Emerging investigator series: post-synthesis modification of reverse osmosis membranes for the enhanced separation of small neutral molecules†
Abstract
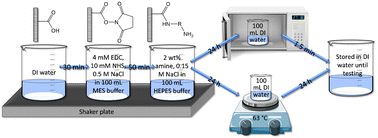
Reverse osmosis (RO) membranes are used ubiquitously for seawater desalination. Ideally, the interfacial polymerization (IP) reaction used to synthesize RO membranes would form a uniform pore or free volume element structure within the polyamide layer. In reality, the self-limiting and chaotic nature of IP prevents the saturation of the RO active layer with the aqueous reactant. Unexploited attachment sites on the organic reactant are negatively charged in an aqueous solution, facilitating the desalination apt of RO membranes. However, these unreacted sites leave the pore structure with sizeable free-volume holes which permit small, neutral molecules (SNMs) to permeate through the membrane. The goal of this research is to decrease free volume space on the surface of the polyamide layer to improve the size exclusion properties of RO membranes and SNM rejection. We hypothesize that conjugating diamines or a branched polyamine to the synthesized polyamide layer will increase cross-linking to facilitate this improvement. To test this hypothesis, the polyamide layer of a commercial RO membrane is activated using carbodiimide chemistry and subsequently modified with an amine. Then, the modified membranes are heat treated in a microwave or hot water bath. The effects of various amines including 1,6-diaminohexane, 1,8-diaminooctane, m-phenylenediamine, and polyethyleneimine (10 000 MW) are evaluated. The results show that combining the application of amine conjugation and heat treatment significantly improves SNM rejection. Specifically, urea rejection was increased from 21% to 61%, and boron rejection was increased from 23% to 59%.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Outstanding Papers 2023 – Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology and Emerging Investigator Series


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...