Themed collection Molecular BioSystems Emerging Investigators 2012

Emerging investigators contributors 2012
Editor Harpal Minhas introduces this themed issue and presents the profiles of the contributing authors.

Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2461-2465
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB90034C
Towards high throughput metabolic flux analysis in plants
Metabolic flux analysis in plants is currently a low-throughput method. This opinion article suggests strategies for shifting towards high throughput.
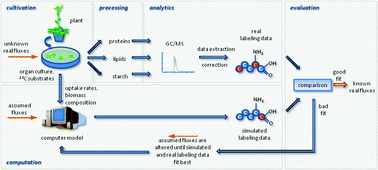
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2466-2469
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25068C
Metabolome 2.0: quantitative genetics and network biology of metabolic phenotypes
This review covers the key developments in the quantitative genetics and network biology of the metabolome to deliver personalized medicine.
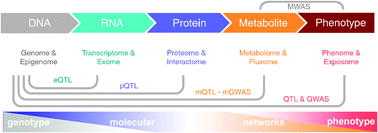
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2494-2502
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25167A
Robustness analysis of cellular systems using the genetic tug-of-war method
In this review we explain the current progress in robustness measurements in vivo using the gTOW method.
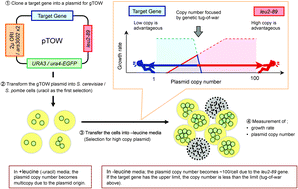
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2513-2522
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25100K
Combining redox-proteomics and epigenomics to explain the involvement of oxidative stress in psychiatric disorders
Oxidative stress is one of the most common alterations among psychiatric disorders.
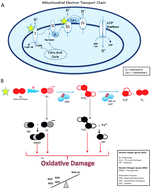
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2503-2512
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25118C
Chemoselective hydroxyl group transformation: an elusive target
Development of chemoselective transformations of the hydroxyl moiety is essential to the study of biological processes and the synthesis of complex natural products, but remains a challenging goal.
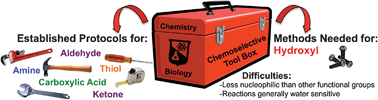
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2484-2493
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25122A
Engineering ecosystems and synthetic ecologies
Emerging advances in systems and synthetic biology enable design, synthesis, and construction of complex consortia of cells toward programmable ecosystems.
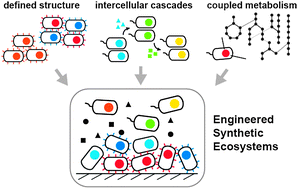
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2470-2483
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25133G
Intramolecular three-colour single pair FRET of intrinsically disordered proteins with increased dynamic range
Triple-colour labelling combined with a measurement and analysis scheme allows us to simultaneously study multiple regions within single intrinsically disordered proteins.
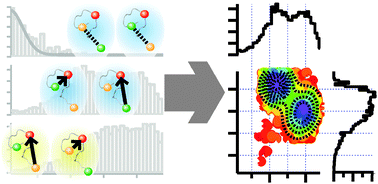
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2531-2534
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25135C
Leveraging kinase inhibitors to develop small molecule tools for imaging kinases by fluorescence microscopy
Probe BI-BODIPY, derived from polo-like kinase inhibitor BI2536, permits imaging of its kinase targets by fluorescence microscopy.
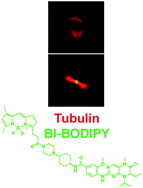
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2523-2526
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25099C
Positional requirements for the stimulation of mRNA nuclear export by ALREX-promoting elements
Signal sequence coding regions can only promote nuclear mRNA export when they are present near the 5′ end of the transcript.
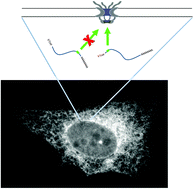
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2527-2530
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25016K
Differential RNAi screening provides insights into the rewiring of signalling networks during oxidative stress
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) are a natural by-product of cellular growth and proliferation, and are required for fundamental processes such as protein-folding and signal transduction.
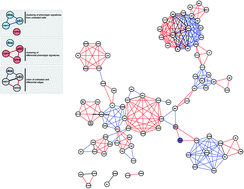
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2605-2613
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25092F
The Core Diseasome
Using H. sapiens protein–protein interaction network for computational isolation of topologically and functionally homogeneous “driver topology” enriched in disease genes, drug targets and driver genes.
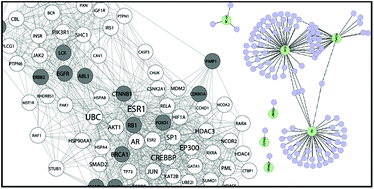
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2614-2625
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25230A
LASSO modeling of the Arabidopsis thaliana seed/seedling transcriptome: a model case for detection of novel mucilage and pectin metabolism genes
LASSO regression on a tissue specific transcriptomic dataset is used to identify novel candidate genes in Arabidopsis seed mucilage biosynthesis. One candidate transcription factor has been described in detail and it shows a similar phenotype as the “bait” gene that was used.
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2566-2574
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25096A
A novel calcineurin-independent activity of cyclosporin A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Our work illuminates the cellular circuitry that controls a novel synergy between two clinically important molecules, cyclosporin A and micafungin, and supports the utility of chemogenomic assays for elucidating mechanisms of drug synergy.
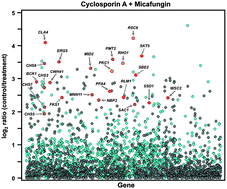
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2575-2584
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25107H
Identifying functional links between genes by evolutionary transcriptomics
We introduce a method by which pairs of genes are identified as functionally related when their expression profiles are more similar within species than the conservation across species.
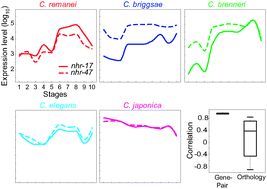
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2585-2592
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25054C
Metabolic regulation analysis of wild-type and arcA mutant Escherichia coli under nitrate conditions using different levels of omics data
We analyzed multi-omics data for wild-type and ΔarcA mutant Escherichia coli cultured under nitrate conditions.
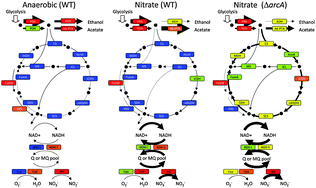
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2593-2604
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25069A
Metabolomic analysis of polar metabolites in lipoprotein fractions identifies lipoprotein -specific metabolic profiles and their association with insulin resistance
Lipoprotein fractions in human blood have distinct profiles of polar metabolites, which differentially associate with insulin resistance.
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2559-2565
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25115A
A compendium of inborn errors of metabolism mapped onto the human metabolic network
The expansion of a human metabolic network by acylcarnitine metabolic pathways enabled the assembly of a comprehensive compendium of inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs) and its use for classification, topological, and functional analysis.
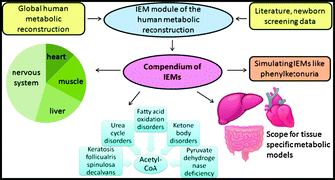
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2545-2558
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25075F
The spectral networks paradigm in high throughput mass spectrometry
Spectral networks algorithms transform the paradigm for analysis of tandem mass spectra by finding and jointly interpreting spectra from related molecules, regardless of the structure or class of molecules.
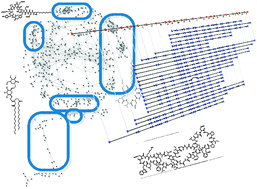
Mol. BioSyst., 2012,8, 2535-2544
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2MB25085C
About this collection
Molecular BioSystems is delighted to publish our fifth themed issue dedicated to the work of new and emerging investigators whose research in chemical biology interfaces with the -omic sciences and systems biology.