Themed collection Most popular 2018-2019 physical and theoretical chemistry articles

Two-dimensional UV spectroscopy: a new insight into the structure and dynamics of biomolecules
Two-dimensional ultraviolet spectroscopy has the potential to deliver rich structural and dynamical information on biomolecules such as DNA and proteins.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 9907-9921
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC03871J
Towards a molecular understanding of cellulose dissolution in ionic liquids: anion/cation effect, synergistic mechanism and physicochemical aspects
This perspective summarizes mechanistic studies on cellulose dissolution in ionic liquids, highlighting the synergistic mechanism, physicochemical aspects and future research trends.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 4027-4043
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC05392D
Polariton chemistry: controlling molecular dynamics with optical cavities
Strong coupling of molecules with confined electromagnetic fields provides novel strategies to control chemical reactivity and spectroscopy.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 6325-6339
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC01043A
Why are photosynthetic reaction centres dimeric?
The dimerisation of photosynthetic reaction centres enhanced their efficiency by improving exciton transfer from an antenna.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 9576-9585
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC03712H
A quantitative uncertainty metric controls error in neural network-driven chemical discovery
A predictive approach for driving down machine learning model errors is introduced and demonstrated across discovery for inorganic and organic chemistry.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 7913-7922
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC02298H
Extensive deep neural networks for transferring small scale learning to large scale systems
We present a physically-motivated topology of a deep neural network that can efficiently infer extensive parameters (such as energy, entropy, or number of particles) of arbitrarily large systems, doing so with 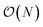 scaling.
scaling.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 4129-4140
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC04578J
Dual-wavelength efficient two-photon photorelease of glycine by π-extended dipolar coumarins
Efficient photolabile protecting groups: how to achieve exceptional photo-triggered amino-acid delivery upon irradiation in the NIR.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 4209-4219
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC00148D
Choosing sides: unusual ultrafast charge transfer pathways in an asymmetric electron-accepting cyclophane that binds an electron donor
Photo-driven electron transfer is faster from an electron donor guest to the harder to reduce acceptor in an asymmetric cyclophane host.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 4282-4292
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC05514A
Determination of the electronic structure of a dinuclear dysprosium single molecule magnet without symmetry idealization
We present the in-depth determination of the magnetic properties and electronic structure of the luminescent and volatile dysprosium-based single molecule magnet [Dy2(bpm)(fod)6] (Hfod = 6,6,7,7,8,8,8-heptafluoro-2,2-dimethyl-3,5-octanedione, bpm = 2,2-bipyrimidine).

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 2101-2110
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC03170C
Density matrix renormalization group pair-density functional theory (DMRG-PDFT): singlet–triplet gaps in polyacenes and polyacetylenes
The density matrix renormalization group (DMRG) is a powerful method to treat static correlation.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 1716-1723
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC03569E
Learning continuous and data-driven molecular descriptors by translating equivalent chemical representations
Translation between semantically equivalent but syntactically different line notations of molecular structures compresses meaningful information into a continuous molecular descriptor.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 1692-1701
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC04175J
Single-molecule photoredox catalysis
Photocatalytic dehalogenation by a common dyestuff under aqueous conditions is driven by energy-additive absorption of two photons on the single-molecule level.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 681-687
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC03860K
A graph-convolutional neural network model for the prediction of chemical reactivity
We present a supervised learning approach to predict the products of organic reactions given their reactants, reagents, and solvent(s).

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 370-377
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC04228D
Photon-upconverting chiral liquid crystal: significantly amplified upconverted circularly polarized luminescence
By blending a chiral acceptor and a sensitizer into a nematic liquid crystal, a chiral nematic liquid crystal showing amplified upconverted circularly polarized luminescence could be obtained.

Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 172-178
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC03806F
Machine learning meets volcano plots: computational discovery of cross-coupling catalysts
The application of modern machine learning to challenges in atomistic simulation is gaining attraction.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 7069-7077
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC01949E
Theory for polariton-assisted remote energy transfer
A comprehensive theory is presented to mechanistically elucidate the long-range energy transfer between molecules strongly coupled to electromagnetic fields.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 6659-6669
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC00171E
“Found in Translation”: predicting outcomes of complex organic chemistry reactions using neural sequence-to-sequence models
Using a text-based representation of molecules, chemical reactions are predicted with a neural machine translation model borrowed from language processing.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 6091-6098
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC02339E
Revitalizing the concept of bond order through delocalization measures in real space
Quantum mechanical bond orders are obtained from integration of the exchange–correlation density between topological atoms.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 5517-5529
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC01338A
Large-scale comparison of machine learning methods for drug target prediction on ChEMBL
The to date largest comparative study of nine state-of-the-art drug target prediction methods finds that deep learning outperforms all other competitors. The results are based on a benchmark of 1300 assays and half a million compounds.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 5441-5451
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC00148K
Deciphering the working mechanism of aggregation-induced emission of tetraphenylethylene derivatives by ultrafast spectroscopy
Photocyclized intermediate formation and quasi C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C twisting are the dominant processes behind the AIE.
C twisting are the dominant processes behind the AIE.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 4662-4670
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC01170B
The enhancement and suppression of immersion mode heterogeneous ice-nucleation by solutes
Heterogeneous nucleation of ice from supercooled liquid water by some atmospherically relevant nucleators is enhanced by ammonium salts and suppressed by alkali halides.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 4142-4151
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC05421A
Molecular mechanism of lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases
The lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) are copper metalloenzymes that can enhance polysaccharide depolymerization through an oxidative mechanism and hence boost generation of biofuel from e.g. cellulose. By employing density functional theory in a combination of quantum mechanics and molecular mechanics (QM/MM), we report a complete description of the molecular mechanism of LPMOs.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 3866-3880
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC00426A
Observation of a new type of aggregation-induced emission in nanoclusters
A novel mechanism of aggregation-induced emission defined as the restriction of the ligand dissociation–aggregation process in the nanocluster range is proposed.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 3062-3068
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC05317G
Cation–π interactions in protein–ligand binding: theory and data-mining reveal different roles for lysine and arginine
The interactions of neutral aromatic ligands with cationic arginine, histidine and lysine amino acid residues have been studied with ab initio calculations, symmetry adapted perturbation theory (SAPT), and a systematic meta-analysis of X-ray structures.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 2655-2665
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04905F
The TensorMol-0.1 model chemistry: a neural network augmented with long-range physics
We construct a robust chemistry consisting of a nearsighted neural network potential, TensorMol-0.1, with screened long-range electrostatic and van der Waals physics. It is offered in an open-source Python package and achieves millihartree accuracy and a scalability to tens-of-thousands of atoms on ordinary laptops.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 2261-2269
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04934J
Machine learning for the structure–energy–property landscapes of molecular crystals
Polymorphism is common in molecular crystals, whose energy landscapes usually contain many structures with similar stability, but very different physical–chemical properties. Machine-learning techniques can accelerate the evaluation of energy and properties by side-stepping accurate but demanding electronic-structure calculations, and provide a data-driven classification of the most important molecular packing motifs.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 1289-1300
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04665K
Tinker-HP: a massively parallel molecular dynamics package for multiscale simulations of large complex systems with advanced point dipole polarizable force fields
Tinker-HP is massively parallel software dedicated to polarizable molecular dynamics.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 956-972
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04531J
MoleculeNet: a benchmark for molecular machine learning
A large scale benchmark for molecular machine learning consisting of multiple public datasets, metrics, featurizations and learning algorithms.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 513-530
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC02664A
One-dimensional diamondoid polyaniline-like nanothreads from compressed crystal aniline
One-dimensional diamondoid polyaniline-like nanothreads combine the outstanding mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes with the versatility of NH2 groups.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 254-260
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC03445H
Small molecular organic nanocrystals resemble carbon nanodots in terms of their properties
We show that hydrothermal treatment of citric acid produces methylenesuccinic acid, which gives rise to hydrogen-bonded nano-assemblies with CND-like properties.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 175-180
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC02528A
About this collection
This specially curated collection pulls together some of the most popular articles from 2018 and 2019 in the field of physical and theoretical chemistry. The collection presents some outstanding contributions to the field, ranging from a study that asks why are photosynthetic reaction centres dimeric to a review of polariton chemistry, and as with all Chemical Science articles – they are all completely free to access and read. We hope you enjoy browsing through this collection.
See also: