Themed collection Recent Open Access Articles

Emerging investigator series: are we undervaluing septage? Rethinking septage management for nutrient recovery and environmental protection
Septage is an untapped waste stream that could be utilized for recovery of beneficial nutrients, energy, and water.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1621-1628
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00998C
A case study of ethical bridges: wastewater-based epidemiology in the Rubbertown Air Toxics and Health Assessment (RATHA) project
This case study underscores both the need for and the feasibility of ethical planning in environmental health research, particularly when using wastewater-based epidemiology in vulnerable communities.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1363-1368
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00234F
Lithium recovery from U.S. oil and gas produced waters: resource quality and siting considerations
Aqueous geochemistry, access to end-users, and workforce availability are important to assess lithium extraction potential from produced brines.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 536-541
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00422A
Moving beyond silver in point-of-use drinking water pathogen control
Managing drinking water-associated pathogens that can cause infections in immunocompromised individuals is a persistent challenge, particularly for healthcare facilities where occupant exposures carry a substantial health risk.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 1009-1018
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00564J
Wastewater research and surveillance: an ethical exploration
This article provides an ethical exploration of wastewater research surveillance, incorporating insights from data ethics, public health ethics, research ethics, and environmental and water ethics.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2431-2438
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00127F
Targeting current and future threats: recent methodological trends in environmental antimicrobial resistance research and their relationships to risk assessment
Recent research on antimicrobial resistance in the environment has emphasized targeted methods. Increased use of non-targeted methods is needed to determine how frequently novel resistance genes arise.
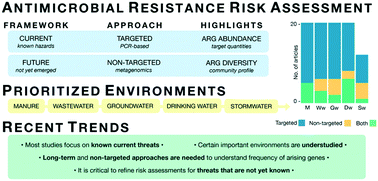
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1787-1802
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00087C
Plant-wide systems microbiology for the wastewater industry
Infiltrating systems microbiology concepts in the water industry requires the development of a language of love and shared endpoints in analytical bioscience and process engineering at the (waste)water line.
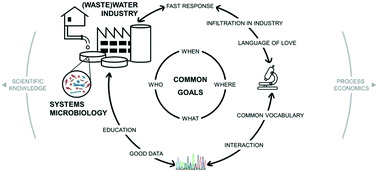
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1687-1706
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00231G
Urban stormwater capture for water supply: look out for persistent, mobile and toxic substances
Urban stormwater is a source of persistent, mobile and toxic substances, however the risk for water resources is unknown.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 3094-3102
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00160A
Emerging investigator series: the role of phage lifestyle in wastewater microbial community structures and functions: insights into diverse microbial environments
Harnessing phage for biological treatment is of growing interest, but an improved understanding of phage diversity, host range, lifestyle, molecular signaling, and genetic potential are needed for microbial community control.
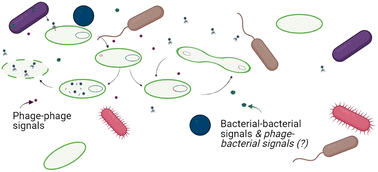
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1982-1991
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00755J
The potential contribution of urine source separation to the SDG agenda – a review of the progress so far and future development options
Closing the human nutrient cycle with decentralized urine separation would help to achieve progress in food security and water protection – especially in poor countries. For this, radical innovation is needed along the whole sanitation value chain.
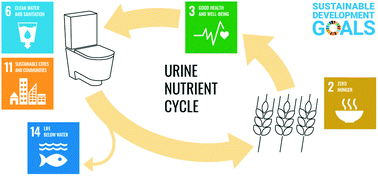
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1161-1176
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW01064B
Review of quantitative microbial risk assessments for potable water reuse
This review identified 30 studies from 1992–2024 that performed quantitative microbial risk assessments on potable reuse and compared individual assumptions, summarized influential parameters, and analyzed results.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 542-559
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00661E
Mechanism of lithium ion selectivity through membranes: a brief review
The ion transportation process through a membrane was divided into 3 sequential stages, where the ion selectivity could be determined by the ion charge, hydration energy, channel size and surface chemistry.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 1305-1318
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00769C
Quantitative sustainable design (QSD) for the prioritization of research, development, and deployment of technologies: a tutorial and review
This tutorial review synthesizes literature on sustainability analyses to introduce quantitative sustainable design (QSD) for technology research, development, and deployment.
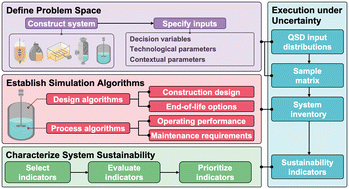
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2439-2465
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00431C
From prescription to pollution: environmental behavior and breakdown of fluoxetine
Schematic overview of fluoxetine's molecular structure, environmental pathways, and persistence, emphasizing existing and future treatment strategies for effective removal from aquatic systems.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2825-2843
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00636H
Covalent organic frameworks enable efficient atmospheric water harvesting in arid climates
This review discusses trends in COF-based atmospheric water harvesting under arid conditions, from mechanistic insights to innovative designs for enhanced performance over traditional sorbents.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2810-2824
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00643K
Iron and manganese removal from groundwater: comprehensive review of filter media performance and pathways to polyfunctional applications
This review uniquely integrates performance evaluation of Fe/Mn removal media with prospects for developing multifunctional catalytic materials.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2499-2515
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00751H
Organic micropollutant removal in stormwater: a review of treatment performance
Stormwater runoff is increasingly recognized as an alternative water resource, but organic micropollutant (OMP) contamination poses challenges to its safe harvesting.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2274-2294
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00306G
Revisiting simultaneous sulfate reduction and ammonium oxidation in wastewater treatment – from inexplicable experimental observations to extended mechanistic hypotheses
Revisiting simultaneous sulfate reduction and ammonium oxidation phenomenon: from inexplicable experimental results to extended mechanistic hypothesis.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1847-1860
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00283D
Assessing the environmental impact of freshwater use in LCA: established practices and current methods
Extensive water use leads to scarcity, adversely affecting human health, ecosystems, and resources. Life cycle assessment (LCA) evaluates these impacts via damage pathways, using characterization models to quantify effects.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 196-221
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00641K
Next generation decentralized water systems: a water-energy-infrastructure-human nexus (WEIHN) approach
This review highlights the pressing need for sustainable water management strategies within the water-energy-infrastructure-human nexus, and accentuates the critical roles of infrastructure and human engagement for sustainable water management.
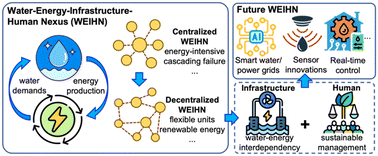
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2446-2471
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00506B
Antibiotic resistance in urban stormwater: a review of the dissemination of resistance elements, their impact, and management opportunities
Traditional stormwater infrastructure facilitates the transport of antibiotic resistance genes while green stormwater infrastructure may capture the genes and promote horizontal gene transfer.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 2188-2212
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00356F
Removal of metals from water using MOF-based composite adsorbents
This review article focuses on metal–organic framework (MOF) composites and the impact of mixing MOFs with other materials, such as polymers, carbon-based materials, and magnetic particles, to increase their performance to remove metals from water.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1305-1330
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00941B
Resource recovery technologies as microbial risk barriers: towards safe use of excreta in agriculture based on hazard analysis and critical control point
Individual resource recovery processes are monitored as health risk barriers.
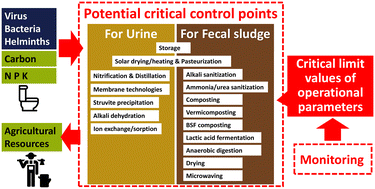
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1008-1029
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00832G
Addressing main challenges in the tertiary treatment of urban wastewater: are homogeneous photodriven AOPs the answer?
Homogeneous photodriven advanced oxidation processes (HP-AOPs) have been increasingly investigated in past years as a possible alternative solution to conventional tertiary treatment methods of urban wastewater.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 2145-2169
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00146B
Macroscopic covalent organic framework architectures for water remediation
This article has critically reviewed the story of macroscopic developments of COFs for water remediation. The various macroscopic COFs for removing toxic organic and inorganic pollutants have been systematically surveyed.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1895-1927
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00408E
Different routes of bismuth mineral transformation during pertechnetate and perrhenate uptake for subsurface remediation
Removal of pertechnetate 99TcO4− and perrhenate ReO4− during mineral transformation of the non-toxic basic bismuth subnitrate for subsurface remediation.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 2646-2654
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00496E
Two weeks after the 2023 Maui wildfires: drinking water experiences and needs
To understand community impacts and needs after the August 2023 Maui wildfires, we conducted a rapid survey-based field investigation two weeks after the incident.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2024,10, 2341-2356
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00216D
Arsenic removal from Peruvian drinking water using milk protein nanofibril–carbon filters: a field study
A field study was carried out in Peru to remove arsenic from water in arsenic-contaminated regions using milk protein nanofibril filters. Results show that this technology can bring back water to drinking standard in both urban and rural settings.
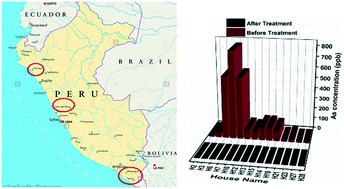
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 2223-2230
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00456E
Standardizing data reporting in the research community to enhance the utility of open data for SARS-CoV-2 wastewater surveillance
We propose a minimum set of meta-information to accompany the reporting of SARS-CoV-2 occurrence in wastewater for improved data interpretation.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1545-1551
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00235J
A novel water-from-air technology: creeping clathrate desalination of deliquescent salt solutions
Clathrate creeping enables clean separation of salt and water in deliquescent systems, highlighting a new route for decentralized and energy-efficient water-from-air harvesting.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2926-2934
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00838G
Low-level N-nitrosamine occurrence in disinfected drinking water and relationships with standard water quality indicators
N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), a probable human carcinogen, and other N-nitrosamines were measured in drinking water, and their relationships with standard water quality indicators were investigated.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 3116-3130
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00861A
Examining the growth and mobilization behavior of early-stage biofilms in a controlled, pilot scale PVC drinking water system laboratory
Early-stage biofilms were grown on the inner pipe wall of PVC pipes. Clusters were observed predominantly on pipe inverts and were able to resist pipe flushing forces.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 3083-3098
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00654F
Importance of a heat snap in RT-PCR quantification of rotavirus double-stranded RNA in wastewater
A heat snap is required for sensitive detection of rotavirus in wastewater.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2919-2925
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00773A
Tyre wear particles in a highway stormwater system during rain: quantification by automatic sampling and pyrolysis-GC/MS, and correlations with metals and solids
Tyre wear particles in a highway stormwater system exhibited high concentrations during rain events, with further transport through the system.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 3001-3013
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00656B
Lognormal distributions capture site-specific variability in enteric virus concentrations in wastewater
As more data on virus concentrations in influent water from wastewater treatment plants becomes available, establishing best practices for measurements, monitoring, and modelling can improve the understanding of virus distributions in wastewater.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2973-2985
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00286A
Wastewater remediation of pharmaceuticals with ozone and granular active carbon: a risk-driven approach
Ozone removed (psycho)pharmaceuticals slightly better than GAC. However, a risk-driven approach indicated that the expected creation of oxidative transformation products the modelled risk to the environment may actually increase after ozonation.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2986-3000
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00600G
Optimizing sodium percarbonate oxidation for wastewater treatment with artificial intelligence
Artificial neural networks optimize sodium percarbonate treatment of m-cresol wastewater, achieving 67.8% TOC removal with superior accuracy over RSM.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2935-2943
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00689A
Tapwater-contaminant mixtures and risk in a biofuel-facility impacted private-well community
We assessed private-well drinking water (DW) at the point of use (i.e., tapwater, TW) within a rural Nebraska community around a state-closed biofuel facility, which used pesticide-treated corn seed as feedstock for ethanol production.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2572-2594
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00490J
Novel MOF grown on Ni foam as an ex situ absorptive medium for the remediation of Hg polluted water in surface water
By coating a nano-porous MOF, as micro-porous crystals, on a macro-porous foam, the availability of active sites for adsorption can be optimized.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2747-2754
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00688K
Improving microalgae harvesting efficiency: electrochemical techniques and parameter optimization
Electrochemical algae harvesting achieved 99% efficiency with BDD–Al electrodes. Lipid, protein, and sugar contents were assessed, while current, pH, and electrolysis time significantly influenced efficiency and energy use.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2650-2664
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00518C
Sustainable and low-cost drinking water production via electrodialysis by addressing membrane fouling mechanisms to optimize cleaning strategies
Groundwater is a vital water source, providing drinking water to at least 50% of the world's population and accounting for 43% of water used in irrigation.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2734-2746
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00498E
Multi-point ozone dissolution for enhanced bromate control with hydrogen peroxide in potable reuse
In the present study, a novel pilot ozone contactor configuration was employed using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and multiple ozone diffusion zones in an over-under contactor to reduce bromate formation in three wastewater effluents.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2638-2649
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00627E
Iodinated disinfection byproduct formation from iohexol in sunlit and chlorinated urban wastewaters
Iodinated disinfection by-products (I-DBPs) are of growing concern due to their elevated toxicity compared to their chlorinated counterparts, with links to adverse health effects such as bladder cancer and miscarriages.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2529-2541
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00709G
Hydrolysis modeling for combined primary and RAS sludge fermentation at water resource recovery facilities
This study models combined primary and return activated sludge fermentation, highlighting anaerobic hydrolysis rate, hydrogen yield, and methanogenic growth. Higher primary sludge content boosts fermentation, assessed with two hydrolysis models.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2608-2619
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00533G
Pyrolysis of faecal sludge and biomass waste for resource recovery in Kampala, Uganda
Resource recovery potential of chars produced from faecal sludge and biomass waste, in Kampala, Uganda. Comparison with fundamental properties of excreta-derived chars allows the quantification of optimisation pathways via source control.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2542-2554
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00434A
Enhancing drinking water quality modeling: leveraging physics informed neural networks for learning with imperfect reaction models and partial data
PINN improves water quality prediction with partial data and imperfect chemical model.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2684-2697
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00682A
Towards sustainable PMR for organic contaminant removal from municipal wastewater
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) resist degradation, posing health and environmental risks. Photocatalytic membrane reactors offer efficient POP breakdown and easy catalyst recovery, enabling safe, reusable water for agriculture and beyond.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2398-2411
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00485C
Efficient preparation of adsorption beds from polycarbonate and cotton fabric wastes: removal of nitroaromatic pollutants from water
The pollution of the environment with explosives and their decomposition products, particularly resulting from armed conflicts and intensive mining activities, poses a serious problem nowadays.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2412-2426
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00669D
Removal of long- and short-chain PFAS from groundwater by foam fractionation
Foam fractionation with cationic surfactants addition can rapidly remove both long-chain and short-chain PFAS from water.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2295-2307
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00440C
Adsorbent modified constructed wetlands for advanced removal of bulk organics and heavy metals from municipal wastewater effluent
The modification of constructed wetlands with biochar, zeolite and activated carbon considerably enhances the removal of bulk organics, nutrients and heavy metals.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2248-2264
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00870G
Isothermal amplification as a water safety tool: rapid detection of viruses in surface water and wastewater
This study introduces a simple and rapid multi-wavelength, semi-quantitative detection strategy for monitoring SARS-CoV-2 and MS2 bacteriophage in water and wastewater using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP).

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2141-2151
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00092K
Well exposed: exploring the chemical and microbial composition in well and municipal drinking waters in Iowa
This study reveals twice the microbial diversity in well vs. municipal waters, highlighting the need for improved private well monitoring.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 2017-2034
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00216H
Oxygen vacancy-engineered Bi2O2CO3 nanosheets for enhanced photodegradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in water
Defect engineering has emerged as a versatile approach for tailoring the properties of materials to meet specific functional applications and improve their properties.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1951-1965
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00367A
Novel coal fly ash–chitosan composite for highly efficient, cost-effective and stable removal of lead and chromium from industrial wastewater
In the present study, a novel and economical adsorbent was synthesized from a coal fly ash–chitosan composite to remove Pb2+ and Cr6+ from aqueous solutions.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1977-2001
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00257E
Elimination of miconazole nitrate from water by electro-Fenton: effect of operating parameters and degradation pathway
This study investigates the removal of miconazole, a widely used pharmaceutical, from water using the electro-Fenton process.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1898-1908
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00508B
Removal of psychopharmaceuticals from WWTP effluent by an algae–mussel trophic cascade: a potential nature-based solution?
Psychopharmaceuticals are an emerging group of hazardous contaminants that pose a risk to the aquatic environment.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1643-1656
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00011D
Insights into the degradation of carbamazepine using a continuous-flow non-thermal plasma: kinetics and comparison with UV-based systems
A continuous-flow DBD plasma reactor was used for carbamazepine degradation in an aqueous solution, with >90% degradation achieved under optimal conditions, surpassing UV-based AOPs in efficiency and energy cost.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1568-1581
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW01042F
Nitrate enhances TCE removal by enriching bifunctional denitrifying/aerobic co-metabolizing microbes in the joint H2/O2 system
TCE removal by adjusting bi-functional microbes in the joint H2/O2 system.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1505-1516
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00046G
Novel fluidized-bed bioreactors with density-graded carriers for the bioremediation of nitrate in uranium industry effluents
Bioremediation of wastewater from the nuclear industry in a 3-phase aerobic airlift system and fluidized-bed anaerobic reactor with floating microbiological carriers.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1339-1351
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00077G
Comparing contaminants of emerging concern and microbial signatures of wastewater treated by membrane bioreactor and oxidation ditch methods
Despite effluent microbiome differences, contaminant of emerging concern signatures were consistent and similar in wastewater effluent treated by membrane bioreactor and oxidation ditch, indicating high-quality effluent from both treatment types.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1296-1312
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00793J
Enhancing fault detection in wastewater treatment plants: a multi-scale principal component analysis approach with the Kantorovich distance
Wavelet-based filtering combined with PCA effectively denoises data. The KD-driven method offers a reliable metric for detecting deviations from normal conditions without needing labelled data, making it suitable for anomaly detection.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1215-1232
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00831F
Energy-saving scheduling for multiple water intake pumping stations in water treatment plants based on personalized federated deep reinforcement learning
This study employs a data-driven personalized federated learning-based multi-agent attention deep reinforcement learning algorithm to address the intake scheduling problem of three water intake pumping stations in urban water treatment plants.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1260-1270
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00685B
Usability of waste plastic pyrolysis liquid/oil as a flotation collector in wastewater treatment
Marble processing industry wastewater contains a high amount of particulate solids. These wastewaters can be treated with high solid removal efficiency in flotation systems where pyrolysis oil is used as a collector.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1233-1245
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EW00027K
Energy recovery from organic matter in municipal wastewater using a two-stage system with high-rate contact stabilization and activated sludge processes under seasonal water temperature variations
A new technology using a high-rate contact stabilization process for wastewater treatment demonstrated superior energy recovery compared to an existing process, even while taking seasonal variations into account.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1016-1025
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00820K
Integrated assessment of the elimination of particle-associated fecal indicators in algal–bacterial granule photobioreactors
Two photo-sequencing batch reactors (PSBR) fed with real wastewater were evaluated to understand the elimination and particle association of fecal indicator bacteria (FIB) and coliphages.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 994-1006
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00927D
Drying reduces the total PFAS concentration in biosolids and alters the PFAS profile
Drying biosolids in a full-scale dryer and lab-scale oven reduces measureable PFAS concentrations in biosolids.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 1007-1015
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00890A
Disparities in potential nitrate exposures within Iowa public water systems
Disparities exist for marginalized populations (i.e., low-income populations) when it comes to potential exposure to elevated nitrate in drinking water.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 959-971
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00907J
Effect of inoculum percentage and hydrogen supply on hydrogenotrophic denitrification driven by anaerobic granular sludge
Hydrogenotrophic denitrification driven by granular sludge is an eco-friendly alternative to conventional separation-based techniques, which ensure process stability, high NO3− removal efficiency and minimal greenhouse gas emissions.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 768-780
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00776J
Bioremediation of uranium contaminated sites through the formation of U(VI) phosphate (bio)minerals
Removal of U(VI) in oxic groundwaters through the formation of low solubility U(VI) phosphate (bio)minerals, expanding the treatment envelope for in situ biomineralisation technologies.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 725-736
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00846D
Behaviour of particle mobilization and reattachment under flushing conditions in PVC pipes using a full-scale laboratory system
Excessive accumulation of particulate material and biofilms on the inner walls of drinking water pipes increases the risk of water discoloration events, known to be the major cause of customer complaints worldwide.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2025,11, 714-724
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EW00764F
About this collection
Please see below for recent Open Access papers published in Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology.