Themed collection SDG13: Climate Action – Ozone Depletion

Environmental effects of stratospheric ozone depletion, UV radiation and interactions with climate change: UNEP Environmental Effects Assessment Panel, update 2019
This assessment provides an update of the interactive effects of solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation, stratospheric ozone, and climate change on human health, terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, biochemical cycles, air quality, and material damage.
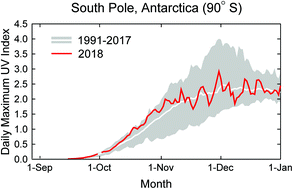
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2020,19, 542-584
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PP90011G
Climate change influence on the levels and trends of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and chemicals of emerging Arctic concern (CEACs) in the Arctic physical environment – a review
Direct and indirect effects of climate change influence contaminant sources, transport, re-distribution and circulation in the physical environment of the Arctic. Linkages of such observations to Arctic ecosystem exposure and effects are needed.
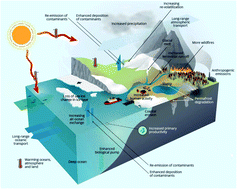
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1577-1615
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00485A
Atmospheric sea-salt and halogen cycles in the Antarctic
Atmospheric sea-salt and halogen cycles play important roles in atmospheric science and chemistry including cloud processes and oxidation capacity in the Antarctic troposphere.
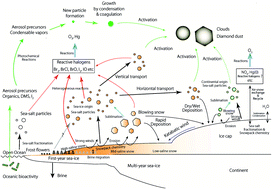
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 2003-2022
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00092B
UV-B radiation enhances the toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to the marine microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa by disrupting the protection function of extracellular polymeric substances
Weakened EPS protection of algal cells contributing to the increased internalization of TiO2 nanoparticles was identified as the key mechanism for the enhanced toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles under UV-B irradiation.
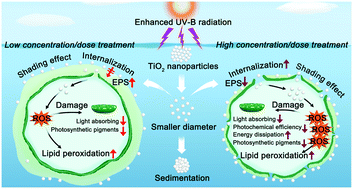
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 1591-1604
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01198G
Impacts of a near-future supersonic aircraft fleet on atmospheric composition and climate
Sulfur aerosols and soot from supersonic aircraft may cause greater climate impacts than the emitted CO2. Both fuel composition and cruise altitude must be considered when evaluating the effects of supersonic aircraft on climate and the ozone layer.
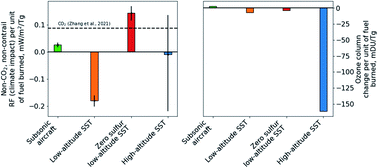
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2022,2, 388-403
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00081K
Causal discovery of drivers of surface ozone variability in Antarctica using a deep learning algorithm
We use a causal discovery algorithm based on a temporal convolution network (TCN) to discover the drivers of surface ozone variability over Antarctica.
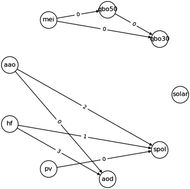
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 447-459
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00383F
The environmental performance of a fossil-free ship propulsion system with onboard carbon capture – a life cycle assessment of the HyMethShip concept
Pre-combustion onboard carbon capture could be part of lowering the environmental impact from the shipping sector.
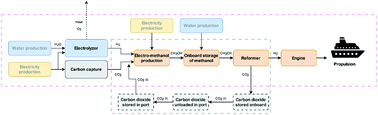
Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2021,5, 2753-2770
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SE00105A
Natural and anthropogenic sources of bromoform and dibromomethane in the oceanographic and biogeochemical regime of the subtropical North East Atlantic
Transport of air masses from the subtropics, enriched in trace gases from the oceans, coasts and islands, towards lower latitudes under the trade inversion and uplift to the stratosphere in tropical deep convection.
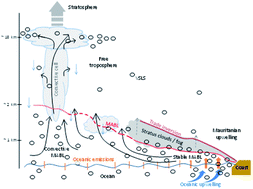
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 679-707
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00599D
Impact of bromide exposure on natural organochlorine loss from coastal wetland soils in the Winyah Bay, South Carolina
Naturally formed halogenated organic compounds are common in terrestrial and marine environments and play an important role in the halogen cycle.
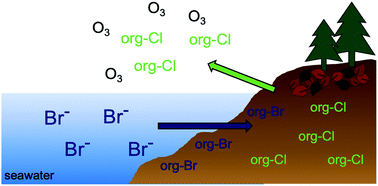
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 642-652
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00604D
Sources and sinks of chloromethane in a salt marsh ecosystem: constraints from concentration and stable isotope measurements of laboratory incubation experiments
Chloromethane (CH3Cl) is the most abundant long-lived chlorinated organic compound in the atmosphere and contributes significantly to natural stratospheric ozone depletion.
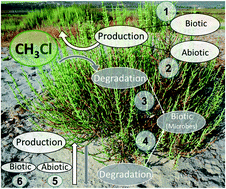
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 627-641
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00540D
Powering sustainable development within planetary boundaries
Designing energy systems within planetary boundaries is crucial to preserving the Earth's ecological capacity given the power sector's environmental footprint.
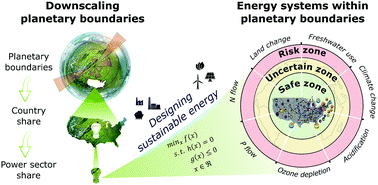
Energy Environ. Sci., 2019,12, 1890-1900
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EE03423K
About this collection
Human activities have caused a gradual thinning of the Earth’s ozone layer through releasing ozone-depleting substances. This collection showcases some of the latest research in Royal Society of Chemistry journals on ozone depletion, from fundamental understanding to observatory measurements. We hope you enjoy reading the papers in this collection and we welcome you to submit your next paper on this theme to our journals.