Themed collection 2021 Materials Horizons Advisory Board collection

Introducing the new Materials Horizons Advisory Board
Highlighting the members of the Materials Horizons Advisory Board.

Mater. Horiz., 2021,8, 1346-1347
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MH90021H
Aggregation-induced emission: fundamental understanding and future developments
In-depth discussion on recent progress of fundamental understanding of AIE mechanisms, identifying the existing challenges and opportunities for future developments.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 428-433
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH01331D
Liquid–liquid interfaces: a unique and advantageous environment to prepare and process thin films of complex materials
This review summarizes the recent progress in a novel route to both synthesize and process complex and multi-component materials as thin films, based on interfaces between immiscible liquids, highlighting different materials and applications.
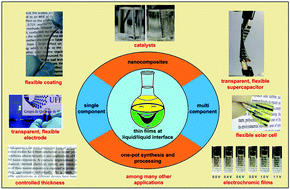
Mater. Horiz., 2021,8, 1409-1432
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH01676D
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in design of mechanical materials
This review revisits the state of the art of research efforts on the design of mechanical materials using machine learning.

Mater. Horiz., 2021,8, 1153-1172
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH01451F
Niobium pentoxide based materials for high rate rechargeable electrochemical energy storage
This review summarizes the crystalline features, electrochemical characteristics, ions intercalation charge storage mechanisms, and recent advances in niobium pentoxide related materials for high-rate electrochemical energy storage.
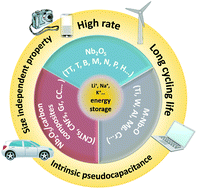
Mater. Horiz., 2021,8, 1130-1152
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH01481H
The damaging effects of the acidity in PEDOT:PSS on semiconductor device performance and solutions based on non-acidic alternatives
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate), PEDOT:PSS, has been widely used as an effective hole transporting material in many different organic semiconductor devices for well over a decade.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 1759-1772
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH01978B
About the amplification factors in organic bioelectronic sensors
A systematic comparison between electrochemical and organic bioelectronic sensors reveals a unified rational description for a transistor amplified detection.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 999-1013
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH01544B
Photocatalytic fixation of nitrogen to ammonia: state-of-the-art advancements and future prospects
The state-of-the-art developments in the photocatalytic reduction of N2 to NH3 are presented by classifying the photocatalysts based on chemical composition. Additionally, the correlation between the modification of catalysts and their photocatalytic activity is highlighted.

Mater. Horiz., 2018,5, 9-27
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MH00557A
Metabolically engineered bacteria as light-controlled living therapeutics for anti-angiogenesis tumor therapy
A living therapeutic system based on attenuated Salmonella was developed via metabolic engineering using an aggregation-induced emission (AIE) photosensitizer MA.

Mater. Horiz., 2021,8, 1454-1460
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH01582B
Probing cell membrane damage using a molecular rotor probe with membrane-to-nucleus translocation
A molecular rotor probe TPAE2 was developed for dynamic and in situ monitoring of membrane damage using a membrane-to-nucleus translocation strategy.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 3226-3233
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH01141J
Charge transfer excitons in a donor–acceptor amphidynamic crystal: the role of dipole orientational order
Large amplitude motions in molecular solids are responsible for anomalous electrical characteristics in amphidynamic crystals. Here we explore the implications for charge transfer excitons photophysics.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 2951-2958
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH01044H
Highly efficient and stable hybrid quantum-dot light-emitting field-effect transistors
A red quantum-dot light-emitting transistor with an EQE of 22.8% and a field-effect mobility of 3.1 cm2 V−1 s−1 is demonstrated.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 2439-2449
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH00951B
On the absence of triplet exciton loss pathways in non-fullerene acceptor based organic solar cells
Recombination to donor and acceptor triplet states should be energetically favourable. However, this recombination channel is not observed in operational devices.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 1641-1649
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH00286K
Key role of the meniscus shape in crystallization of organic semiconductors during meniscus-guided coating
The crystallization and film formation of organic semiconductors are controlled by the meniscus shape during meniscus guided coating for field-effect transistors.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 1631-1640
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH00141D
Polarized blue photoluminescence of mesoscopically ordered electrospun non-conjugated polyacrylonitrile nanofibers
Electrospun fibres from the non-conjugated polymer polyacrylonitrile are aligned by heat-stretching. These aligned fibers emit polarized blue fluorescence and green phosphorescence.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 1605-1612
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH00002G
One-step in vivo metabolic labeling as a theranostic approach for overcoming drug-resistant bacterial infections
A bacterial metabolic probe with AIE characteristics shows great potential in in vivo light-up imaging of bacteria and antibacterial therapy.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 1138-1143
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH01675A
Suppression of electron trapping by quantum dot emitters using a grafted polystyrene shell
Reduced electron trapping by a quantum dot using a thin polystyrene (PS) insulating shell with controllable thickness.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 2024-2031
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH00551J
A self-healing hydrogel with pressure sensitive photoluminescence for remote force measurement and healing assessment
A self-healing hydrogel with a triple network structure and pressure sensitive photoluminescence for remote force measurement and healing assessment was successfully fabricated.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 703-710
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH01441H
MoS2-capped CuxS nanocrystals: a new heterostructured geometry of transition metal dichalcogenides for broadband optoelectronics
Heterostructuring of different transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) leads to interesting band alignment and performance improvement, and thus enables new routes for the development of materials for next-generation semiconductor electronics.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 587-594
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00809D
Identifying glioblastoma margins using dual-targeted organic nanoparticles for efficient in vivo fluorescence image-guided photothermal therapy
Dual-targeted organic nanoparticles efficiently target the margin of glioblastoma and successfully suppress the tumour growth through photothermal therapy.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 311-317
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00946E
Host dependence of the electron affinity of molecular dopants
Accurate molecular modeling reveal the surprisingly large impact of the solid-state environment on the electron acceptor levels of molecular dopants.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 107-114
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00921J
Bioinspired hierarchical composite design using machine learning: simulation, additive manufacturing, and experiment
A new approach to design hierarchical materials using convolutional neural networks is proposed and validated through additive manufacturing and testing.

Mater. Horiz., 2018,5, 939-945
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00653A
How to interpret absorption and fluorescence spectra of charge transfer states in an organic solar cell
Energetic disorder is crucial to consistently model both absorption and photoluminescence spectra of charge transfer states in organic solar cells.

Mater. Horiz., 2018,5, 837-848
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00564H
Unidirectional water delivery on a superhydrophilic surface with two-dimensional asymmetrical wettability barriers
A superhydrophilic surface decorated with 2D hydrophobic water barriers is proven to be a potential platform for unidirectional liquid transport.

Mater. Horiz., 2018,5, 303-308
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MH01138E
Human ability to discriminate surface chemistry by touch
Human ability to discriminate between hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces is attributed to differences in vibrational frequencies generated while sliding at particular velocities and normal forces.

Mater. Horiz., 2018,5, 70-77
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MH00800G
About this collection
To celebrate the addition of several new members to the Materials Horizons Advisory Board, we have gathered a selection of papers by Advisory Board members that were published in Materials Horizons in recent years.