Themed collection Emerging Investigator Series

Emerging investigator series: are we undervaluing septage? Rethinking septage management for nutrient recovery and environmental protection
Septage is an untapped waste stream that could be utilized for recovery of beneficial nutrients, energy, and water.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1621-1628
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00998C
Emerging investigator series: modeling of wastewater treatment bioprocesses: current development and future opportunities
Potential modeling framework of integrating mechanistic and data-driven models to address the microbiological composition and functions that are currently underrepresented in standalone models.
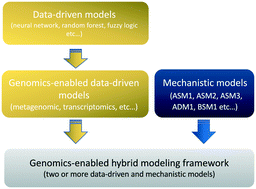
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 208-225
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00739D
Emerging investigator series: moving beyond resilience by considering antifragility in potable water systems
By incorporating antifragility, water systems may move beyond resilience and improve performance with extreme events.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 8-21
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00732G
Emerging investigator series: could the superoxide radical be implemented in decontamination processes?
The superoxide radical (O2˙−) is an important reactive oxygen species (ROS) in diverse natural aquatic systems and engineered water treatment processes.
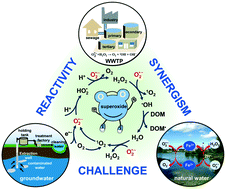
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1966-1970
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00463H
Emerging investigators series: advances and challenges of graphitic carbon nitride as a visible-light-responsive photocatalyst for sustainable water purification
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is a promising visible-light-responsive photocatalyst for sustainable water purification.
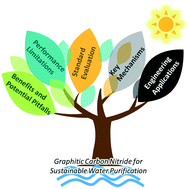
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2017,3, 982-1001
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EW00159B
Emerging investigator series: the role of phage lifestyle in wastewater microbial community structures and functions: insights into diverse microbial environments
Harnessing phage for biological treatment is of growing interest, but an improved understanding of phage diversity, host range, lifestyle, molecular signaling, and genetic potential are needed for microbial community control.
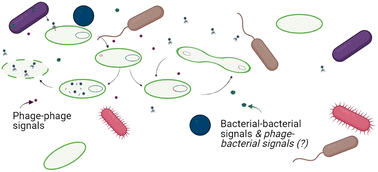
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1982-1991
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00755J
Emerging investigator series: emerging biotechnologies in wastewater treatment: from biomolecular engineering to multiscale integration
Bottom-up engineering approaches are transforming biological wastewater treatment.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1967-1985
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00393J
Emerging investigators series: frontier review: occurrence and speciation of chromium in drinking water distribution systems
Chromium can exist as both trivalent Cr(III) and hexavalent Cr(VI) in typical drinking water conditions, with Cr(VI) being of particular concern due to its high toxicity and new regulatory perspectives.
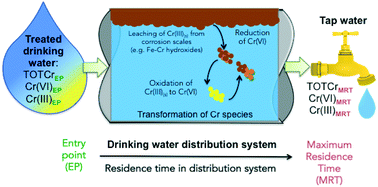
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 906-914
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00214E
Emerging investigators series: sewer surveillance for monitoring antibiotic use and prevalence of antibiotic resistance: urban sewer epidemiology
Sewer surveillance may be a useful tool for epidemiology that would benefit from improved understanding of the fate of microbial agents and prescription antibiotics during conveyance in sewer systems.
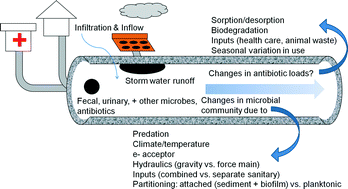
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 788-799
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00158K
Emerging investigator series: photocatalytic membrane reactors: fundamentals and advances in preparation and application in wastewater treatment
Photocatalytic membrane reactors (PMRs) can degrade organic compounds in wastewater and in water from different real matrices. The PMR surface can be modified for anti-fouling/self-cleaning properties, enabling reuse and extending lifespan.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 22-46
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00513H
Emerging investigator series: membrane distillation and high salinity: analysis and implications
In energy efficient membrane distillation, the low transmembrane temperature difference exacerbates salinity's effect on water flux and specific energy consumption.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1538-1552
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EW01055F
Emerging investigator series: a state-of-the-art review on large-scale desalination technologies and their brine management
Freshwater scarcity, caused by population growth and climate change, has boosted the demand for desalination technologies.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 167-195
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00662C
Emerging investigators series: revisiting greenhouse gas mitigation from conventional activated sludge and anaerobic-based wastewater treatment systems
Elucidation of N2O formation mechanisms in aerobic-based wastewater treatment is essential for effective greenhouse gas mitigation, whereas mainstream anaerobic treatment requires improved methane recoverability.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2018,4, 1739-1758
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00545A
Emerging investigators series: prospects and challenges for high-pressure reverse osmosis in minimizing concentrated waste streams
If challenges such as mechanical stability, scaling, biofouling and concentration polarization at high pressures are addressed, high-pressure RO could be used to efficiently remove water from high-salinity waste brines as part of a zero-liquid-discharge disposal process.
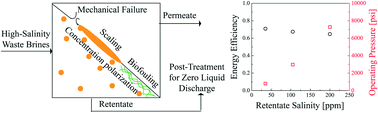
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2018,4, 894-908
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00137E
Emerging investigator series: the role of vegetation in bioretention for stormwater treatment in the built environment: pollutant removal, hydrologic function, and ancillary benefits
Bioretention vegetation contributes to both the hydrologic and pollutant removal functions of bioretention.
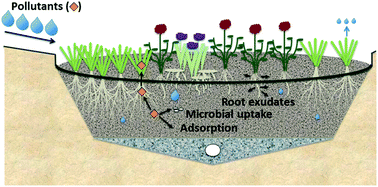
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2018,4, 592-612
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EW00511C
Emerging investigators series: a critical review of decision support systems for water treatment: making the case for incorporating climate change and climate extremes
We present potential impacts of climate on drinking water treatment and review decision support systems for these utilities.
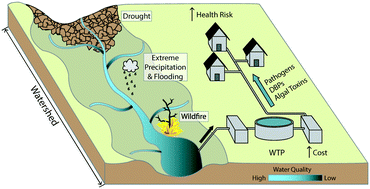
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2017,3, 18-36
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00121A
Emerging investigators series: the efficacy of chlorine photolysis as an advanced oxidation process for drinking water treatment
The photolysis of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and hypochlorite (OCl−) produces a suite of reactive oxidants, including hydroxyl radicals (˙OH), chlorine radicals (Cl˙), and ozone (O3).
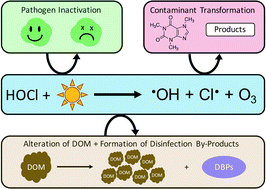
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 565-579
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00029K
Emerging investigators series: virus mitigation by coagulation: recent discoveries and future directions
Forces influencing virion sorption and recent findings of coagulation-based inactivation inform new research directions for mitigating waterborne viruses by coagulation.
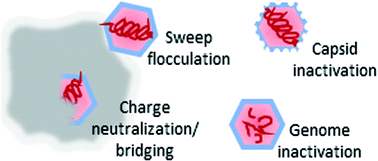
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 443-459
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00060F
Emerging investigators series: the source and fate of pandemic viruses in the urban water cycle
This review provides a comprehensive look at whether a pandemic enveloped virus would pose challenges for the wastewater and drinking water industries.
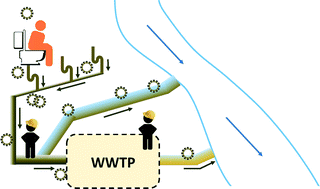
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2015,1, 735-746
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EW00125K
Emerging investigator series: Inactivation of antibiotic resistant bacteria and inhibition of horizontal resistance gene transfer is more effective by 222 than 254 nm UV
Disinfection of antibiotic-resistant B. subtilis, damage of its intracellular antibiotic resistance gene (ARG), and prevention of horizontal ARG transfer were greater by 222 than 254 nm, despite similar extracted ARG damage between UV wavelengths.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 306-316
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00530A
Emerging investigator series: mitigation of harmful algal blooms by electrochemical ozonation: from bench-scale studies to field applications
Harmful algal blooms threaten ecosystems and water safety, necessitating rapid treatment strategies. This study developed an electrochemical ozonation process to realize simultaneous cyanobacteria inactivation and microcystin removal.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 2381-2391
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00490F
Emerging investigator series: photocatalytic treatment of PFAS in a single-step ultrafiltration membrane reactor
Combining ultrafiltration and advanced oxidation processes, a single-step reactor removes aqueous PFAS and destroys them in situ, allowing long-term reuse of the effective photocatalyst.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 2062-2074
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00224E
Emerging investigator series: optimisation of drinking water biofilm cell detachment and sample homogenisation methods for rapid quantification via flow cytometry
Establishing an optimized method to harvest and quantify cells of biofilms from drinking water systems.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 797-813
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00553D
Emerging investigator series: post-synthesis modification of reverse osmosis membranes for the enhanced separation of small neutral molecules
Diamine modification of polyamide reverse osmosis membranes using carbodiimide chemistry and heat treatment improves the removal of small neutral molecules.
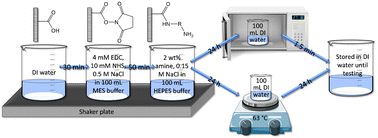
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2836-2846
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00401E
Emerging investigator series: low doses of electron beam irradiation effectively degrade 1,4-dioxane in water within a few seconds
The application of electron beam technology for water treatment has been proposed as a faster & safer approach to decomposing persistent contaminants, because it can rapidly generate high amounts of both oxidizing and reducing reactive species without added chemicals.
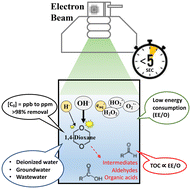
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2226-2237
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00111C
Emerging investigator series: enhancing the degradation of ciprofloxacin in water using Oxone activated by urchin-like cubic and hollow-structured cobalt@N-doped carbon prepared by etching-engineering: a comparative study with mechanistic and eco-toxic assessments
Enhancing the degradation of ciprofloxacin in water using Oxone activated by urchin-like cubic and hollow-structured cobalt@N-doped carbon.
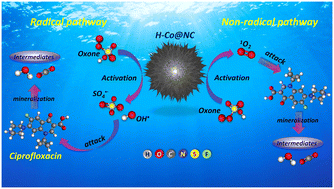
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1992-2007
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00009E
Emerging investigator series: impacts of aeration flow rates and bubble sizes on PFOA/PFOS removal in electrocoagulation
The impacts of aeration (in terms of bubble sizes and airflow rates) on PFOA/PFOS removal as well as electrocoagulation performance were examined in this study.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1783-1791
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00208J
Emerging investigator series: microplastic-based leachate formation under UV irradiation: the extent, characteristics, and mechanisms
Aqueous microplastic were tested in terms of leachate formation and surface oxidation during UV irradiation. Surface properties (FTIR, RAMAN, XPS) and leachate characteristics (UV254, DOC, fluorescence spectroscopy) were analyzed concurrently.
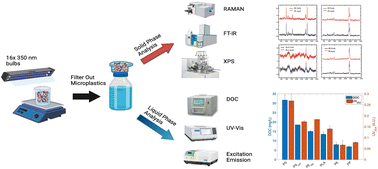
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 363-374
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00423B
Emerging investigator series: environment-specific auxiliary substrates tailored for effective cometabolic bioremediation of 1,4-dioxane
DD4 can coordinate with native microbiomes to degrade 1,4-dioxane when fueled with propane and 1-propanol in biomass-rich and -poor environments, respectively.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2521-2530
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00524G
Elucidating morphological effects in membrane mineral fouling using real-time particle imaging and impedance spectroscopy
Mineral fouling is a major hindrance to high recovery effluent nanofiltration, with calcium phosphate (Ca-P) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3) the most prevalent mineral foulants.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1444-1457
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00155A
Emerging investigator series: meta-analyses on SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA levels in wastewater and their correlations to epidemiological indicators
Recent applications of wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) have demonstrated its ability to track the spread and dynamics of COVID-19 at the community level.
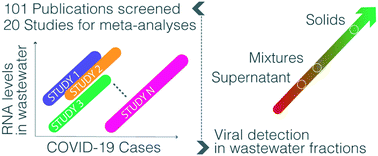
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1391-1407
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00084A
Emerging investigator series: a comparison of strong and weak-acid functionalized carbon electrodes in capacitive deionization
Strong-acid functionalized cathode is pH stable and sulfonic groups are stable to charge–discharge cycling.
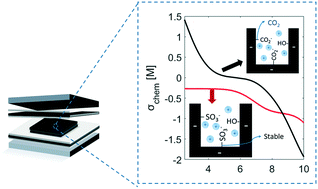
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 949-956
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00967B
Emerging investigator series: effects of sediment particle size on the spatial distributions of contaminants and bacterial communities in the reservoir sediments
This study investigates the effects of sediment particle size on the spatial distributions of contaminants and bacterial communities in the reservoir sediments, which can guide the implementation of partial desilting in the reservoirs.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 957-967
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00877C
Emerging investigator series: electrochemically-mediated remediation of GenX using redox-copolymers
GenX is a major per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) of environmental concern. Redox-copolymers are explored as selective adsorbents for the electrochemically-mediated separation and remediation of GenX from water.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 2231-2240
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00544H
Emerging investigator series: thermodynamic and energy analysis of nitrogen and phosphorous recovery from wastewaters
This study quantified the theoretical minimum energy required to recover fertilizer products from different environmental waste streams.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 2075-2088
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00554E
Emerging investigator series: rapid defluorination of 22 per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water using sulfite irradiated by medium-pressure UV
The removal of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water supplies is crucial to protect the public and the environment.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1552-1562
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00221J
Emerging investigator series: toward the ultimate limit of seawater desalination with mesopelagic open reverse osmosis
Operating reverse osmosis (RO) in the mesopelagic zone (i.e., a few hundred meters under the ocean surface) with open modules can potentially reduce the energy consumption of seawater desalination by over 50% to approach the thermodynamic limit.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1212-1219
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00153A
Emerging investigator series: local pH effects on carbon oxidation in capacitive deionization architectures
Ion exchange membranes provide stabilized local pH in MCDI.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 861-869
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00005E
Emerging investigator series: interacting effects of environmental factors on Daphnia magna removal of Escherichia coli from wastewater
Zooplankton can significantly impact E. coli inactivation in wastewater, but inactivation rates are dependent on environmental conditions.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 726-738
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00008J
Emerging investigator series: 3D graphene anchored zerovalent Fe/Cu aerogel activating persulfate for efficiently 2,4 dichlorophenol degradation over a broad pH range
3D graphene anchored zerovalent metal aerogel as an alternative route for the efficient removal of organic pollutants from wastewater.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 714-725
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW01091J
Emerging investigator series: disaggregating residential sector high-resolution smart water meter data into appliance end-uses with unsupervised machine learning
Disaggregation of residential smart water meter data can support peak demand quantification and customized conservation and efficiency recommendations.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 487-503
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00724B
Emerging investigator series: emerging disinfection by-product quantification method for wastewater reuse: trace level assessment using tandem mass spectrometry
A sensitive analytical method was developed that simultaneously characterizes 25 unregulated DBPs in wastewater effluents. DBP formation potential with HOCl and NH2Cl was evaluated across a full-scale wastewater reuse facility for the first time.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 285-297
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00947D
Emerging investigator series: quaternary treatment with algae-assisted oxidation for antibiotics removal and refractory organics degradation in livestock wastewater effluent
This study deals with algae-induced alkalization of refractory wastewater, focusing on improving the performance of subsequent oxidation processes along with direct removal of antibiotics resistant to certain oxidation methods.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 3262-3275
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00634C
Emerging investigator series: bacterial opportunistic pathogen gene markers in municipal drinking water are associated with distribution system and household plumbing characteristics
Municipally-treated drinking water (DW) is a potential source of exposure to bacterial opportunistic pathogens (OPs), which can cause infection in susceptible individuals.
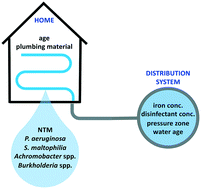
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 3032-3043
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00723D
Emerging investigator series: onsite recycling of saline–alkaline soil washing water by forward osmosis: techno-economic evaluation and implication
This study investigated the techno-economic feasibility of forward osmosis (FO) for onsite recycling of saline–alkaline soil washing water with an all-purpose liquid fertiliser as a draw solution.
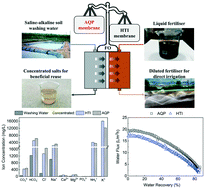
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 2881-2890
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00490A
Emerging investigator series: engineering membrane distillation with nanofabrication: design, performance and mechanisms
Anti-fouling and durability are two important parameters that are closely associated with the development and deployment of membrane distillation (MD).

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1786-1793
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00100G
Emerging investigator series: phosphorus recovery from municipal wastewater by adsorption on steelmaking slag preceding forward osmosis: an integrated process
Phosphorus is a critical non-renewable mineral essential for sustainable crop production.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1559-1567
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00187B
Emerging investigator series: activated sludge upon antibiotic shock loading: mechanistic description of functional stability and microbial community dynamics
Elucidating the functional stability upon environmental stressors is of great practical importance for managing the system performance of various environmental biological processes (e.g., activated sludge).

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1262-1271
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00069H
Emerging investigator series: carbon electrodes are effective for the detection and reduction of hexavalent chromium in water
Electrochemical methods using carbon electrodes are an attractive option for the detection and reduction of toxic Cr(VI) to benign Cr(III) in drinking water.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1256-1261
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00146E
Emerging investigator series: formation of brominated haloacetamides from trihalomethanes during zero-valent iron reduction and subsequent booster chlorination in drinking water distribution
This study investigated the transformation of a THM mixture and the change of toxicity risk in drinking water distribution systems for the first time.
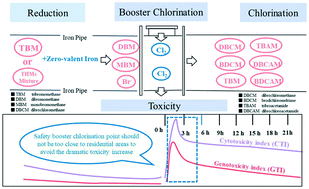
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1244-1255
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EW00977A
Emerging investigator series: control of membrane fouling by dissolved algal organic matter using pre-oxidation with coagulation as seawater pretreatment
High AOM removal achieved by pre-oxidation with coagulation–flocculation-dissolved air flotation. In situ ferrate was formed by wet chemical oxidation of NaOCl-Fe3+. Membrane fouling was significantly alleviated and assessed by OCT technique.
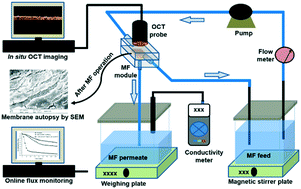
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 935-944
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EW00955H
Emerging investigator series: capacitive deionization for selective removal of nitrate and perchlorate: impacts of ion selectivity and operating constraints on treatment costs
A parameterized costing model was used to investigate the impacts of ion selectivity on water treatment price for selective ion removal with capacitive deionization (CDI) systems.
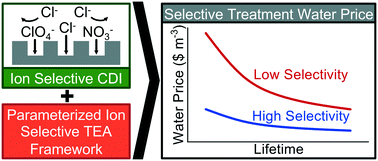
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 925-934
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EW01105F
Emerging investigator series: transformation of common antibiotics during water disinfection with chlorine and formation of antibacterially active products
This study determined that at chlorination conditions representative of wastewater treatment, fluoroquinolones, one of the common antibiotic classes, form antibacterially active products.
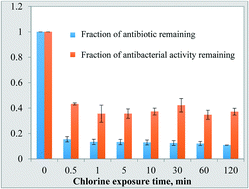
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2019,5, 1222-1233
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EW00182D
Emerging investigator series: photocatalysis for MBR effluent post-treatment: assessing the effects of effluent organic matter characteristics
Organic matter from a membrane bioreactor is fractionated and characterized in novel ways to understand component-specific inhibition of photooxidation reactions.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2019,5, 482-494
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00734A
Emerging investigator series: inhibition and recovery of anaerobic granular sludge performance in response to short-term polystyrene nanoparticle exposure
Microbial communities and methanogenic genes are main reasons for AGS performance recovery from PS-NPs exposure.
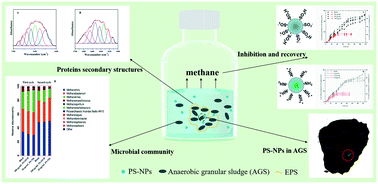
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2018,4, 1902-1911
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00535D
Emerging investigators series: occurrence and fate of emerging organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plants with an enhanced nitrification step
The goal of this study is to investigate the occurrence and removal of emerging organic contaminants (EOCs) during wastewater treatment processes and understand the role of enhanced nitrification treatment in removing EOCs.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2018,4, 1412-1426
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00278A
Emerging investigators series: ultraviolet and free chlorine aqueous-phase advanced oxidation process: kinetic simulations and experimental validation
An elementary reaction based kinetic model was developed for the fate of acetone degradation in UV/free chlorine advanced oxidation process.
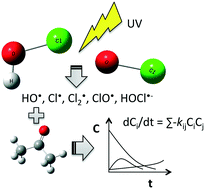
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2018,4, 1231-1238
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00196K
Emerging investigators series: comparative study of naproxen degradation by the UV/chlorine and the UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation processes
The UV/chlorine and UV/H2O2 AOPs on the degradation of naproxen were compared. The efficiency of naproxen was much higher by UV/chlorine compared to UV/H2O2 under all the tested conditions. ClO˙ and CO3˙− played important roles in the degradation of naproxen.
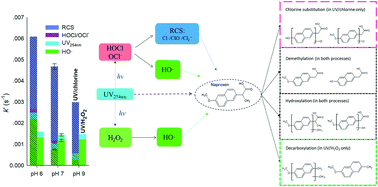
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2018,4, 1219-1230
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00105G
Emerging investigators series: a steric pore-flow model to predict the transport of small and uncharged solutes through a reverse osmosis membrane
This study proposed a new approach to apply the steric pore-flow model to predict the rejection of eight N-nitrosamines and seven VOCs that are of great concern in potable water reuse through an RO membrane.
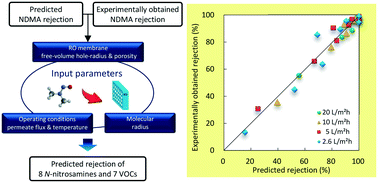
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2018,4, 493-504
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EW00194K
Emerging investigators series: comparing the inherent reactivity of often-overlooked aqueous chlorinating and brominating agents toward salicylic acid
Rates and selectivity of salicylic acid halogenation can be influenced by highly electrophilic species such as Cl2, BrCl, and BrOCl.
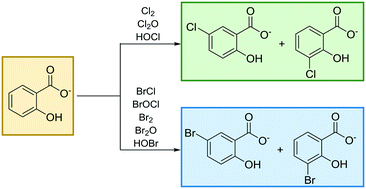
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2018,4, 369-384
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EW00491E
Emerging investigators series: trihalomethane, dihaloacetonitrile, and total N-nitrosamine precursor adsorption by modified carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and CNT micropillars
Modified carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and CNT micropillars are shown to adsorb organic precursors of disinfection byproducts, most notably those of total N-nitrosamines.
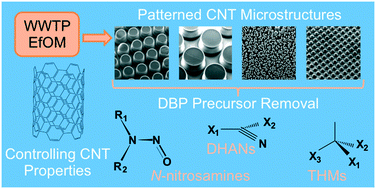
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2017,3, 1042-1050
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EW00173H
Emerging investigators series: hydrogen sulfide production in municipal stormwater retention ponds under ice covered conditions: a study of water quality and SRB populations
Sulfide production in stormwater ponds is a result of increased ubiquitous SRB activity.
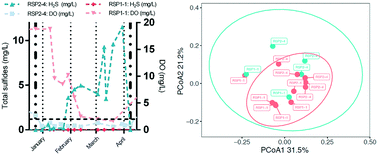
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2017,3, 686-698
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EW00117G
Emerging investigators series: highly effective adsorption of organic aromatic molecules from aqueous environments by electronically sorted single-walled carbon nanotubes
The use of electronically sorted (i.e. semiconducting or metallic) single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) for the removal of organic compounds from aqueous environments is investigated.
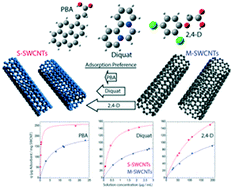
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2017,3, 203-212
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00284F
Emerging investigators series: prioritization of suspect hits in a sensitive suspect screening workflow for comprehensive micropollutant characterization in environmental samples
A suspect screening workflow was developed and applied to a series of samples collected from a small urban water system to identify and confirm the occurrence of 112 organic micropollutants.
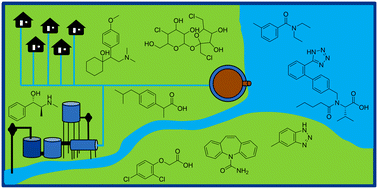
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2017,3, 54-65
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00248J
Emerging investigators series: building a theory for smart stormwater systems
Smart stormwater systems will transform cities into coordinated and real-time controlled treatment plants.
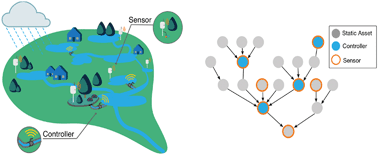
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2017,3, 66-77
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00211K
Emerging investigators series: using an analytical solution approach to permit high volume groundwater withdrawals
Sustainable water management is paramount to ensuring continued access to fresh water resources.
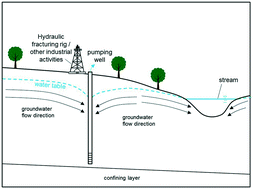
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 942-952
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00108D
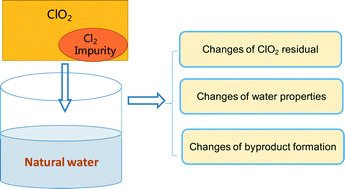
Emerging investigators series: disinfection by-products in mixed chlorine dioxide and chlorine water treatment
On-site generation of ClO2 often involves the production of Cl2 as impurity and the changes of disinfection by-products formation by mixed disinfectant (ClO2/Cl2) was presented.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 838-847
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00061D
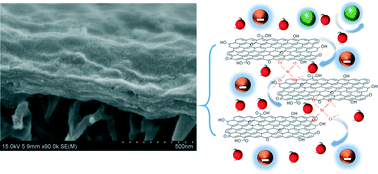
Emerging investigators series: silica-crosslinked graphene oxide membrane and its unique capability in removing neutral organic molecules from water
A new graphene oxide (GO) membrane was synthesized by crosslinking GO nanosheets via silica. This membrane was found to remove neutral organic molecules much more efficiently than negatively charged ionic species.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 717-725
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00070C
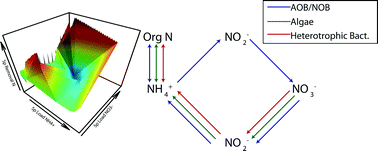
Emerging investigators series: untangling the microbial ecosystem and kinetics in a nitrogen removing photosynthetic high density bioreactor
Metabolic kinetics, microscopy, metagenomic analysis, and real-time PCR are applied to characterize nitrogen species transformation and identify and quantify the organisms key to these transformational processes.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 705-716
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00078A
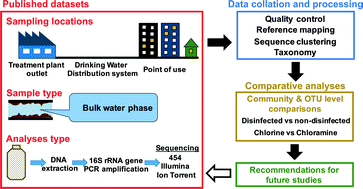
Emerging investigators series: microbial communities in full-scale drinking water distribution systems – a meta-analysis
In this study, we co-analyze all available 16S rRNA gene sequencing studies from bulk drinking water samples in full-scale drinking water distribution systems.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 631-644
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00030D
About this collection
Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology is pleased to present this growing web collection, showcasing the work being conducted by Emerging Investigators in water engineering and technology across the globe. It highlights up-and-coming scientists in the early stages of their independent careers, who have been identified as having the potential to influence future directions in the field.
This collection will be updated when new Emerging Investigator Series papers are published – so keep checking this page and watch the collection grow.
More details about the Emerging Investigator Series can be found on the blog, including details on how to apply for consideration and interviews with the corresponding authors featured in this collection. Direct links to each of these interviews can be found below.
- Andrea Achilli
- Onur Apul
- Kevin Bisceglia
- Tom Bond
- Roland Cusick
- Robert Delatolla
- Noémie Elgrishi
- Nicole Fahrenfeld
- Julian Fairey
- Takahiro Fujioka
- Jingyun Fang
- Li Gao
- Daniel Gerrity
- Joseph Goodwill
- Changseok Han
- David Hanigan
- Damian Helbling
- Xiaocheng Jiang
- Joseph Kasprzyk
- Oyla Keen
- Kyoung-Yeol Kim
- Manish Kumar
- James Landon
- Greg LeFevre
- Mengyang Li
- Kun-Yi Andrew Lin
- Haizhou Liu
- Brooke Mayer
- Patrick McNamara
- Yujie Men
- Baoxia Mi
- Daisuke Minakata
- Oded Nir
- Seungdae Oh
- Alexandre Pinto
- Ameet Pinto
- Biplob Pramanik
- Christy Remucal
- John-David Rocha
- Reginald Rogers
- Christopher Sales
- Danmeng Shaui
- John Sivey
- Adam Smith
- Samuel Snow
- Xiao Su
- Jeseth Delgado Vela
- Arjun Venkatesan
- Chu Wenhai
- Krista Wigginton
- Ray Xiao
- Xin Yang
- Xian-Zheng Yuan
- Heyang Yuan