mineral systems.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1037-1049
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00092J
Identification of chlorpyrifos-degrading microorganisms in farmland soils via cultivation-independent and -dependent approaches
This study shows a feasible cultivation-independent method by MMI coupled with high-throughput sequencing to identify in situ microbes actively, various microbes were recognized for the first time, the OPH genes were involved in CPF metabolism.
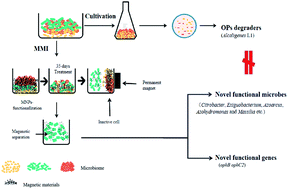
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1050-1059
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00095D
Quantifying the impacts of non-carbonic acid (NCA) stress on dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) generation in the granitic-hosted watershed, Huangshan UNESCO Global Geopark, China
DIC generation in carbonate dissolution in acidic granitic-soil is promoted by H2SO4, perturbed by HNO3, little affected by organic acids.
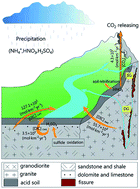
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 960-972
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00071G
Implications of sample treatment on characterization of riverine dissolved organic matter
We compared how FTICR-MS characterization of riverine dissolved organic matter varied across four sample pre-treatment and instrument ionization methods to provide guidelines for future researchers utilizing FTICR-MS in environmental analyses.
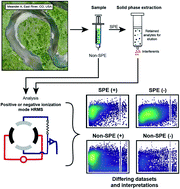
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 773-782
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00044J
Spatial distribution and biogeochemistry of redox active species in arctic sedimentary porewaters and seeps
Schematic showing how voltammetric microelectrodes were used to profile arctic lake sediments, where different locations contained different distributions of redox-active species.
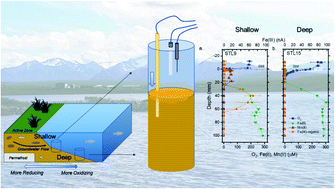
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 426-438
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00505G
Interactions of ferrous iron with clay mineral surfaces during sorption and subsequent oxidation
Under anoxic conditions, clay minerals sorb dissolved Fe(II) predominantly by forming surface precipitates, which transform into Fe(III)-phases upon aeration.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 1355-1367
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00063A
Assessing the prevalence, products, and pathways of dissolved organic matter partial photo-oxidation in arctic surface waters
Isotope tracer experiments reveal that rates of dissolved organic matter partial photochemical oxidation are considerably underestimated in arctic surface waters.
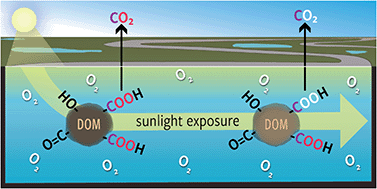
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 1214-1223
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00504H
Quantitative measures of myo-IP6 in soil using solution 31P NMR spectroscopy and spectral deconvolution fitting including a broad signal
Inositol phosphates, particularly myo-inositol hexakisphosphate (myo-IP6), are an important pool of soil organic phosphorus (P) in terrestrial ecosystems.
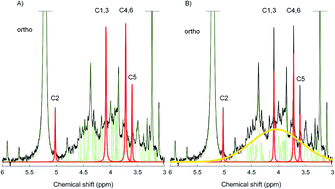
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 1084-1094
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00485H
Use of optical properties for evaluating the presence of pyrogenic organic matter in thermally altered soil leachates
Optical measurements reveal the presence of pyrogenic organic matter in laboratory heated soil leachates, indicating their potential for application in field measurements.
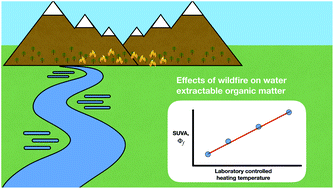
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 981-992
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00413K
Impact of bromide exposure on natural organochlorine loss from coastal wetland soils in the Winyah Bay, South Carolina
Naturally formed halogenated organic compounds are common in terrestrial and marine environments and play an important role in the halogen cycle.
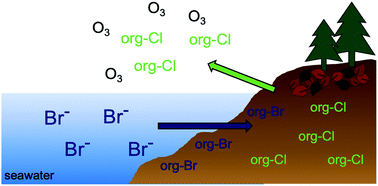
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 642-652
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00604D
Sources and sinks of chloromethane in a salt marsh ecosystem: constraints from concentration and stable isotope measurements of laboratory incubation experiments
Chloromethane (CH3Cl) is the most abundant long-lived chlorinated organic compound in the atmosphere and contributes significantly to natural stratospheric ozone depletion.
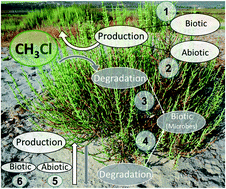
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 627-641
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00540D
How did the bacterial community respond to the level of urbanization along the Yangtze River?
The response of bacteria communities to the urbanization level.
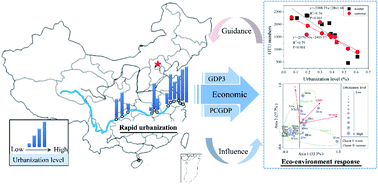
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 161-172
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00399A
Emerging investigator series: mercury mobility and methylmercury formation in a contaminated agricultural flood plain: influence of flooding and manure addition
We investigated the release of mercury from soil to soil solution and the formation of methylmercury in polluted agricultural floodplain fields during a flooding incubation experiment.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2019,21, 2008-2019
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00257J
Plant rhizosphere, soil microenvironment, and functional genes in the nitrogen removal process of bioretention
The coupling effect of plant, soil, and microbes in bioretention provides conditions conductive for nitrogen (N) removal via nitrification, accretion, denitrification, and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA).
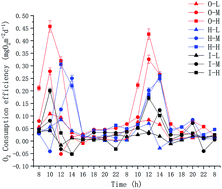
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2019,21, 2070-2079
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00296K
Potential impacts of anthropogenic nutrient enrichment on coral reefs in the South China Sea: evidence from nutrient and chlorophyll a levels in seawater
Anthropogenic nutrient enrichment caused macroalgal blooms and further resulted in coral reef degradation in coastal and some remote reef areas of the SCS.
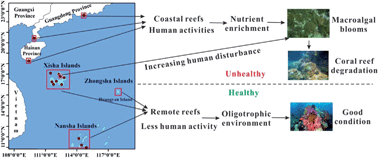
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2019,21, 1745-1753
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00331B
Assessing thermodynamic parameter sensitivity for simulating temperature responses of soil nitrification
The sensitivity of SQRT model-estimated parameters varied over a temperature gradient whereas no variation in MMRT model-estimated parameters, in simulating temperature responses of soil nitrification over the temperature range, was observed.
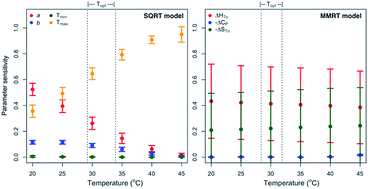
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2019,21, 1596-1608
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00310J
About this collection
This web collection features research articles published in Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts focussed on geochemistry and biogeochemistry.