Themed collection High performance computing in the chemistry of materials

High performance computing in the chemistry of materials
Computational modelling is now an integral component of almost all areas of chemistry, physics and materials sciences.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21001-21001
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP90126F
How does an amorphous surface influence molecular binding? – ovocleidin-17 and amorphous calcium carbonate
Molecular dynamics simulations of the protein ovocleidin-17 binding to the surface of amorphous calcium carbonate highlighting the residues contacting the surface.
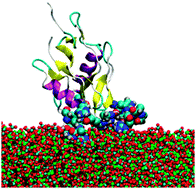
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 17494-17500
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00434A
Are Re(I) phenanthroline complexes suitable candidates for OLEDs? Answers from DFT and TD-DFT investigations
The electronic structure and spectroscopic properties of seven recently reported rhenium(I) phenanthroline complexes were investigated theoretically by density functional theory (DFT) and time dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) methods.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21157-21171
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01135J
Acoustic phonons and negative thermal expansion in MOF-5
An acoustic phonon with a mechanism not previously documented (motion of rigid benzene dicarboxylate ligands and ZnO4 tetrahedra) makes a sizeable contribution to the overall NTE in MOF-5.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21144-21152
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01701C
The reactivity of CO2 and H2 at trapped electron sites at an oxide surface
A series of model catalytic cycles for CO2 conversion at metal oxide surface vacancy sites is presented.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21153-21156
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP02610A
On the structure of biomedical silver-doped phosphate-based glasses from molecular dynamics simulations
First-principles and classical molecular dynamics simulations have been carried out on undoped and silver-doped phosphate-based glasses with 50 mol% P2O5, 0–20 mol% Ag2O, and varying amounts of Na2O and CaO.
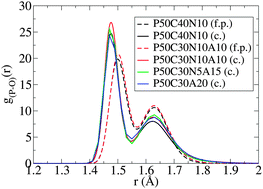
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21135-21143
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP00574K
Lithium-ion diffusion mechanisms in the battery anode material Li1+xV1−xO2
Layered Li1+xV1−xO2 has attracted recent interest as a potential low voltage and high energy density anode material for lithium-ion batteries.
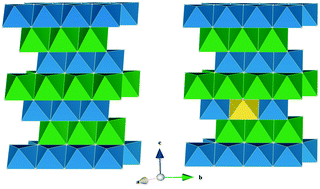
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21114-21118
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01640H
Structure prediction of nanoclusters; a direct or a pre-screened search on the DFT energy landscape?
Atomic structure prediction, using KLMC (Lamarckian evolutionary algorithm search), and properties comparison of (KF)n, (MgO)n, (ZnO)n and (CdSe)n nanoclusters.
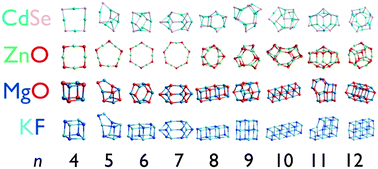
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21119-21134
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01825G
Diffraction of helium on MgO(100) surface calculated from first-principles
In this work we simulate the diffraction peak intensities of He beams scattered on the MgO(100) surface using hierarchical protocol, based on periodic and finite-cluster quantum-chemical calculations.
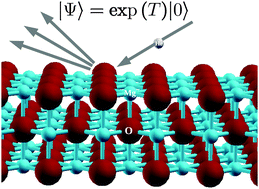
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21106-21113
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01145G
A quantum mechanical study of water adsorption on the (110) surfaces of rutile SnO2 and TiO2: investigating the effects of intermolecular interactions using hybrid-exchange density functional theory
Periodic hybrid-exchange DFT is used to explore the structure and properties of SnO2(110) and TiO2(110) surfaces in contact with water.
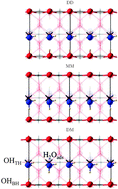
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21002-21015
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01824A
Double bubbles: a new structural motif for enhanced electron–hole separation in solids
Edge-sharing (GaN)12@(ZnO)48 framework, with the hole (excited electron) localised on nitrogen (zinc) within the inner (outer) bubbles.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21098-21105
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01900H
Reported and predicted structures of Ba(Co,Nb)1−δO3 hexagonal perovskite phases
The Extended Module Materials Assembly method was implemented for close-packed hexagonal structures and applied to doped barium niobate perovskites.
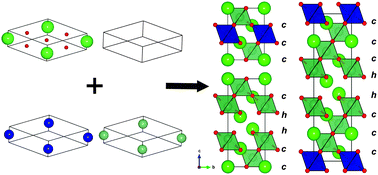
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21073-21081
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01542H
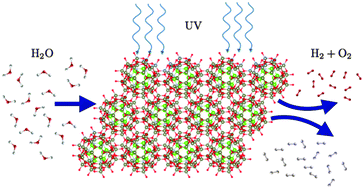
A DFT study of the structures, stabilities and redox behaviour of the major surfaces of magnetite Fe3O4
Redox behaviour of magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles in thermodynamic equilibrium conditions enclosed by non-dipolar reconstructed surfaces.
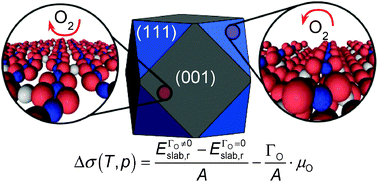
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21082-21097
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP00529E
Occupation matrix control of d- and f-electron localisations using DFT + U
A methodology for controlling the site and orbital localisation of d- and f-states applied to TiO2 and CeO2 using DFT + U.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21016-21031
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01083C
Cation-exchanged SAPO-34 for adsorption-based hydrocarbon separations: predictions from dispersion-corrected DFT calculations
The interaction of C2 and C3 hydrocarbons with cation-exchanged SAPO-34 materials is studied using DFT-D calculations, permitting predictions regarding their suitability for alkene–alkane separations.
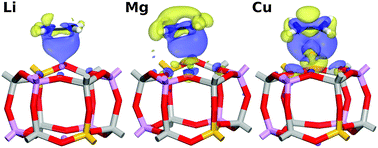
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21062-21072
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP01049C
The influence of the Hubbard U parameter in simulating the catalytic behaviour of cerium oxide
The redox properties of cerium dioxide lead to broad application in catalysis, however obtaining a consistent description from DFT is troublesome. Herein we present an approach to choose the U parameter based on adsorption energetics and apply it to construct metal-oxide parings for model catalysts.
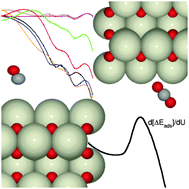
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21032-21038
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP00928B
Segregation effects on the properties of (AuAg)147
AuAg nanoclusters are promising supported co-catalysts for photocatalytic hydrogen reduction.
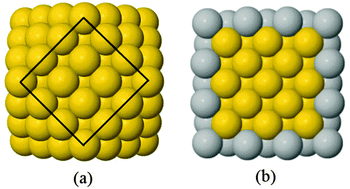
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21049-21061
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP00753K
A theoretical study of the structures and optical spectra of helical copper–silver clusters
Optical response spectra of AgnCu13−n+ Bernal spiral clusters show subtle variations by dopant site and loading. Comparison to nanorod-like and icosahedral clusters shows local geometry plays a significant role in electronic transitions at the sub-nanoscale.
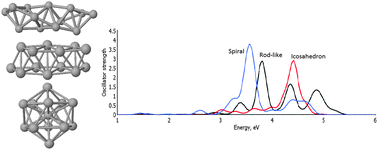
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 21039-21048
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP55507K
About this collection
High performance computing (HPC) now plays a major role in almost all areas of chemistry and this exciting and timely themed issue demonstrates how HPC is being used in both increasingly predictive methods and in a complementary manner with experiments.
The themed issue is guest edited by Richard Catlow and Scott Woodley (University College London) and aims to highlight the state-of-the-art in the field of HPC and to cover a wide variety of application areas.