Themed collection Sustainable Composites

Introduction to sustainable composites
Professor Ian Hamerton, Dr Lois Jane Hobson & Dr Jonathan Wagner introduce the Royal Society of Chemistry cross-journal themed collection on sustainable composites.

RSC Sustainability, 2024,2, 261-264
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SU90060F
Some of the challenges faced by the Composites Industry in its bid to become more sustainable
The Composites Industry needs to participate in future circular chemical economies. Cooperation, standardisation and increased availability of transparent industry data for life cycle analysis, are seen as critical to a more sustainable future.

RSC Sustainability, 2023,1, 1737-1742
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SU00200D
Nanocarbon-based sensors for the structural health monitoring of smart biocomposites
Smart biocomposites with integrated nano-carbons based sensors for structural health monitoring advances the real-world applications.

Nanoscale, 2024,16, 1490-1525
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3NR05522A
Processing and properties of jute (Corchorus olitorius L.) fibres and their sustainable composite materials: a review
Jute fibres and their composites have attracted attention from researchers and have been used in many fields.

J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024,12, 1923-1997
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TA05481K
Self-healable fiber-reinforced vitrimer composites: overview and future prospects
The article covers the outstanding features of fiber-reinforced vitrimer composites, including their reprocessing, recycling and self-healing properties.
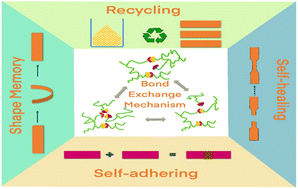
RSC Adv., 2022,12, 32569-32582
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA05103F
An algae-derived partially renewable epoxy resin formulation for glass fibre-reinforced sustainable polymer composites
A brown algae-based renewable epoxy monomer can outperform bisphenol-A based epoxy resin and composite systems by means of thermomechanical properties.

RSC Appl. Polym., 2024,2, 149-154
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3LP00174A
A rapid electrochemical method to recycle carbon fiber composites using methyl radicals
We report an electrochemical system for selective deconstruction and re-manufacture of epoxy-carbon fiber composite using a Kolbe-like mechanism for generating methyl radicals from CH3COOH. These cleave C–N bonds via hydrogen atom abstraction.

Green Chem., 2023,25, 7058-7061
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3GC01765F
Ultra-violet light-driven green oxygen scavenging composite made of PVA/NRL for active packaging: an alternative to metallic oxygen scavengers
Fabrication of biodegradable oxygen-scavenging films and their activity at different temperatures for food packaging.
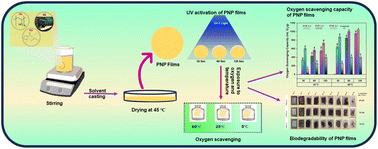
Green Chem., 2024,26, 5293-5307
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3GC03264G
A hierarchically modified fibre-reinforced polymer composite laminate with graphene nanotube coatings operating as an efficient thermoelectric generator
SWCNT-p-type TE films on GF with a power factor of 96 μW m−1 K−2. SWCNT-n-type TE films on GF with a power factor of 82 μW m−1 K−2. The GFRP–OTEG exhibited: VOC = 1.01 V, ISC = 850 μA, Pmax = 215 μW.

Mater. Adv., 2024,5, 3721-3734
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA01000G
B(C6F5)3 grafted inorganic fillers for supported titanium-catalyzed synthesis of UHMWPE composites
The preparation of polyolefin composites using inorganic fillers is one of the most important strategies for cost reduction and property enhancement.

Polym. Chem., 2024,15, 1393-1398
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4PY00096J
Structure and properties of biobased polyamide 36,9/cellulose nanocomposites
The presence of renewable fillers, cellulose nanocrystals, enhances the Young's modulus of a biobased elastomer, polyamide 36,9. The modulus of the resulting fully biobased nanocomposites closely follows a classical theory of composite mechanics.

RSC Sustainability, 2023,1, 2254-2260
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SU00302G
Surface modification of aramid fiber meshes – the key to chemically recyclable epoxy composites
Fiber surface functionalization can play a dual role in the development of fiber reinforced polymer composites; improving the overall performance and enabling recovery of high-quality fibers.

RSC Sustainability, 2023,1, 1967-1981
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SU00258F
Pyrene-based covalent organic polymers with nano carbonaceous composites for efficient supercapacitive energy storage
We prepared Py-DSDA-COP/SWCNTs and this material showed a capacitance of 171 F g−1 and energy density of 23.7 W h kg−1 which is superior to those of Py-DSDA-COP/MWCNTs and Py-DSDA-COP/C60 nanocomposites.

J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023,11, 22868-22883
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TA02741D
Bio-based captodative ligands for redox polymerization of Elium® thermoplastic composites under mild conditions
Thermoplastic polymers obtained from Elium® combine desirable properties including recyclability/reusability. In this work new biobased redox initiating systems are proposed for Elium.

Green Chem., 2023,25, 8226-8240
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3GC03001F
Fully recyclable high-performance polyacylsemicarbazide/carbon fiber composites
Realizing the complete and non-destructive recycling of carbon fiber reinforced composite materials is of great significance for the pursuit of sustainability and a circular economy.
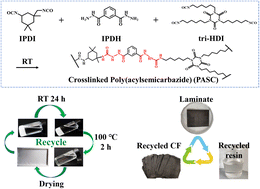
J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023,11, 21231-21243
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TA01841E
Solvent-free preparation of imine vitrimers: leveraging benzoxazine crosslinking for melt processability and tunable mechanical performance
Orthogonal benzoxazine crosslinking enables the solvent-free preparation of dynamic imine vitrimers with tailorable thermomechanical performance, efficient reprocessability, and chemical degradation.
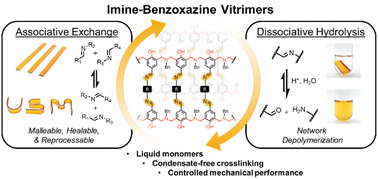
J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023,11, 20568-20582
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TA04351G
A molecular dynamics approach to modelling oxygen diffusion in PLA and PLA clay nanocomposites
Computational techniques predict the barrier performance of poly(lactide) composites, studying the relationship between free volume, polymer morphology and gas diffusion.

Mater. Adv., 2023,4, 2281-2291
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00158J
A mild and efficient oxidative degradation system of epoxy thermosets: full recovery and degradation mechanism
An efficient oxidation degradation is achieved together with full recovery of the degradation product via the selective cleavage of the C–C and C–O bonds in the hydroxyethyl ether unit, and the C–N bonds using the ammonium ceric nitrate system.

Green Chem., 2022,24, 7082-7091
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2GC01678H
Catalyst-free dynamic transesterification towards a high-performance and fire-safe epoxy vitrimer and its carbon fiber composite
A new strategy was proposed to design a fire-safe vitrimer with catalyst-free adaptable ester-linked networks and its composite. Furthermore, the vitrimer matrix in the composite was degraded to achieve carbon fibers with nearly 100% recyclability.
Green Chem., 2022,24, 6980-6988
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2GC01405J
Recyclable CFRPs with extremely high Tg: hydrothermal recyclability in pure water and upcycling of the recyclates for new composite preparation
In this work, a recyclable epoxy system with superior mechanical performance and high Tg (>200 °C) is developed for CFRPs, and a simple and feasible approach for highly efficient closed-loop recycling of CFRPs is demonstrated.

J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022,10, 15623-15633
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TA03161B
A novel eco-friendly strategy on the interfacial modification of a carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer composite via chitosan encapsulation
The interfacial properties are the key factors affecting the properties of carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites.

Mater. Chem. Front., 2022,6, 765-774
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1QM01587G
About this collection
The Royal Society of Chemistry is delighted to present this cross-journal themed collection on Sustainable Composites, guest edited by Professor Ian Hamerton (University of Bristol), Dr Lois Hobson (Centre for Process Innovation) and Dr Jonathan Wagner (Loughborough University).
The Royal Society of Chemistry is committed to championing new research and promoting skills and development in the composites sector. This cross-journal themed collection contributes to the action plan from the Sustainable Composite Materials report by the RSC. This cross-journal themed collection on Sustainable Composites creates opportunities for researchers to publish peer-reviewed studies on sustainable composites. It intends to bring together articles tackling the sustainability of the entire composite lifecycle, including new composite feedstocks, low-energy manufacturing, design for end-of-life, in-use benefits, extended composite lifetime and repair, material recovery and recycling.