Themed collection Carbon dioxide conversion

Catalytic conversion and use of carbon dioxide
Welcome to this themed issue describing the latest advances made in the area of CO2 catalysis and conversion with a focus on its use in organic synthesis.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1481-1481
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CY90014F
Recent progress in catalytic conversions of carbon dioxide
The latest progress in chemical conversions of CO2 into useful compounds is overviewed.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1482-1497
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00993A
Synthesis of cyclic carbonates from CO2 and epoxides using ionic liquids and related catalysts including choline chloride–metal halide mixtures
In this mini-review, progress made in the use of ionic liquid catalysts and related systems for cycloaddition reactions of carbon dioxide with epoxides is described with the primary focus on results from the past eight years.
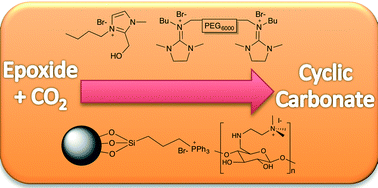
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1513-1528
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00998J
Homogeneous hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to methanol
Homogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 into fuel-related products, e.g. methanol, is highlighted in combination with mechanistic understanding on a molecular level.
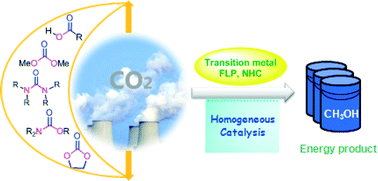
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1498-1512
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00564J
Nucleophile-directed selectivity towards linear carbonates in the niobium pentaethoxide-catalysed cycloaddition of CO2 and propylene oxide
The reaction between CO2 and propylene oxide in the presence of Nb(EtO)5 and 4-dimethylaminopyridine leads to the formation of an acyclic carbonate through an unprecedented pathway.
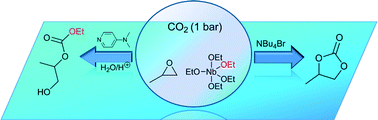
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1534-1538
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CY00003J
Iron-catalyzed hydrosilylation of CO2: CO2 conversion to formamides and methylamines
Catalytic hydrosilylation of CO2 is an efficient and selective approach to form chemicals. Herein, we describe the first iron catalysts able to promote the reductive functionalization of CO2 using hydrosilanes as reductants. Iron(II) salts supported by phosphine donors enable the conversion of CO2 to formamide and methylamine derivatives under mild reaction conditions.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1529-1533
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CY00130C
New air-stable zinc complexes formed from cyanoacrylate- and methylenemalonate-based [N2O2]-ligands and their role as catalysts in epoxide–CO2 coupling
The synthesis of a range of zinc complexes based on ligands displaying an N2O2-framework with cyanoacrylate and/or malonate functionality is presented.
![Graphical abstract: New air-stable zinc complexes formed from cyanoacrylate- and methylenemalonate-based [N2O2]-ligands and their role as catalysts in epoxide–CO2 coupling](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C4CY00125G&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2014)
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1658-1673
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CY00125G
Copper based TiO2 honeycomb monoliths for CO2 photoreduction
Copper based TiO2 monolithic structures threaded with optical fibers exhibit better activity than pure TiO2 for CO2 reduction under visible or UV light irradiation.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1631-1637
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00991B
Highly active Cr(III) catalysts for the reaction of CO2 with epoxides
This paper describes the synthesis and characterization of [Cr(babhq)OAcF(EtOH)] (OAcF− = CF3CO2−) as well as the application of the complex as the catalyst in the reaction of CO2 with epoxides.
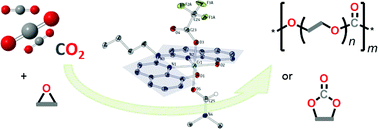
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1652-1657
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY01087B
Niobium(V) chloride and imidazolium bromides as efficient dual catalyst systems for the cycloaddition of carbon dioxide and propylene oxide
Imidazolium bromides combined with niobium(V) choride were used as catalyst system for the reaction of CO2 with epoxides to cyclic carbonates. The variation of the cation structure strongly affects the properties of the imidazolium salt and therefore the catalytic activity.
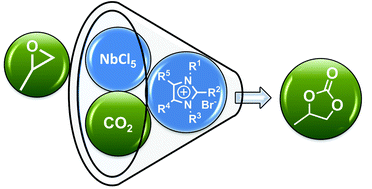
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1638-1643
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY01057K
Photocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide into methanol in reverse fuel cells with tungsten oxide and layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for solar fuel generation
Photofuel cells comprising WO3 and layered double hydroxide converted gaseous CO2 into methanol whereas hydrogen was formed in the aqueous phase.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1644-1651
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00959A
Reduction of bicarbonate and carbonate to formate in molecular zinc complexes
The zinc bicarbonate complex, [κ4-Tptm]ZnOCO2H, is reduced by PhSiH3 to give the formate derivative, [κ4-Tptm]ZnO2CH, via a sequence that involves release of CO2 followed by insertion into a zinc–hydride bond.
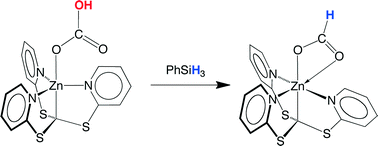
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1578-1584
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY01065A
A single centre aluminium(III) catalyst and TBAB as an ionic organo-catalyst for the homogeneous catalytic synthesis of styrene carbonate
Cyclic carbonate synthesis from an epoxide is achieved by sparging CO2 at 1 bar into the solution using an aluminium/TBAB catalyst.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1622-1630
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY01015E
Easily accessible bifunctional Zn(salpyr) catalysts for the formation of organic carbonates
Alkylated Zn(salpyr) complexes (salpyr = N,N′-bis[salicylidene]-3,4-pyridinediamine) were prepared and used as catalyst precursors for the formation of cyclic carbonates from a range of (functional) epoxides and CO2.
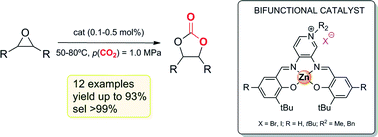
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1615-1621
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY01043K
Synthesis and high-throughput testing of multilayered supported ionic liquid catalysts for the conversion of CO2 and epoxides into cyclic carbonates
Multilayered covalently supported ionic liquid catalysts achieve excellent TON and productivity in the reaction of CO2 with various epoxides to produce cyclic carbonates.
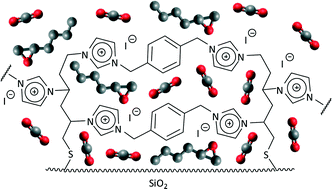
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1598-1607
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY01000G
Theoretical study on the chemical fixation of carbon dioxide with propylene oxide catalyzed by ammonium and guanidinium salts
A catalytic mechanism involved in the cycloaddition of propylene oxide onto CO2 catalyzed by ammonium and guanidinium salts is proposed.
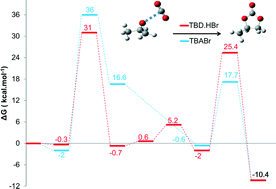
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1585-1597
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00955F
Synthesis of quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione from carbon dioxide and 2-aminobenzonitrile using mesoporous smectites incorporating alkali hydroxide
Incorporation of alkali hydroxide into smectite significantly enhances the catalytic activity for the synthesis of quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione from carbon dioxide and 2-aminobenzonitrile, which has been ascribed to the formation of NaOH particles on the surface of the smectite layer.
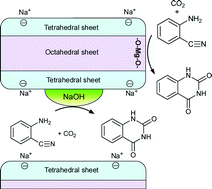
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1563-1569
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00977G
Chromium(III) amine-bis(phenolate) complexes as catalysts for copolymerization of cyclohexene oxide and CO2
Chromium complexes of tri- and tetradentate amine-bis(phenolate) ligands in combination with chloride, azide or DMAP nucleophiles are effective catalysts for the copolymerization of CO2 with cyclohexene oxide to give polycarbonates.
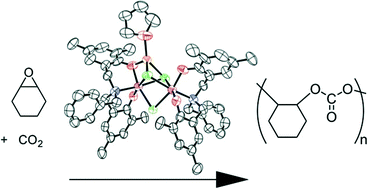
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1547-1555
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY01002C
Amine functionalized MCM-41: an efficient heterogeneous recyclable catalyst for the synthesis of quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones from carbon dioxide and 2-aminobenzonitriles in water
Covalently linked amine functionalized MCM-41 was investigated as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of various quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione derivatives from 2-aminobenzonitriles and carbon dioxide in water.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1608-1614
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00992K
Cu(I)-catalyzed chemical fixation of CO2 with 2-alkynylaniline into 4-hydroxyquinolin-2(1H)-one
A copper(I)-catalyzed reaction of 2-alkynylaniline with CO2 using DBU as base to produce 4-hydroxyquinolin-2(1H)-one derivatives in moderate to good yield is presented.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1570-1577
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00858D
CO2 photoreduction with H2O vapor by porous MgO–TiO2 microspheres: effects of surface MgO dispersion and CO2 adsorption–desorption dynamics
Porous MgO–TiO2 microspheres prepared by a one-pot spray pyrolysis method significantly enhance the activity and stability in CO2 photoreduction with water vapor.
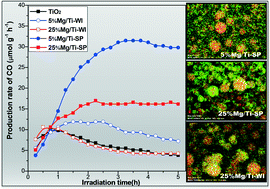
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1539-1546
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00807J
Synthesis of cyclic carbonates catalysed by aluminium heteroscorpionate complexes
A trimetallic aluminium complex catalyses the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from epoxides and CO2 at room temperature and pressure.
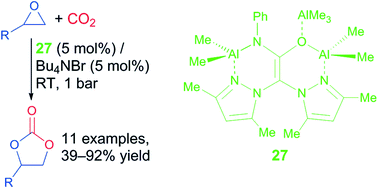
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1674-1684
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00810J
Urea-derived graphitic carbon nitride as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for CO2 conversion into cyclic carbonates
Urea-derived graphitic carbon nitrides (u-g-C3N4) were prepared under different temperatures as catalysts for CO2 conversion into cyclic carbonates.
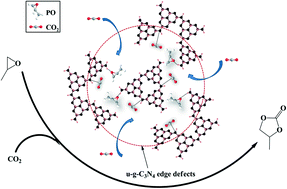
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014,4, 1556-1562
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00921A
About this collection
This themed issue on the use of carbon dioxide with the aim to convert it into more useful organic matter intends to present leading groups in the area of CO 2 research to showcase the most recent developments and advances made.