Themed collection Environmental Science: Nano Recent Review Articles

Practical considerations to optimize aquatic testing of particulate material, with focus on nanomaterials
Following available approaches included e.g., in existing OECD Test Guidelines and Guidance Documents for the aquatic testing of particulate materials such as nanomaterials and microplastics leads to various challenges to be considered.
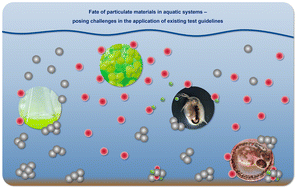
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2352-2371
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00056K
Electrified CO2 valorization in emerging nanotechnologies: a technical analysis of gas feedstock purity and nanomaterials in electrocatalytic and bio-electrocatalytic CO2 conversion
This perspective illuminates the crucial need to consider gas feedstock purity and source when designing new electrified CO2 conversion nanomaterials.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1770-1783
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00912B
Sustainable synthesis: natural processes shaping the nanocircular economy
This perspective aims to shed light on the transformative potential of sustainable synthesis in guiding the transition towards circular economy conceptions in the nanotechnology domain.
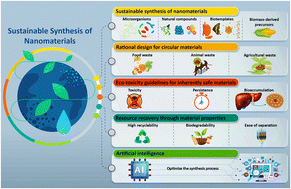
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 688-707
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00973D
Recycling of non-product outputs containing rare elements originating in nanomaterial syntheses
Recycling of non-product outputs containing substantial amounts of rare elements originating in nanomaterial syntheses is relatively attractive as rare elements tend to be more valuable than abundant elements.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 684-687
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00795B
Modern materials provoke ancient behavior: bacterial resistance to metal nanomaterials
Engineered nanomaterials are increasingly being used in a range of applications; it is important to characterize bacterial response to these novel materials.
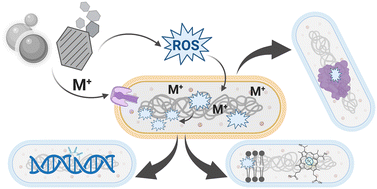
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 483-493
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00420A
U. S. federal perspective on critical research issues in nanoEHS
This article discusses critical issues and opportunities in nanotechnology environmental, health, and safety (nanoEHS) research from the perspective of many U.S. NEHI agencies.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2623-2633
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00062A
In vitro-based human toxicity effect factors: challenges and opportunities for nanomaterial impact assessment
Drawing the picture of the opportunities and challenges of using in vitro data to calculate effect factors in LCA.
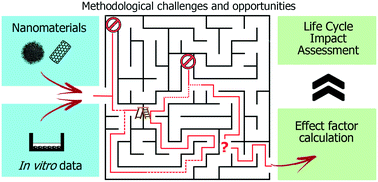
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 1913-1925
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01014J
Emerging investigator series: perspectives on toxicokinetics of nanoscale plastic debris in organisms
Fragmentation of plastic waste in the environment can lead to the formation of nanoscale plastic debris (NPD) of size < 1 μm.
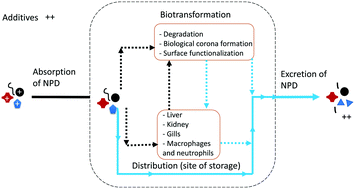
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 1566-1577
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00425E
Carbon nanomaterials and their impact on membrane separation applications
Design, use, and recyclability of carbon nanomaterials in membranes provide new opportunities for advancing separation applications.
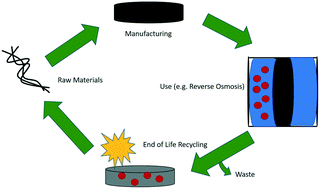
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 3056-3066
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00263E
What is “Environmentally Relevant”? A framework to advance research on the environmental fate and effects of engineered nanomaterials
FRAME: Framework for Relevance And Methods Evaluation.
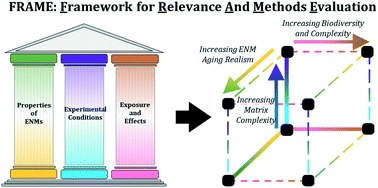
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 2414-2429
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00162K
Perspectives on palladium-based nanomaterials: green synthesis, ecotoxicity, and risk assessment
By comprehensively analyzing and discussing the application progress, environmental behavior and ecotoxicology of palladium-based nanomaterials (Pd-NMs), guidelines are provided for the sustainable development of Pd-NMs.
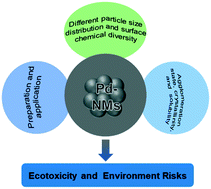
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 20-36
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EN01048K
Recent advances in the environmental application of graphene-based composites
Graphene-based composites have been widely applied in environmental remediation owing to their high removal capacity.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2302-2323
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00340C
An insight into the role of carbon dots in the agriculture system: a review
CDs in sustainable agricultural production can significantly aid in meeting global food demand while maintaining environmental resilience.
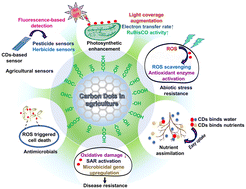
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 959-995
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00954D
Recent advances in the design of controlled- and sustained-release micro/nanocarriers of pesticide
Diagram of components of controlled- and sustained-release micro/nanocarriers of pesticide: nanomaterials and stimuli-responsive triggers (R stands for different groups).
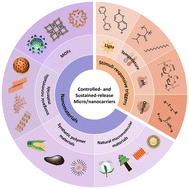
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 351-371
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00446A
2D MXene nanocomposites: electrochemical and biomedical applications
In this review article, key factors about the 2D MXene nanomaterials in electrochemical and biomedical applications have been reviewed and discussed.
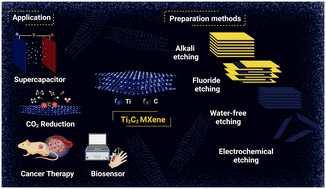
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 4038-4068
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00527A
Recent advances in the application of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) in environmental remediation: a review
The removal of gases, organics, heavy metals and radionuclides on zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs).
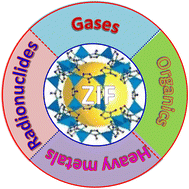
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 4069-4092
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00601D
Manipulation of the halloysite clay nanotube lumen for environmental remediation: a review
The halloysite clay nanotube lumen has shown great application potential in the field of environmental remediation. This relies on delicate manipulation of the clay nanotube lumen and benefits from the unique functionality of the nanotube lumen.
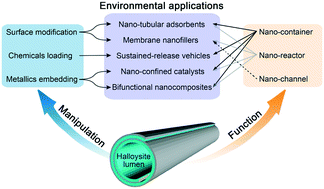
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 841-866
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01032H
Adsorption and desorption mechanism of aromatic VOCs onto porous carbon adsorbents for emission control and resource recovery: recent progress and challenges
This review highlights the characteristics of adsorption and desorption of aromatic VOCs on various PCAs as well as the integrated technologies for emission control and resource recovery of industrial VOC exhaust.
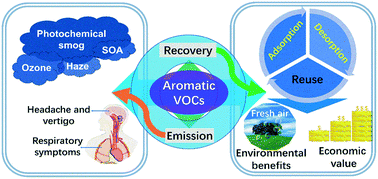
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 81-104
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00929J
Strategies for enhancing the perylene diimide photocatalytic degradation activity: method, effect factor, and mechanism
Strategies to improve the photocatalytic activity of PDI are summarized. The system factor and water chemistry affecting the photocatalytic activity for organic pollutant removal are discussed. The stability and future challenges are discussed.
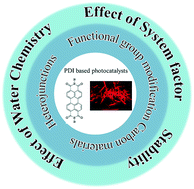
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 602-618
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EN01245A
A critical review investigating the use of nanoparticles in cosmetic skin products
This review article focuses on current cosmetic ingredients claiming a nano nature, the unique characteristics of nanomaterials and their behaviour on the skin, how they can be suitable for natural cosmetics and nanocosmetic environmental fate.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3674-3692
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00489B
Challenges and prospects: graphene oxide-based materials for water remediation including metal ions and organic pollutants
The remediation of polluted water via graphene oxide or derived materials has captivated the momentous attention of the scientific community over the past few years.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3693-3720
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00143E
Mechanistic approaches for crosstalk between nanomaterials and plants: plant immunomodulation, defense mechanisms, stress resilience, toxicity, and perspectives
This review provides new insights for the development of nanomaterials with potential immunomodulatory effects in plants towards resistance against biotic and abiotic stresses.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2324-2351
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00053F
Classification, uptake, translocation, and detection methods of nanoparticles in crop plants: a review
Nanotechnology offers a viable solution to enhancing agricultural sustainability by supporting seed germination and crop growth.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1847-1870
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00059E
The pulmonary effects of nickel-containing nanoparticles: cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, and their underlying mechanisms
This review summarized the cytotoxic, genotoxic, and carcinogenic effects of Ni-containing NPs on humans, lung cells in vitro, and rodent lungs in vivo, and the underlying mechanisms. Their extra-pulmonary effects were also briefly mentioned.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1817-1846
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00929G
Magnetically recyclable nanophotocatalysts in photocatalysis-involving processes for organic pollutant removal from wastewater: current status and perspectives
The critical review covers the applications, associated mechanisms, challenges, and prospects of magnetically recyclable nanophotocatalysts in photocatalysis-related processes.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1784-1816
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00906H
Recycling and repurposing of waste carbon nanofiber polymers: a critical review
Carbon nanofibers are a class of lightweight, high-performance composite materials.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1394-1411
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00784G
Understanding the active sites and associated reaction pathways of metal-free carbocatalysts in persulfate activation and pollutant degradation
Environmental remediation based on peroxomonosulfate- and peroxydisulfate-activation-enabled radical/non-radical oxidation has gained growing interest due to the strong oxidation power, long life of reactive oxygen species, and wide pH adaptability.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1368-1393
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00988B
Applications of bismuth-based nanoparticles for the removal of pollutants in wastewater: a review
This review discusses the characteristics and synthesis methods of Bi-based NPs. It delves into the removal efficiency in wastewater, emphasizing traditional/emerging strategies to enhance the performance, mechanisms, toxicology, and challenges.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1332-1367
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00983A
Nanozymes: powerful catalytic materials for environmental pollutant detection and degradation
Here we made a critical review on nanozyme-involved detection and degradation of environmental pollutants, and the research progress achieved in the last five years was emphatically concluded.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 766-796
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00844D
Recent advances in II–VI group semiconductor- and carbon-based quantum dots for fluorescence-based sensing of metal ions in water
Quantum dots (QD), semiconductor nanoparticles of size <10 nm, have recently emerged as an intriguing field in materials science due to their size-dependent opto-electronic properties, chemical stability, and potential for a wide range of applications.
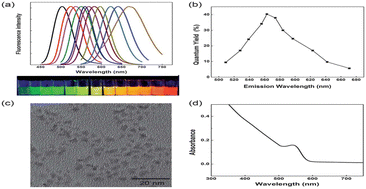
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 739-765
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00541K
The nanosafety assessment of ENMs under a dermal exposure scenario: from key molecular events to in silico modeling tools
This review provides insights into key molecular events underlying ENMs toxicity under the dermal exposure scenario and the application of computational modeling tools in predicting the fate and toxicity of ENMs in nano-skin interactions.
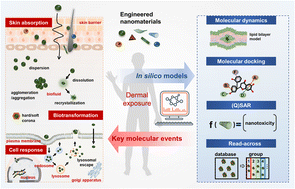
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 708-738
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00585B
Immobilization of biogenic metal nanoparticles on sustainable materials – green approach applied to wastewater treatment: a systematic review
The simultaneous use of bio-resources and sustainable materials as reducing/capping agents and supporting materials to obtain supported metal nanoparticles is a significant green approach applied to wastewater treatment.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 36-60
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00623A
A critical review on the toxicity regulation and ecological risks of zinc oxide nanoparticles to plants
This review clarifies the translocation of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) in plants, reveals the molecular mechanisms of toxicity regulation, and emphasizes the potential risks of composite systems of NPs.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 14-35
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00630A
Nano–eco interactions: a crucial principle for nanotoxicity evaluation
A corona of thorns in ENMs dramatically alters the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of ENMs, and as a consequence influences their behavior and fate.
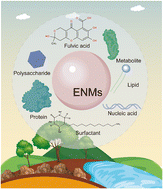
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3253-3270
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00617D
Nanomaterials in plant management: functions, mechanisms and prospects
Efficient, sustainable agricultural methods are critical to meet the food requirements of a rapidly growing global population.
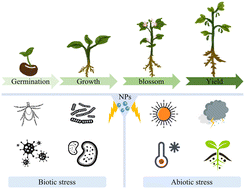
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3232-3252
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00014A
Evaluating metal oxide nanoparticle (MeOx NP) toxicity with different types of nano descriptors mainly focusing on simple periodic table-based descriptors: a mini-review
Given the rapid growth of nanotechnology, it is essential to know the hazardous effects of metal oxide nanoparticles (MeOx NPs) posed to living organisms within the ecosystem.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2989-3011
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00598D
Prospects of 2D graphene nanomaterials in plant-based agriculture and their fate in terrestrial soil: a critical review
To achieve a world without hunger, it is imperative to address the inefficiencies within the current agricultural system by adopting innovative and sustainable approaches.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2936-2956
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00511A
Recent trends on MIL-Fe metal–organic frameworks: synthesis approaches, structural insights, and applications in organic pollutant adsorption and photocatalytic degradation
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are gaining considerable interest for various uses ranging from adsorption, photocatalysis, electrocatalysis, chemical sensing, catalysis and gas separation.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2957-2988
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00332A
Degradation of organic contaminants by peroxymonosulfate activated with zeolitic imidazolate framework-based catalysts: performances, mechanisms and stability
ZIF-based catalysts have great potential for PMS activation in environmental treatment. State of the art and prospects in recent breakthroughs are presented in this review.
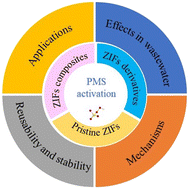
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1528-1552
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00007A
Interplay of metal-based nanoparticles with plant rhizosphere microenvironment: implications for nanosafety and nano-enabled sustainable agriculture
The development of nanotechnology and the widespread application of metal-based nanoparticles (MNPs) in various consumer products have released a large number of nanoparticles into soil environment, especially agricultural systems.
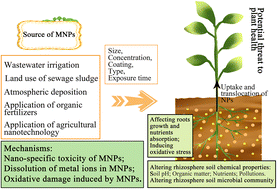
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 372-392
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00803C
Environmental routes of virus transmission and the application of nanomaterial-based sensors for virus detection
Many outbreaks of emerging disease (e.g., avian influenza, COVID-19) are enhanced by the environmental dissemination of viruses. Nanotechnology enabled tools have the potential to detect viruses in complex environmental matrices.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 393-423
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00600F
Biological effects of AgNPs on crop plants: environmental implications and agricultural applications
The varied use and disposal of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) has allowed their presence in reclaimed water and sewage sludge, making them possibly available in agricultural soils.
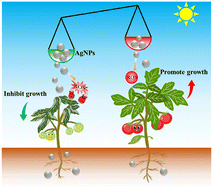
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 62-71
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00801G
Nanobiopesticides in sustainable agriculture: developments, challenges, and perspectives
Applications of nanotechnology in biopesticides could achieve controlled release, increase the solubility, and exhibit location targeting and strong compatibility.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 41-61
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00605G
Carbon nanomaterial-based membranes for water and wastewater treatment under electrochemical assistance
Carbon nanomaterial-based membranes exhibit fascinating permselectivity for water and wastewater treatment, and their performance could be further improved under electrochemical assistance, benefiting from their good electrical conductivity.
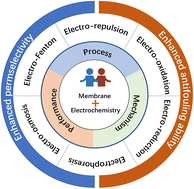
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 11-40
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00545J
Application of nano-agricultural technology for biotic stress management: mechanisms, optimization, and future perspectives
Nano-agricultural technology is a promising alternative for sustainable control crop biotic stress that has more economic and environmental benefits as compared with conventional analogues.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 4336-4353
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00651K
Graphene-based nanomaterials and microbial communities: a review of their interactions, from ecotoxicology to bioprocess engineering perspectives
This review discusses the interactions between graphene-based nanomaterials and microbial communities in different environmental compartments reconstituted in microcosms, from soil and freshwater to bioprocesses treating waste.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3725-3741
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00547F
Are nanomaterials leading to more efficient agriculture? Outputs from 2009 to 2022 research metadata analysis
By compiling quantitative information obtained from 1154 publications, the present study aims at offering an overview on how the interaction between nanomaterials & plants has been approached.
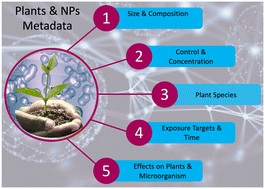
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3711-3724
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01078F
Recent advances on gold and silver nanoparticle-based colorimetric strategies for the detection of different substances and SARS-CoV-2: a comprehensive review
Nanoparticle (NP)-based colorimetric methods are extensively used for the rapid detection of different substances and SARS-CoV-2 in various fields such as environmental science, virology, pollution research, food industry, as well as biomedicine.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3684-3710
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00503D
Nanomaterials for enhancing photosynthesis: interaction with plant photosystems and scope of nanobionics in agriculture
The complex process of photosynthesis requires precise arrangements of light harvesting molecules in the photosynthetic system.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3659-3683
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00451H
New insights into the safety assessment of quantum dots: potential release pathways, environmental transformations, and health risks
Potential release pathways, environmental transformations and health risks of QDs.
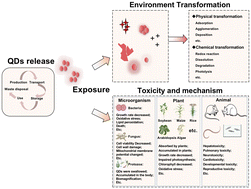
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3277-3311
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00252C
Construction of adsorbents with graphene and its derivatives for wastewater treatment: a review
A comprehensive and critical overview of graphene-based adsorbents in capturing various water contaminants within the recent five years is presented to drive the rational development of high-performance adsorbents with graphene and its derivatives.
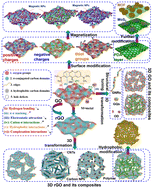
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3226-3276
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00248E
Synchrotron radiation-based analysis of interactions at the nano–bio interface
This review highlights the importance and advantages of synchrotron radiation (SR)-based techniques for revealing the interactions at the nano–bio interface.
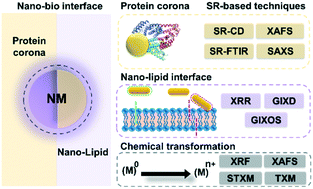
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3152-3167
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00408A
Carbon dots derived from natural sources and their biological and environmental impacts
Carbon dots derived from natural sources have drawn tremendous interest due to their superior characteristics. However, it is essential to evaluate both their biological and environmental impacts on contributions and the emerging concerns.
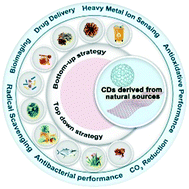
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3206-3225
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00435F
Recent progress in environmental remediation, colloidal behavior and biological effects of MXene: a review
Recent progress in environmental remediation, colloidal behavior and biological effects of MXene was summarized.
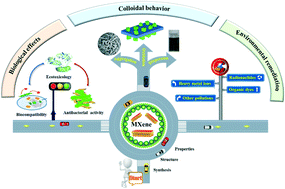
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3168-3205
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00340F
Nanocomposite-based high-performance adsorptive water filters: recent advances, limitations, nanotoxicity and environmental implications
Herein, high-performance functional nanomaterials which are demonstrated as efficient adsorbents, membrane materials, and membrane-based water treatment devices are reviewed envisaging simple and scalable water purification technologies.
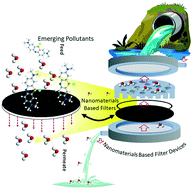
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 2320-2341
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00155A
Chemical degradation kinetics for two-dimensional materials in natural and biological environments – a data-driven review
Many 2D materials undergo chemical degradation in the environment or living systems. This review converts raw literature data into standard kinetic parameters for meta-analysis, and discusses implications for 2D technologies and risk assessment.
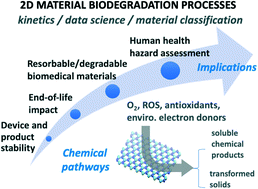
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 2297-2319
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01171E
Emerging investigator series: metal nanoparticles in freshwater: transformation, bioavailability and effects on invertebrates
MNPs may undergo different environmental transformations in aquatic systems, consequently changing their mobility, bioavailability and toxicity to freshwater invertebrates.
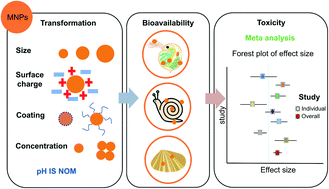
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 2237-2263
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00052K
Advances and challenges of broadband solar absorbers for efficient solar steam generation
This review provides guidance for solar absorber design, selection, and optimization, and evaporation system engineering for efficient solar-driven evaporation.
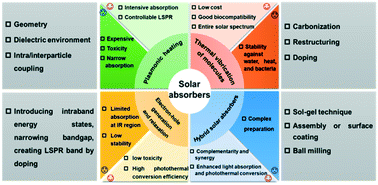
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 2264-2296
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00070A
The potential of nanomaterials for sustainable modern agriculture: present findings and future perspectives
Nanotechnology has received attention in the recent decade due to a plethora of advantages over conventional agriculture techniques, in terms of improved effectiveness, decreased input needs, and lesser environmental toxicity.
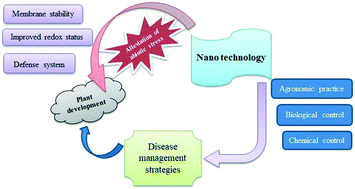
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 1926-1951
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01124C
Recent advances in the applications of nanozymes for the efficient detection/removal of organic pollutants: a review
Recent advances in the applications of nanozymes for the efficient detection/removal of organic pollutants.
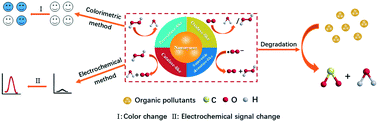
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 1212-1235
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00027J
Toxicological impact of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and food-grade titanium dioxide (E171) on human and environmental health
This review focuses on the correlation between the physico-chemical characteristics of TiO2 nanoparticles, their passage through biological barriers, and the impact of this nanomaterial on human and environmental health.
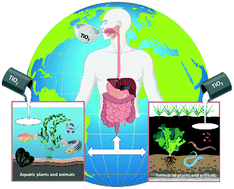
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 1199-1211
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00833A
Boosting CO2 electroreduction towards C2+ products via CO* intermediate manipulation on copper-based catalysts
An overview of the strategies for boosting C2+ selectivity by manipulating CO*(CO).

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 911-953
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00977J
Assessing the environmental effects related to quantum dot structure, function, synthesis and exposure
Quantum dots (QDs) have unique properties, which make them valuable in some commercial technologies. This review discusses the major types and applications of QDs, their potential environmental exposures, fates, and adverse effects on organisms.
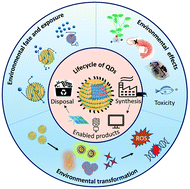
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 867-910
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00712B
Determination of metallic nanoparticles in biological samples by single particle ICP-MS: a systematic review from sample collection to analysis
A systematic review of the use of single particle ICP-MS to analyse engineered nanomaterials in biological samples has highlighted that efforts have focused on a select few compositions and there is a lack of information for some important tissues.
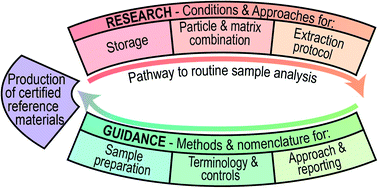
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 420-453
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00680K
Effects of microenvironmental factors on assessing nanoparticle toxicity
Nanoparticles, such as dust or fine particles, are regarded as hazardous materials to human organs, and the interest in understanding their biological mechanisms and cellular response of nanoparticles is growing.
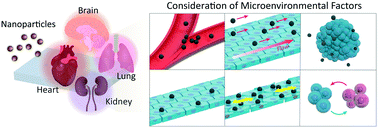
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 454-476
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00925G
A critical review on surface-modified nano-catalyst application for the photocatalytic degradation of volatile organic compounds
Surface modified nano-catalysts to improve the performance of photocatalytic degradation of VOC.
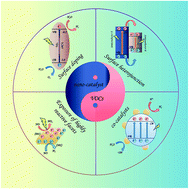
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 61-80
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00955A
Dimension dependency of tungsten oxide for efficient gas sensing
In this review, the impact of the structure dimensionality and surface morphologies of WO3 for efficient detection of gases such as H2, NH3, H2S, CO, O3, VOCs etc. along with the influence of surface functionalization and doping has been discussed.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 40-60
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00872B
Uptake, translocation, and transformation of silver nanoparticles in plants
This article reviews the plant uptake of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) that occurred in soil systems and the in planta fate of Ag.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 12-39
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00870F
Porous materials confining noble metals for the catalytic reduction of nitroaromatics: controllable synthesis and enhanced mechanism
In the field of nanocatalysis, noble metal nanoparticles (NPs) have aroused tremendous attention owing to their superb catalytic efficiency, especially in the catalytic reduction of nitroaromatics.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 3067-3097
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00628B
Advances in nanofluidics for water purification and filtration: molecular dynamics (MD) perspective
Worldwide industrialization and population growth have caused dramatic environmental pollution that has led to a water crisis.
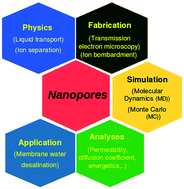
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 2120-2151
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00269D
About this collection
In addition to high quality research papers, Environmental Science: Nano features topical review articles. Reviews will be added to this webpage as soon as possible after publication.