Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSeparation of samarium and europium by solvent extraction with an undiluted quaternary ammonium ionic liquid: towards high-purity medical samarium-153†
Michiel Van de Voorde ab,
Karen Van Hecke
ab,
Karen Van Hecke a,
Koen Binnemans
a,
Koen Binnemans b and
Thomas Cardinaels
b and
Thomas Cardinaels *ab
*ab
aSCK•CEN, Belgian Nuclear Research Centre, Institute for Nuclear Materials Science, Boeretang 200, B-2400 Mol, Belgium. E-mail: thomas.cardinaels@sckcen.be
bKU Leuven, Department of Chemistry, Celestijnenlaan 200F, P. O. 2404, B-3001 Heverlee, Belgium
First published on 4th June 2018
Abstract
Long-lived europium-154 impurities are formed during the production of medical samarium-153 in a high-flux nuclear reactor. A method to separate these europium impurities from samarium was investigated using the hydrophobic quaternary ammonium ionic liquid Aliquat 336 nitrate. The separation method consists of the selective reduction of Eu3+ by zinc metal in an aqueous feed solution containing a high nitrate salt concentration. Subsequent extraction using undiluted Aliquat 336 nitrate leads to an efficient separation of both lanthanides in a relatively short time frame. Sm3+ was extracted to the neat ionic liquid phase much more efficiently than Eu2+. An initial approach using the addition of dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 to capture Eu2+ in the ionic liquid phase was less efficient.
Introduction
The radiolanthanide samarium-153 (153Sm) is applied in nuclear medicine, where it is known under its commercial names Quadramet and Lexidronam.1,2 In these radiopharmaceuticals, the 153Sm radioisotope is coordinated to an ethylenediamine tetra(methylene phosphonate) chelating ligand (153Sm EDTMP, Fig. 1).3 153Sm serves well in nuclear medicine because of its favorable half-life of 46.284 h and because it decays to the stable 153Eu nuclide. This causes no severe additional side effects in the human body after treatment. 153Sm EDTMP is very selective towards the skeleton.4–7 The 153Sm radionuclide is commonly produced via neutron-irradiation of an enriched 152Sm2O3 target, in a nuclear reactor with a high thermal neutron flux.8 A product with high yield, high purity and high specific activity is formed. However, since the target is usually irradiated for several days, part of the 153Sm is already decaying during irradiation and the daughter isotope 153Eu will be neutron-irradiated as well, leading to the simultaneous production of trace amounts of 154Eu.9,10 This radiochemical impurity has a much longer half-life (8.593 year) compared to that of 153Sm. Relatively large quantities of 154Eu lead to an unacceptable radiation dose delivered to the patient. The maximum level of impurities is strictly regulated by international and national organizations (e.g. WHO, IAEA, FDA). Consequently, Quadramet has a limited shelf life of only a few days after being produced, since expiration is reached at the threshold ratio of 0.093 μCi (=3400 Bq) of 154Eu per mCi (37 MBq) of 153Sm.9–11 Additionally, long-lived 154Eu impurities end up in the waste generated in the hospitals. Removal of these 154Eu impurities would imply a longer product shelf-life for medical use, leading to an increased availability of 153Sm and a lower background radioactivity of the treated patient. Waste treatment procedures in hospitals can become easier because waste containing short-lived isotopes only can be treated via decay storage. Moreover, distribution and transportation deadlines can become more flexible, opening perspectives of feeding a world-wide market. This way, an unexpected outage of a research reactor can be backed-up more easily by another research reactor, ensuring the supply of 153Sm. Valuable and expensive enriched target material can also be used more efficiently by increasing the irradiation time because the long-lived side-products are removed afterwards. Undeniably, purification of the irradiated target material by separation of 154Eu from 153Sm would be beneficial in medical and economical perspective.Separation of two neighboring lanthanides is very challenging because of their very similar chemical properties. A separation method based on a very small difference in complexation behavior would be too time-consuming to be feasible for the separation of these relatively short-lived radionuclides. Approaches based on the selective reduction of europium from the trivalent to the divalent state, either chemically or electrochemically, changing the chemical properties of europium significantly, have proven to be efficient for the recovery of highly valuable europium from rare-earth ores on an industrial scale.12–17 In these processes, a phosphorus-containing acidic extractant with high affinity for lanthanides (Ln3+) is used most frequently, leaving the Eu2+ unaffected in the aqueous phase. The use of ion exchange resins is another popular purification method. Taking into account the relatively short half-lives of the medical radionuclides, gravimetrical separation methods are too time-consuming to be used. High performance ion chromatography (HPIC) methods to separate radiolanthanides are more suitable, but require more advanced equipment.18
In this paper, we conducted a feasibility study to separate samarium and europium via two different solvent extraction processes. Prior to the separation process, Eu3+ was selectively reduced to Eu2+ by Zn0. The water-immiscible phase of the extraction system consisted of the highly hydrophobic ionic liquid (IL) Aliquat 336 nitrate ([A336][NO3], Fig. 2a). Ionic liquids are solvents that consist entirely of ions. Moreover, previous studies have shown that the use of undiluted ionic liquids in solvent extraction is a very promising approach for separation of rare-earth elements (REEs).19–23
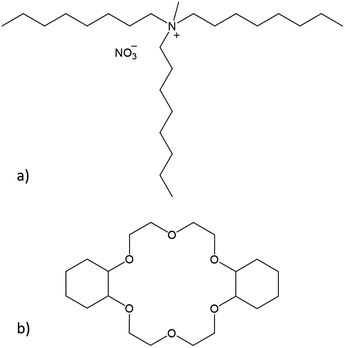 | ||
| Fig. 2 Chemical structures of (a) the main component of Aliquat 336 nitrate ([A336][NO3]) and (b) dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6). | ||
The separation process was performed with and without the addition of a size-selective extractant. The size-selective extractant dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6, Fig. 2b) was selected because of its capability to efficiently extract Sr2+, which has a comparable ionic radius and charge density as Eu2+.24–27 The process including DCH18C6 was aimed at the size-selective extraction of Eu2+ to the water-immiscible phase, while leaving Sm3+ in the aqueous phase. The process without addition of DCH18C6 uses the alkaline extraction capacities of the ionic liquid itself to separate samarium and europium.
Experimental
Materials
Tricaprylammonium chloride (Aliquat® 336, [A336][Cl], 88.2–90.6%), dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6, ≥98%), LiCl (99%) and HNO3 (≥65%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Diegem, Belgium). SmCl3·6H2O (99.9%) and Eu(NO3)3·6H2O (99.9%) were purchased from Strem Chemicals, Inc. (Newburyport, USA). Sm(NO3)3·6H2O (99.9%) and LiNO3 (anhydrous, 99%) were purchased from Alfa Aesar (Karlsruhe, Germany). EuCl3·6H2O (99.9%), Sr(NO3)2 (99.9%) and granular zinc (30 mesh, ≥99.7%) were purchased from Acros Organics (Geel, Belgium). SrCl2·6H2O (≥99%), NH4Cl (≥99.8%), Na2SO4 (≥99%) and acetonitrile (≥99.5%) were purchased from Chem-Lab (Zedelgem, Belgium), as well as the Sm, Eu, Zn and Cu standard solutions (≥99.99%, 1000 μg mL−1, 2–5% HNO3, Plasma HIQU). NH4NO3 (≥99%) was purchased from Merck Millipore (Darmstadt, Germany). All products were used as received, without any further purification steps. Aqueous samples were prepared with Milli-Q water (18.2 MΩ cm at 25 °C).Reduction of Eu3+
In all experiments, Eu3+ (E0 = −0.43 V) was reduced chemically using zinc granules (E0 = −0.76 V) taking into account the minimal requirements to obtain maximal reduction established by Sayed et al.28 This study proved that a minimal contact time of 1 h and a minimal zinc-to-europium molar ratio of 2.5 are needed to reach maximum reduction of Eu3+. Therefore, the aqueous feed solutions, both chloride and nitrate ones, were mixed with a large excess of granular zinc (30 mesh) for 2 h at room temperature. The remarkably high stability of Eu2+ in aqueous solutions containing high nitrate salt concentrations will be discussed in a dedicated separate publication. The aqueous solutions were purged with nitrogen gas during reduction of Eu3+ to remove atmospheric and dissolved oxygen. This is necessary to prevent re-oxidation of Eu2+ by O2 (E0 = +1.23 V). The pH of the aqueous feed solution was kept between 4 and 6.5. This way, the pH of the final feed solution remained sufficiently high to avoid re-oxidation of Eu2+ by H+ (E0 = 0.00 V) and sufficiently low to prevent hydrolysis of Sm3+ or Eu3+. Too low pH levels lead to preferential H2 generation in contact with Zn0, i.e. Eu3+ will only be reduced as soon as the H+ concentration is sufficiently low. Therefore, pH of the aqueous feed solution after reduction will only be slightly acidic. The pH was measured after Eu3+ reduction and after extraction by means of a Hamilton Slimtrode pH electrode coupled to a Mettler-Toledo SevenCompact pH meter.Preparation of the water-immiscible phase
The water-immiscible phase consisted of neat [A336][NO3] or [A336][NO3] containing 0.05 M DCH18C6. Neat [A336][NO3] was prepared from commercially available [A336][Cl] by a metathesis reaction. [A336][Cl] was dissolved in acetonitrile to decrease the viscosity of the IL and to enhance phase separation. An aqueous solution containing 8 M NH4NO3 was mixed intensively with the [A336][Cl]–acetonitrile solution. This way, chloride anions were replaced by nitrate anions, a process that is favorable according to the Hofmeister series since nitrate ions are less strongly solvated than chloride ions.29 After mixing and phase separation, the aqueous phase was removed and tested for remaining chloride by addition of a AgNO3 solution. This process was repeated until no chloride traces could be found in the aqueous phase. After achieving full conversion of [A336][Cl] to [A336][NO3], acetonitrile was removed by means of a rotary evaporator, followed by treatment at high vacuum using a Schlenk line. Analysis of the final, dry [A336][NO3] by total reflection X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) showed a remaining chloride concentration of ca. 4 ppm (analysis procedure in ESI†).30 The ionic liquid was equilibrated with water (Milli-Q) prior to its use in solvent extraction experiments to avoid any significant volume changes during the extraction experiment.Extraction experiments
The aqueous feed solutions contained both Sm and Eu. The concentration of each lanthanide was 1 g L−1 (6.6 × 10−3 M). Only stable isotopes of samarium and europium were used. The chloride or nitrate concentrations in the aqueous feed solutions were adjusted by the addition of the respective ammonium or lithium salts. Exact concentrations of samarium and europium in the solution after reduction by zinc were determined by ICP-OES. A 1 mL aliquot of the aqueous feed solution was mixed with 1 mL of organic phase, after the reduction of Eu3+ to Eu2+. This organic phase consisted of neat [A336][NO3] or [A336][NO3] containing 0.05 M DCH18C6. Both phases were purged intensively with nitrogen gas before extraction to prevent oxidation of Eu2+ by dissolved oxygen. Both phases were mixed in a 4 mL glass reaction vial at 1700 rpm making use of an Allsheng TMS-200 thermoshaker. Various mixing times (5, 15, 30 and 60 min) and temperatures (25, 40 and 60 °C) were tested in triplicate to find the most suitable separation conditions. After mixing, the reaction vials were centrifuged for 1 min at 5300 rpm using a Thermo Scientific Heraeus 200 Centrifuge to accelerate phase disengagement. Next, the aqueous phase was separated from the ionic liquid phase prior to analysis by ICP-OES. The efficiency of the separation method was evaluated by means of the distribution ratio, the fraction extracted and the separation factor. The distribution ratio (D) of a compound is defined as the ratio of the total concentration of this compound in the extract phase to its total concentration in the initial phase:
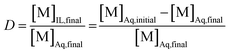 | (1) |
In this equation, the volumes of both phases are equal. [M]Aq,initial represents the initial concentration of the compound in the aqueous feed solution, [M]Aq,final and [M]IL,final represent the concentration of the compound in the aqueous and ionic liquid phase, respectively, after extraction. The fraction extracted (% E, also percentage extraction) is defined as the ratio of the amount of compound extracted to its total amount in the system. In case both phases are present in equal volume, the fraction extracted can be expressed as:
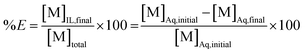 | (2) |
In case more elements are present, one can describe the separation factor (α), which is the ratio of the distribution ratios of two compounds A and B:
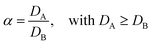 | (3) |
Aqueous solutions, i.e. the feed solution after reduction by Zn0 and the aqueous phase after extraction, were analyzed by using a Perkin Elmer Optima 8300 inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) in axial view, with a GemTip CrossFlow II nebulizer, a Scott spray chamber assembly, a sapphire injector and a Hybrid XLT quartz-ceramic torch. Calibration curves were constructed by fitting the results of standard solutions containing 0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10 mg L−1 Sm, Eu, Sr and/or Zn through the origin. Samples of the aqueous solutions to be measured by ICP-OES were diluted 100 times by a 2 wt% HNO3 solution.
Results
Selection of anion source and concentration
In a first series of screening experiments, the extraction behavior of Sr2+ by the crown-ether-containing ionic liquid solution was studied as a simulant for Eu2+. Different anion concentrations were used in the aqueous feed solution, i.e. 0, 1, 3, 6 and 8 M. Three different sources were used to vary the anion concentration, i.e. HX, NH4X and LiX (with X = Cl− or NO3−). Extractions were performed using both [A336][NO3] (IL) and [A336][NO3] + 0.05 M DCH18C6 (IL + CE). Results of these screening experiments are reported in the ESI.† Based on these results, following experiments were conducted with a 6 M lithium salt aqueous feed solution.Time dependence of Sm3+/Eu2+ separation
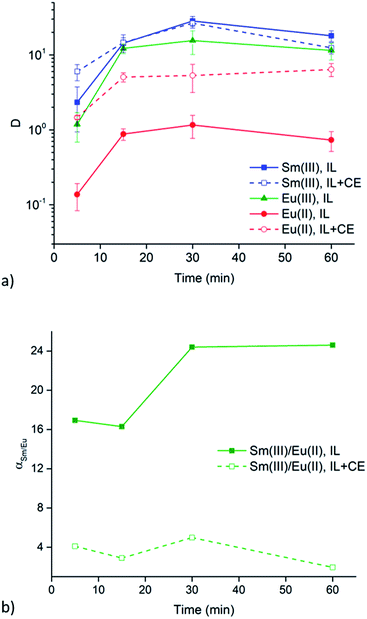
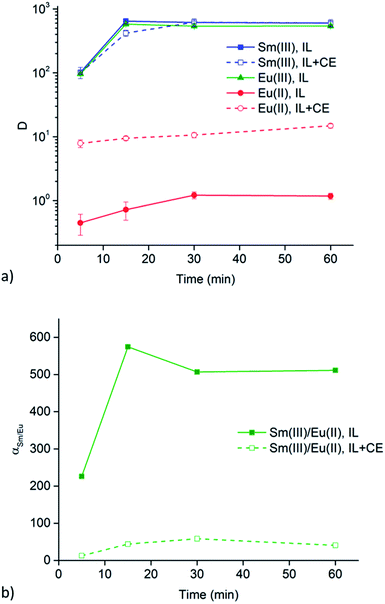
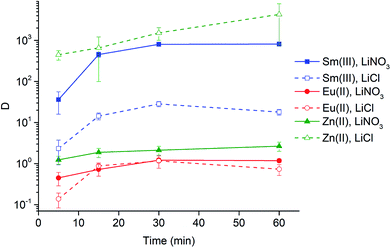
Extraction experiments with 6 M LiX (with X = Cl− or NO3−) aqueous feed solutions were performed to study the extraction rates of Sm3+ and Eu2+. For comparison and completeness, the extraction of Eu3+ in the same conditions was studied as well. The feed solutions were mixed with both [A336][NO3] (IL) and [A336][NO3] + 0.05 M DCH18C6 (IL + CE). The distribution ratios of both lanthanides after extraction from a 6 M LiCl and a 6 M LiNO3 aqueous feed solution are plotted as a function of time in Fig. 3a and 4a. It is immediately clear that high distribution ratios were obtained for the trivalent lanthanides in both systems, especially when using a nitrate aqueous feed solution. As expected, the presence of the crown ether did not influence the extraction behavior of Sm3+. Eu2+ was only reasonably well extracted in presence of the crown ether. Therefore, highest separation factors were reached without the use of a crown ether (Fig. 3b and 4b). It is also clear that separation of the Sm3+–Eu2+ couple from a nitrate aqueous feed solution is much more efficient compared to a chloride aqueous feed solution.Temperature dependence of Sm3+/Eu2+ separation
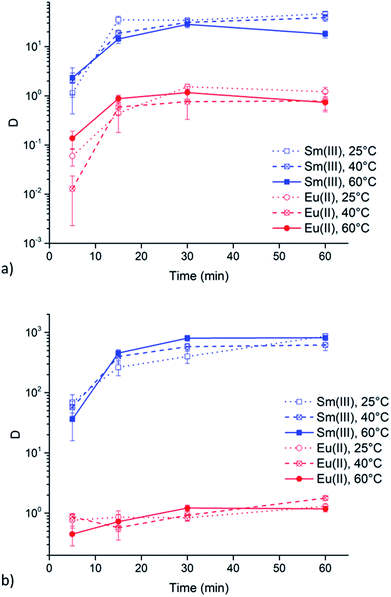
Extractions of Sm3+ and Eu2+ were executed at 25, 40 and 60 °C to evaluate the influence of the viscosity of the ionic liquid phase. Results of these extractions from chloride and nitrate aqueous feed solution (6 M of the respective lithium salt) are presented in Fig. 5a and b, respectively. Both graphs show that a change in temperature, and thus a change in viscosity, does not lead to any significant changes in extraction behavior of both Sm3+ and Eu2+.Extraction behavior of Zn2+ impurities
Eu3+ can be efficiently and selectively reduced by Zn0, generating Zn2+ in the feed solution. Therefore, the extraction behavior of Zn2+ from both chloride and nitrate aqueous feed solutions was studied and compared to the extraction behavior of Sm3+ and Eu2+. From Fig. 6, it is clear that the extraction of Zn2+ strongly depends on the anions present in the extraction system. The extraction of Zn2+ proceeded very efficient in case of a high chloride concentration. Therefore, the extraction of Zn2+ from chloride media led to very high distribution ratios. On the contrary, Zn2+ was hardly extracted in case only nitrate anions were present in the extraction system. The extraction behavior of Zn2+ in nitrate media proved to be comparable to the one of Eu2+.Discussion
Defining two separation approaches
In this study, the separation of samarium and europium was investigated with and without the use of a size selective extractant. Many studies report on the efficient extraction of Sr2+ by a 18-crown-6 (18C6) derivative as extractant.31–34 These 18C6-based crown ethers are able to capture a metal ion with a specific ion size in their cavity (2.6–3.2 Å). The six oxygen atoms of the crown ether serve as donor atoms to coordinate the metal ion.35 Therefore, they are considered to be highly size-selective.36 Ions that are either too large or too small do not interact properly with the crown ether. This also accounts for the trivalent lanthanides (Ln3+), which have an ionic radius varying from 0.977 Å for Lu3+ to 1.16 Å for La3+ (values given for coordination number 8). Moreover, the considerable hydration energy of trivalent lanthanide ions prevents efficient coordination by the crown ether. Lowering of the oxidation state, i.e. the addition of an electron, leads to an increased ionic radius, a decreased charge density and a decreased hydration enthalpy. Thus, Ln2+ ions are more favorable to properly interact with 18C6-based extractants.37 In the lanthanide series, only europium has a relatively stable divalent state in aqueous solutions because of its half-filled 4f subshell. Therefore, the use of a size-selective extractant to selectively trap the Eu2+ impurities in the 18C6-cavity in the organic phase was studied as a first approach to separate the Sm/Eu couple, leaving Sm3+ behind in the aqueous phase. In this study, dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6) was used because of its high hydrophobicity and because DCH18C6 already served well in extracting Sr2+ in numerous studies. The ionic radius of Eu2+ (1.25 Å) is similar to the one of Sr2+ (1.26 Å). Moreover, DCH18C6 already proved to be significantly radiation-resistant.38–42The alkaline extraction capacities of the ionic liquid itself were used in a second approach, without the addition of any extractants. Trivalent lanthanide ions have the advantage of being able to form anionic complexes with bidentate nitrate ligands, whereas divalent metal ions are unable to form these species.23,43 Sm3+ will thus be extracted to the water-immiscible ionic liquid phase, while Eu2+ remains in the aqueous phase. Vander Hoogerstraete et al. showed the efficiency of this strategy to recycle rare-earth elements from permanent magnets and nickel metal hydride batteries.23 Both approaches were studied in parallel throughout the experiments.
In both approaches, the water-immiscible phase consisted of the highly hydrophobic ionic liquid Aliquat 336 nitrate ([A336][NO3]). Indeed, the use of this type undiluted ionic liquids proved to be selective for separation of rare earth elements (REEs) in previous solvent extraction studies.19–23,43 The rationale behind the use of [A336][NO3] is fourfold. (1) The use of [A336][NO3] ensures a system complying completely with the CHON principle, making use of compounds containing only carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and nitrogen (N).44,45 This is highly important for the final disposal and waste treatment of the ionic liquid, which becomes radioactively contaminated when applied for separation of radiolanthanides, an aspect that is frequently overlooked in nuclear applications on ionic liquids. (2) Ionic liquids have promising properties compared to conventional molecular solvents, leading to processes with increased safety, chemical stability and radiation-resistivity.46–48 (3) [A336][NO3] possesses a highly hydrophobic cation whereas the inorganic anion is well soluble in both the aqueous and ionic liquid phase. This ensures a minimal amount of organic compounds ending up in the aqueous phase after extraction. This is opposite to the [Cnmim][Tf2N] ionic liquids that are frequently used in combination with 18C6-based crown ethers.31,34,49 These ionic liquids operate via a cation extraction mechanism in case a short alkyl chain (Cn) is used, losing ionic liquid cations to the aqueous phase. This, however, is unfavorable because these contaminations are not compatible with any pharmaceutical application. Additionally, radiolysis of the fluorinated anion can generate harmful and hazardous compounds. (4) [A336][NO3] is a source of nitrate ions for improved extraction efficiency in a split-anion extraction mechanism in case the feed solution contains chloride ions.50 Nitrate ions are more efficient in coordinating the metal ions in crown ether complexes compared to chloride ions. The small bite angle of nitrate ions allows them to coordinate the metal ions bidentately, i.e. taking up little space in the coordination sphere, whereas chloride can only coordinate monodentately. The formation of two M–O bonds is energetically more favorable than the formation of one M–Cl bond, outweighing the considerable M–OH2 bond energy. This way, the neutral [Sr(NO3)2–DCH18C6] and [Eu(NO3)2–DCH18C6] complexes are formed preferentially. Extraction to the ionic liquid phase occurs via neutral complex partitioning, indicated by the increase in extraction efficiency (reflected in the rising distribution ratio) with increasing anion concentration (Fig. S2, ESI†).34 This is similar to the extraction of alkaline earth metals by crown ethers in molecular diluents, like 1-octanol.49 Ion exchange mechanisms, like observed by Garvey et al. for [Cnmim][Tf2N], are unlikely to happen. In the proposed extraction mechanism, anions have to be co-extracted to maintain charge-neutrality. When extracting from chloride aqueous media, chloride anions replace the nitrate anions of the ionic liquid (eqn (4)), similar to the so-called split-anion extraction by Larsson and Binnemans.50
| M2+Aq + 2Cl−Aq + 2[A336][NO3]org + DCH18C6org ⇌ [M(NO3)2–DCH18C6]org + 2[A336][Cl]org | (4) |
This reaction, however, might be hampered because of the considerable hydration energy of the chloride ions.33,34,50 Dehydration, extraction and solvation by the ionic liquid might thus be unfavorable. The use of high salt concentrations in the aqueous feed increases the ionic strength significantly, resulting in less hydrated ions. This way, the ions are more prone to form extractable species. Extraction from nitrate aqueous solutions can proceed more efficiently because of their lower hydration energy (eqn (5)). Moreover, the ionic liquid phase is composed of nitrate ions, resulting in a more favorable transfer according to the Hofmeister series.29
| M2+Aq + 2NO3−Aq + DCH18C6org ⇌ [M(NO3)2–DCH18C6]org | (5) |
Selection of anion source and concentration
In a first series of screening experiments, the extraction behavior of Sr2+ as Eu2+ simulant was studied to find the optimal extraction parameters. Different anion concentrations and anion sources were used in the aqueous feed solution. Most efficient extraction of Sr2+ by [A336][NO3]-DCH18C6 was obtained using an aqueous phase with high lithium salt concentration (Fig. S1, ESI†). The use of other anion sources, i.e. HX and NH4X (with X = Cl− or NO3−), proved to be much less efficient, resulting in much lower distribution ratios. The lower efficiency by using HX and NH4X was most probably due to the occupation of the crown ether cavity by H3O+ and NH4+. Previous studies already proved that these ions could properly fit in this cavity because of their ion size.51,52 Li+ has a smaller ionic radius and therefore interacts less efficiently with the crown ether, resulting in better extraction results. Thus, the selection of a non-interfering source of additional anions is of high importance in these crown-ether-based extraction systems.After irradiation, the target material, i.e. Sm2O3, has to be dissolved. Most frequently, this is done by means of concentrated mineral acids, like HCl or HNO3. However, high acid concentrations are disadvantageous for two reasons. First of all, Eu2+ is extracted less efficiently by the crown ether from highly acidic media because the H3O+ ions occupy the cavity of the crown ether. Secondly, Eu2+ is unable to be stabilized in a high H+ concentration. Additionally, significant volumes of hydrogen gas would be generated during the reduction step, leading to unsafe situations. Therefore, the mixture should be adjusted to the most ideal extraction conditions after dissolution, meaning an increase in pH and anion concentration by the addition of non-interfering compounds. Evaporation to almost dryness followed by dissolution in other aqueous media is another possibility.
Because of their similar charge density and ionic radius, comparable extraction trends for Eu2+ and Sr2+ were to be expected. It was observed that Eu2+ follows indeed a similar trend as Sr2+ when extracted by DCH18C6 from chloride and nitrate aqueous media (Fig. S2, ESI†). Reasonably high distribution ratios were obtained using high salt concentrations, i.e. ≥6 M LiX. Again, the use of nitrate aqueous media yielded in much higher extraction efficiency compared to the use of chloride aqueous media, leading to distribution ratios well above (1).
It was noted that a significant amount of Eu2+, was also extracted towards the DCH18C6-free ionic liquid phase when using high salt concentrations. Significant extraction of Eu2+ in a DCH18C6-free system was not expected since it deviates from the behavior of Sr2+, where no extraction was observed at all. Therefore, it is believed that a partial re-oxidation of Eu2+ to Eu3+ have occurred during these experiments, whereby Eu3+ is extracted towards the organic phase without the interaction of a crown ether. Therefore, it is important to keep the extraction time as low as possible.
Time dependence of Sm3+/Eu2+ separation
The significant extractability of Eu2+ by [A336][NO3] + 0.05 M DCH18C6 and the low extractability of Eu2+ by [A336][NO3] seem to support both separation approaches so far. To arrive at a separation system, it is important to study the extraction behavior of Sm3+ as well. A fast separation is advantageous taking into account the decay of 153Sm and possible re-oxidation of Eu2+. Therefore, the distribution ratios of samarium and europium were studied as a function of time. For comparison and completeness, the distribution ratio of Eu3+ in the same conditions was studied in parallel.From the extraction results in Fig. 3a and 4a, from chloride and nitrate media, respectively, it was immediately clear that much higher distribution ratios were obtained for Sm3+ compared to Eu2+, with and without the use of DCH18C6. As expected, the presence of DCH18C6 in the ionic liquid did not influence the extraction behavior of Sm3+ because of its smaller ionic radius and higher hydration energy. The high difference in distribution ratio allows an efficient Sm/Eu separation. The DCH18C6-free system is favored because of the much lower Eu2+ extraction. Separation factors of 24 were reached using chloride media (Fig. 3b), whereas separation factors well above 600 were reached using nitrate media (Fig. 4b). Sm3+ was extracted to the ionic liquid phase via the split-anion extraction mechanism, as was described by Larsson and Binnemans (eqn (6)).50 This extraction mechanism makes use of the strong affinity of nitrate ions for the IL phase, while the chloride ions have a higher affinity for the aqueous phase.
| Sm3+Aq + 3Cl−Aq + 5[A336][NO3]org ⇌ [A336]2[Sm(NO3)5]org + 3[A336][Cl]org | (6) |
According to this extraction mechanism, the ionic liquid phase serves as a source of complexing anions. This way, no additional extractants are needed. However, chloride ions have to be transferred to the ionic liquid phase as well to ensure charge neutrality. The extraction of chloride ions is hampered because of their considerable hydration energy, as was also the case for the extraction of M2+ by DCH18C6 from chloride media. The much higher extraction efficiency for Sm3+ from nitrate aqueous media can be attributed to the lower hydration energy and higher hydrophobicity of nitrate ions.29,34 The high nitrate concentrations are needed to form extractable species. Trivalent lanthanide ions show the advantage of being able to form anionic complexes with bidentate nitrate ligands, whereas other elements cannot.23 Vander Hoogerstraete et al. already showed that the trivalent lanthanides (Ln3+) are extracted as pentanitrato complexes [Ln(NO3)5]2− (eqn (7)). Speciation studies using extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) support this extraction behavior (ESI).
| Sm3+Aq + 3NO3−Aq + 2[A336][NO3]org ⇌ [A336]2[Sm(NO3)5]org | (7) |
Larsson and Binnemans already pointed out that all trivalent lanthanides (Ln3+) show a similar extraction behavior with quaternary ammonium ionic liquids, with a decreasing trend in extraction efficiency across the lanthanide series.50 Thus, the slightly lower extraction efficiency of Eu3+ compared to Sm3+ is in full agreement with these findings (Fig. 3b and 4b). The slightly lower extractability of Eu3+ can probably be attributed to its slightly higher hydration energy because of its smaller ionic radius.53,54 Nevertheless, it is obvious that no efficient separation can be achieved without reduction of europium.
The high distribution ratios of Sm3+ are favorable for the second separation approach, i.e. the extraction of Sm3+ to the ionic liquid phase, while Eu2+ remains in the aqueous phase. Therefore, it can be concluded that the first separation approach, making use of a size-selective extractant to extract Eu2+, becomes superfluous. This also implies that different chloride or nitrate salts can be used to increase the salt concentration in the aqueous feed solution, i.e. the origin of the salt is less of importance regarding the separation method. Therefore, a salt causing less problems regarding the intended medical application can be chosen. Of course, the salt has to be highly soluble in the aqueous feed to reach the required concentration for optimal separation.
Efficient stripping of Sm3+ from the loaded IL phase can be achieved by decreasing the salt concentration in the aqueous phase, i.e. Sm3+ can be stripped by water.43 Reduction of the salt concentration in the system leads to a lower ionic strength. Sm3+ can thus be hydrated more easily, i.e. Sm3+ gains higher affinity for the aqueous phase. Therefore, no harsh conditions, like highly acidic media, are needed. Sm3+ was quantitatively (>98%) back-extracted to the aqueous phase by water in a single step. The strip solution can be slightly acidified to prevent any hydrolysis of Sm3+.
Temperature dependence of Sm3+/Eu2+ separation
Undiluted ionic liquids are highly viscous at room temperature. This is also the case for quaternary ammonium ionic liquids containing long carbon chains, like [A336][NO3]. This high viscosity implies a more difficult mass transfer, leading to reduced extraction speed. However, the viscosity drastically decreases with increasing temperature. Therefore, the above mentioned results were all obtained at 60 °C, a temperature at which [A336][NO3] has a significant lower viscosity but at which experiments are still easy to handle. The viscosity of water-saturated [A336][NO3] decreases from 204 mPa s at 25 °C to 95 mPa s at 40 °C and 42 mPa s at 60 °C. Extractions of Sm3+ and Eu2+ were executed at these temperatures to evaluate the influence of a changing viscosity of the ionic liquid phase. The results in Fig. 5 show that a change in temperature, and thus a change in viscosity, does not lead to significant changes in the extraction behavior of both Sm3+ and Eu2+. Therefore, mass transfer might not be the rate-determining step.Extraction behavior of Zn2+ impurities
Eu3+ can be efficiently and selectively reduced using chemical or electrochemical reduction methods. The chemical method makes use of Zn0 grains, which are oxidized to Zn2+. Hence, the introduction of extra impurities in the feed solution must be taken into account when using this chemical reduction method. Therefore, the extraction behavior of Zn2+ from both chloride and nitrate aqueous feed solution was studied and compared to the extraction behavior of Sm3+. The results in Fig. 6 clearly show that the extraction of Zn2+ is highly dependent on the anions present in the extraction system, i.e. Zn2+ is hardly extracted in case only nitrate anions are present in the extraction system, whereas the extraction of Zn2+ is very high in case of high chloride concentrations. This observation was expected because it is well known that the extraction of transition metals to quaternary ammonium and phosphonium chloride ionic liquids proceeds efficiently.19,55 Therefore, the extraction of Zn2+ from chloride media gives very high distribution ratios. Hence, Sm3+ can be efficiently separated from Zn2+ via selective stripping of the loaded [A336][NO3] phase. Sm3+ is transferred back to the aqueous phase upon reduction of the salt concentration in the system, while Zn2+ remains in the organic phase because of its high affinity for the ionic liquid. However, another approach is needed in case of an extraction from nitrate media, considering the low extractability of Zn2+ from nitrate media. In fact, the extraction behavior of Zn2+ is comparable to that of Eu2+. Therefore, reasonably good separation from samarium can already be achieved in the forward extraction step. Considering these results, Zn2+ impurities originating from the chemical reduction method can be efficiently removed.Outlook: separation scheme for the purification of samarium-153
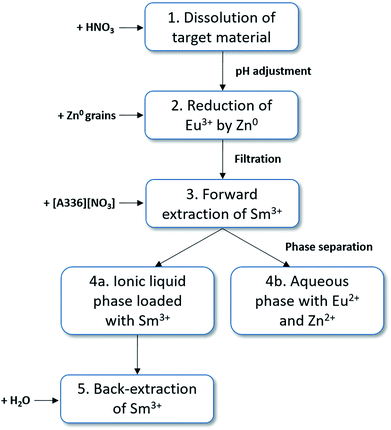
Based on this feasibility study, following full separation process concept to produce high purity samarium-153 can be proposed (Fig. 7): (1) dissolution of the target material by HNO3 and adjustment of the pH (4–6.5) and anion concentration (6 M NO3−) by the addition of a non-interfering nitrate salt (e.g. NH4NO3 or LiNO3). The total europium concentration must be adjusted by the addition of stable isotopes to facilitate the separation procedure. (2) The selective reduction of europium to its divalent state by zinc metal. (3) The forward extraction of Sm3+ to the ionic liquid phase, consisting of undiluted [A336][NO3]. Eu2+ and Zn2+ remain in the aqueous phase. (4) Separation of both phases. (5) Stripping (=back-extraction) of Sm3+ from the loaded ionic liquid phase can be easily performed by the addition of water, lowering the total salt concentration.Conclusion
A feasibility study to develop an efficient method to separate samarium and europium was conducted in scope of the purification process to produce high-purity 153Sm for medical applications. The separation method consists of the selective reduction of Eu3+ by zinc metal in an aqueous feed solution containing a high chloride or nitrate salt concentration (6 M). Subsequent extraction using the quaternary ammonium ionic liquid [A336][NO3] leads to a good separation of both lanthanides in a relatively short time frame. Sm3+ proved to be extracted to the neat [A336][NO3] phase much more efficiently compared to Eu2+. A first approach using the addition of DCH18C6 to capture Eu2+ in the ionic liquid phase proved to be less efficient. Therefore, the separation process using neat [A336][NO3] is the preferred approach, extracting Sm3+ to the ionic liquid phase while Eu2+ remains in the aqueous phase. Moreover, it was shown that the use of a nitrate aqueous feed solution leads to a more efficient separation method compared to the use of a chloride aqueous feed solution. Zn2+ ions originating from the chemical reduction method showed a very low extractability in nitrate media. This way, simultaneous removal of Eu2+ and Zn2+ from Sm3+ can be achieved in the forward extraction step. Therefore, this separation method can be used to arrive at a purified product with extended shelf-life. This leads to an increased availability of 153Sm radioisotopes and a decreased background radiation of 154Eu in the patient after treatment. The separation method can also be applied for efficient removal of Eu2+ from any other Ln3+ because all trivalent lanthanide ions tend to have a similar extraction behavior as Sm3+.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful for the funding provided by SCK•CEN Academy (granted to MV). Tom Vander Hoogerstraete and Bieke Onghena are acknowledged for their help with EXAFS measurements and data treatment. The DUBBLE beamline team at ESRF (Grenoble, France) and the financial support of FWO-NWO are acknowledged for granting the possibility to conduct EXAFS speciation studies.References
- P. Anderson and R. Nunez, Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther., 2007, 7, 1517–1527 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. J. Blower, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 4819–4844 RSC.
- A. J. Amoroso, I. A. Fallis and S. J. A. Pope, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2017, 340, 198–219 CrossRef.
- M. Castro and A. Portilla, Sm-153 EDTMP - a new palliative therapy agent against pain in cases of bone metastases, in Modern trends in radiopharmaceuticals for diagnosis and therapy, IAEA-TECDOC-1029, IAEA, Vienna, 1998 Search PubMed.
- C. L. Maini, S. Bergomi, L. Romano and R. Sciuto, Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging, 2004, 31, S171–S178 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. F. Sandeman, R. S. Budd and J. J. Martin, Clinical Oncology, 1992, 4, 160–164 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Bhattacharyya and M. Dixit, Dalton Trans., 2011, 40, 6112–6128 RSC.
- B. Ponsard, J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm., 2007, 50, 333–337 CrossRef.
- T. Loebe, B. Hettwig and H. W. Fischer, Appl. Radiat. Isot., 2014, 94, 40–43 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Moro, D. Fantinato, F. Frigerio, G. Shamhan and G. Angelovski, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2006, 41, 535–537 CrossRef.
- J. A. Kalef-Ezra, S. T. Valakis and S. Pallada, Phys. Med., 2015, 31, 104–107 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. S. Preston and A. C. du Preez, Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev., 1998, 18, 175–200 CrossRef.
- J. S. Preston and A. C. du Preez, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 1996, 65, 93–101 CrossRef.
- J. Garcia and M. J. Allen, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2012, 4550–4563 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Hirai and I. Komasawa, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 1992, 25, 644–648 CrossRef.
- T. Hirai and I. Komasawa, Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev., 1997, 17, 81–107 CrossRef.
- S. Nishihama, T. Hirai and I. Komasawa, J. Solid State Chem., 2003, 171, 101–108 CrossRef.
- K. Van Hoecke, J. Bussé, M. Gysemans, L. Adriaensen, A. Dobney and T. Cardinaels, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 2017, 314, 1727–1739 CrossRef.
- C. Deferm, M. Van de Voorde, J. Luyten, H. Oosterhof, J. Fransaer and K. Binnemans, Green Chem., 2016, 18, 4116–4127 RSC.
- D. Dupont and K. Binnemans, Green Chem., 2015, 17, 856–868 RSC.
- B. Onghena and K. Binnemans, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2015, 54, 1887–1898 CrossRef.
- A. Rout and K. Binnemans, Dalton Trans., 2014, 43, 1862–1872 RSC.
- T. Vander Hoogerstraete and K. Binnemans, Green Chem., 2014, 16, 1594–1606 RSC.
- G. Ye, F. Bai, J. Wei, J. Wang and J. Chen, J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 225–226, 8–14 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Y. Zhou, T. L. Yu, Y. Y. Ao, J. Peng and M. L. Zhai, Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2014, 30, 1581–1586 Search PubMed.
- G. Moreau, L. Helm, J. Purans and A. E. Merbach, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2002, 106, 3034–3043 CrossRef.
- G. Moreau, R. Scopelliti, L. Helm, J. Purans and A. E. Merbach, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2002, 106, 9612–9622 CrossRef.
- S. A. Sayed, K. A. Rabie and I. E. Salama, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2005, 46, 145–154 CrossRef.
- D. Dupont, D. Depuydt and K. Binnemans, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2015, 119, 6747–6757 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Vander Hoogerstraete, S. Jamar, S. Wellens and K. Binnemans, Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 3931–3938 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Dai, Y. H. Ju and C. E. Barnes, Dalton Trans., 1999, 1201–1202 RSC.
- D. I. Djigailo, S. V. Smirnova, I. I. Torocheshnikova, A. G. Vendilo, K. I. Popov and I. V. Pletnev, Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull., 2009, 64, 130–133 CrossRef.
- E. P. Horwitz, M. L. Dietz and D. E. Fisher, Solvent Extr. Ion Exch., 1990, 8, 199–208 CrossRef.
- S. L. Garvey, C. A. Hawkins and M. L. Dietz, Talanta, 2012, 95, 25–30 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. J. Pedersen, Science, 1988, 241, 536–540 Search PubMed.
- A. H. Bond, M. L. Dietz and R. Chiarizia, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2000, 39, 3442–3464 CrossRef.
- J. Christoffers and P. Starynowicz, Polyhedron, 2008, 27, 2688–2692 CrossRef.
- V. M. Abashkin, D. W. Wester, J. A. Campbell and K. E. Grant, Radiat. Phys. Chem., 1996, 48, 463–472 CrossRef.
- Y. Ao, W. Yuan, T. Yu, J. Peng, J. Li, M. Zhai and L. Zhao, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 3457–3462 RSC.
- M. Draye, A. Favre-Réguillon, R. Faure and M. Lemaire, Radiat. Phys. Chem., 2008, 77, 581–584 CrossRef.
- E. I. Grigorev, O. V. Mikhalitsyna, S. V. Nesterov and L. I. Trakhtenberg, High Energy Chem., 1997, 31, 16–19 Search PubMed.
- S. V. Nesterov, Russ. Chem. Rev., 2000, 69, 769–782 CrossRef.
- K. Larsson and K. Binnemans, J. Sustain. Metall., 2017, 3, 73–78 CrossRef.
- H. H. Dam, D. N. Reinhoudt and W. Verboom, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2007, 36, 367–377 RSC.
- J. Rydberg, M. Cox, C. Musikas and G. R. Choppin, Solvent Extraction Principles and Practice, Marcel Dekker Inc., USA, 2nd edn, 2004 Search PubMed.
- J. N. Chubb, P. Lagos and J. Lienlaf, J. Electrost., 2005, 63, 119–127 CrossRef.
- G. L. Hearn, J. Loss Prev. Process Ind., 2002, 15, 105–109 CrossRef.
- D. Allen, G. Baston, A. E. Bradley, T. Gorman, A. Haile, I. Hamblett, J. E. Hatter, M. J. F. Healey, B. Hodgson, R. Lewin, K. V. Lovell, B. Newton, W. R. Pitner, D. W. Rooney, D. Sanders, K. R. Seddon, H. E. Sims and R. C. Thied, Green Chem., 2002, 4, 152–158 RSC.
- M. L. Dietz and J. A. Dzielawa, Chem. Commun., 2001, 2124–2125 RSC.
- K. Larsson and K. Binnemans, Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 156, 206–214 CrossRef.
- E. Makrlík, P. Toman and P. Vaňura, Acta Chim. Slov., 2013, 60, 193–197 Search PubMed.
- P. Vaňura and E. Makrlík, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 2001, 250, 369–371 CrossRef.
- S. Andersson, K. Eberhardt, C. Ekberg, J.-O. Liljenzin, M. Nilsson and G. Skarnemark, Radiochim. Acta, 2006, 94, 469–474 Search PubMed.
- M. R. Antonio, D. R. McAlister and E. P. Horwitz, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 515–521 RSC.
- K. Larsson and K. Binnemans, Green Chem., 2014, 16, 4595–4603 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c8ra03279c |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 |