Themed collection Mechanobiology

Front cover

Contents list
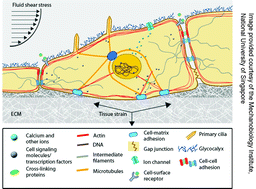
Mechanobiology
Guest editors G. V. Shivashankar, Michael Sheetz and Paul Matsudaira introduce the Mechanobiology themed issue of Integrative Biology.
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1091-1092
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB90040A
Multiscale mechanobiology: computational models for integrating molecules to multicellular systems
We review recent computational approaches and supporting experimental work in mechanobiology across multiple scales, from molecules to multicellular systems.
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1093-1108
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00043B
Regulation of epithelial cell organization by tuning cell–substrate adhesion
Combining live cell imaging, particle image velocimetry and numerical simulations, we show the role of extracellular matrix and intercellular adhesion on the expansion of epithelial cells.

Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1228-1241
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00196J
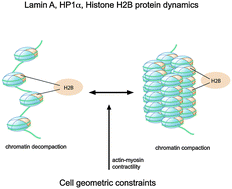
Actin cytoskeleton differentially alters the dynamics of lamin A, HP1α and H2B core histone proteins to remodel chromatin condensation state in living cells
Cellular mechanical signals via the actin cytoskeleton regulate DNA packing by altering the dynamics of nuclear structure proteins.
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1309-1317
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00027K
Micropatterning of TCR and LFA-1 ligands reveals complementary effects on cytoskeleton mechanics in T cells
Micropatterning of T cell ligands reveals their specific contributions to actin assembly and the generation of cytoskeletal forces in immunesynapse formation.

Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1272-1284
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00032G
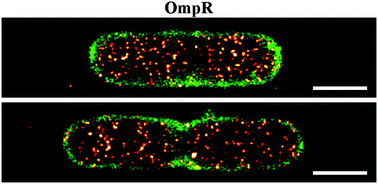
Single cell super-resolution imaging of E. coli OmpR during environmental stress
We used super-resolution microscopy to visualize the bacterial transcriptional regulator OmpR, the bacterial membrane and the chromosome.
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1297-1308
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00077G
Single molecular force across single integrins dictates cell spreading
Molecular forces via single integrins at the cell-substrate interface control the degree of cell spreading.
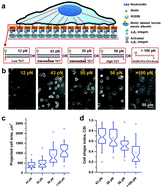
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1265-1271
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00080G
Mechanisms of integrin and filamin binding and their interplay with talin during early focal adhesion formation
Mechanisms of the interplay among filamin, integrin and talin during early focal adhesion formation were explored using molecular dynamics simulations.
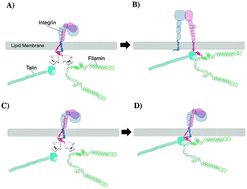
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1285-1296
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00133A
Modelling wound closure in an epithelial cell sheet using the cellular Potts model
We use a two-dimensional cellular Potts model to represent the behavior of an epithelial cell layer and describe its dynamics in response to a microscopic wound.
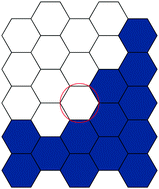
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1253-1264
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00053J
Modeling the finger instability in an expanding cell monolayer
Curvature-controlled cellular forces at the edge of an expanding monolayer are sufficient for the initiation and growth of finger-like instability.
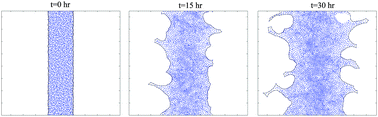
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1218-1227
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00092K
Ratio of total traction force to projected cell area is preserved in differentiating adipocytes
During obesity development, preadipocytes proliferate and differentiate into new mature adipocytes, to increase the storage capacity of triglycerides.

Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1212-1217
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00056D
Deterministic control of mean alignment and elongation of neuron-like cells by grating geometry: a computational approach
Combinatorial simulations are able to relate alignment and elongation of neuron-like cells on gratings.
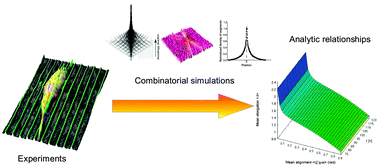
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1242-1252
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00045A
Traction stress analysis and modeling reveal that amoeboid migration in confined spaces is accompanied by expansive forces and requires the structural integrity of the membrane–cortex interactions
Neutrophil-like cells, confined between two non-fibronectin-coated gels, form blebs and generate expansive forces against opposing surfaces during amoeboid cell “chimneying”.
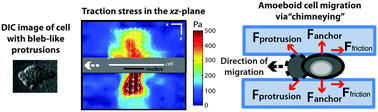
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1196-1211
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4IB00245H
Quantifying cell-induced matrix deformation in three dimensions based on imaging matrix fibers
An experimental technique that images fibers of an extracellular matrix to quantify cell-induced deformations and microstructural changes in three dimensions.
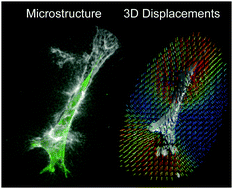
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1186-1195
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00013K
Non-monotonic cellular responses to heterogeneity in talin protein expression-level
Correlative imaging in single-cells of both live migration and post-fixation talin-labeling revealed non-monotonic correspondences between cellular properties and talin expression-levels.
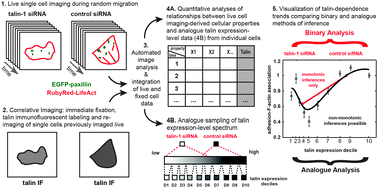
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1171-1185
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4IB00291A
Human breast cancer invasion and aggression correlates with ECM stiffening and immune cell infiltration
Human tumors are stiff and data suggest that the extracellular matrix stiffening is consistent with experimental mammary tumor models in which stiffness drives tumor invasion and metastasis.
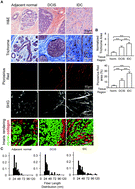
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1120-1134
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00040H
Oxygen governs gonococcal microcolony stability by enhancing the interaction force between type IV pili
Bacterial cell clusters disassemble after having depleted oxygen because the interaction force between their surface appendages is reduced.
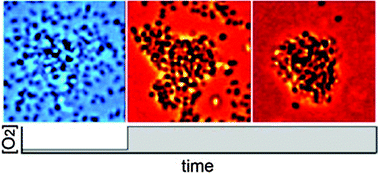
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1161-1170
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00018A
Thermodynamics of force-dependent folding and unfolding of small protein and nucleic acid structures
A theoretical framework for understanding equilibrium mechanical stretching of single proteins.
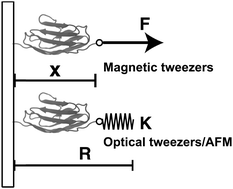
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1154-1160
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00038F
Microtubule appendages mediating T-cell motility and polarity
Motility and polarity of T cells are mediated in large measure by differential adhesion through the long, flexible microtubule-based appendages.
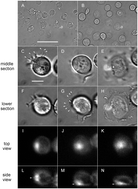
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1143-1153
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4IB00300D
Substrate elasticity modulates the responsiveness of mesenchymal stem cells to commitment cues
Fate choices of stem cells are regulated in response to a complex array of biochemical and physical signals from their microenvironmental niche.
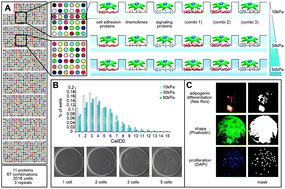
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1135-1142
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4IB00176A
High-throughput screening for modulators of cellular contractile force
Using cellular contractile force as the target, we report a new high-throughput screening technology.
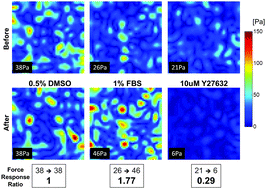
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1318-1324
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00054H
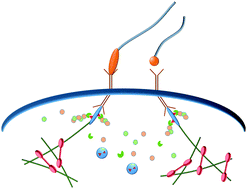
The mechanotransduction machinery at work at adherens junctions
α-Catenin, the core mechanosensor of adherens junctions, allows cells to sense, transduce mechanical constrain in biochemical signals by force-dependent conformational changes regulating protein interactions.
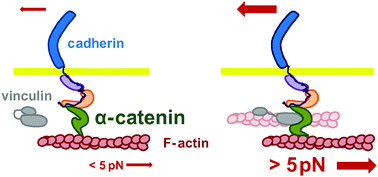
Integr. Biol., 2015,7, 1109-1119
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5IB00070J
About this collection
This themed issue on mechanobiology, guest edited by G. V. Shivashankar, M .P. Sheetz and P. Matsudaira, features original research and topical mini review articles on all areas of mechanobiology from molecular to organ scale, experimental, theoretical and computational analysis. Topics covered include: molecules and motors, mechanics of molecular motors in living cells, cell models of mechanobiology, mechanotransduction & genome regulation, mechanics of cellular differentiation/reprogramming, collective cell migration & tissue mechanics, mechanobiology of pathogenesis and cancer, bacterial mechanics and multiscale modeling in mechanobiology. We hope you enjoy this collection.