Themed collection Metal-Organic Framework Catalysis

Metal–organic framework catalysis
Welcome to this CrystEngComm themed issue entitled “Metal–organic framework catalysis.”

CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4044-4048
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE90106B
Photocatalytic metal–organic frameworks for organic transformations
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have attracted increasing attention for applications in heterogeneous photocatalysis.
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4126-4136
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00398F
Perspectives on metal–organic frameworks with intrinsic electrocatalytic activity
This highlight article focuses on the rapidly emerging area of electrocatalytic metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) with a particular emphasis on those systems displaying intrinsic activity.
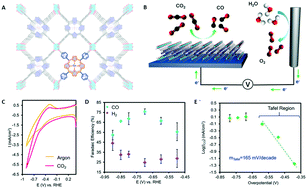
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4049-4065
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00215G
Metal–organic frameworks with Lewis acidity: synthesis, characterization, and catalytic applications
In this highlight, we review the recent development in the design and synthesis of metal–organic frameworks with Lewis acidity, the characterization techniques of Lewis acid sites, and their applications in heterogeneous catalysis.
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4066-4081
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CE02660E
Enzyme encapsulation in metal–organic frameworks for applications in catalysis
Various methods for encapsulating enzymes in metal–organic frameworks are discussed and the catalytic activity of biocomposites prepared using these methods is highlighted.
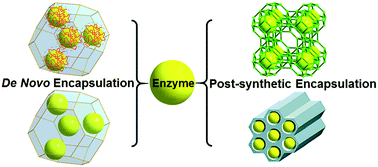
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4082-4091
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00022G
Understanding metal–organic frameworks for photocatalytic solar fuel production
The fascinating chemical and physical properties of MOFs have recently stimulated exploration of their application for photocatalysis. Design guidelines for these materials in photocatalytic solar fuel generation can be developed by applying the right spectroscopic tools.
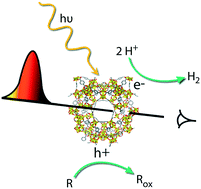
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4118-4125
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00006E
MOF catalysts in biomass upgrading towards value-added fine chemicals
The development of new synthetic routes from biomass sources towards already existing molecules, which are then called bio-based molecules, or the transformation of biomass into new building blocks and materials will be of great impact. This review presents a critical comparison between MOFs and other catalysts (e.g. zeolites) for biomass transformation.
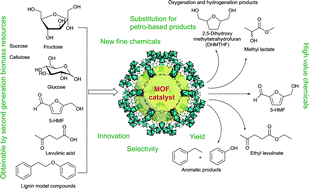
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4092-4117
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CE01782G
Solution-based sequential modification of LiCoO2 particle surfaces with iron(II) oxalate nanolayers
Facile creation of hybrid metal oxide-core/MOF-shell structures is achieved by stepwise solution-based modification of the core surface with a framework compound.
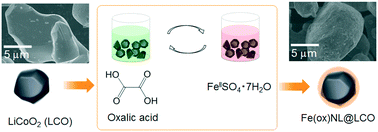
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4175-4181
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00552K
Acid–base directed supramolecular isomers of isophthalate based MOFs for CO2 adsorption and transformation
Directing supramolecular isomers using an acid versus a base, two MOFs with the same composition yet different topologies show differences in their catalytic efficacy to transform CO2 and epoxides into cyclic carbonates.
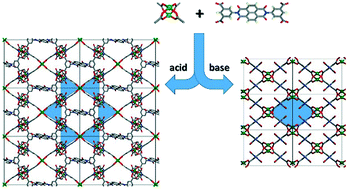
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4171-4174
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00405B
Base free transfer hydrogenation using a covalent triazine framework based catalyst
Isomerisation of allylic alcohols to saturated ketones can be efficiently catalysed by a heterogeneous molecular system resulting from IrIIICp* anchoring to a covalent triazine framework.
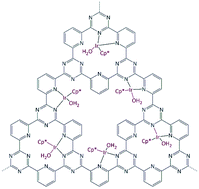
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4166-4170
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00561J
Surface acid–base catalytic activity of ZIF-8 revealed by super-resolution fluorescence microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy uncovers the surface-only catalytic activity of ZIF-8, but its accessibility is improved via extra porosity introduction by oleic acid treatment.
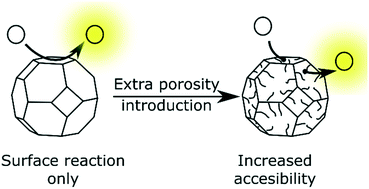
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4162-4165
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00074J
Two metal–organic frameworks sharing the same basic framework show distinct interpenetration degrees and different performances in CO2 catalytic conversion
Two metal–organic frameworks having the same basic framework but different interpenetration degrees show different catalytic activities in CO2 cycloaddition reactions.
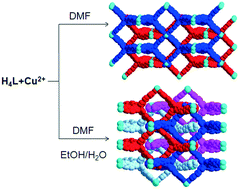
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4157-4161
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00100B
Using water adsorption measurements to access the chemistry of defects in the metal–organic framework UiO-66
Defects in UiO-66 were investigated for the first time by water adsorption measurements and then the materials were tested for the cyanosilylation of benzaldehyde.
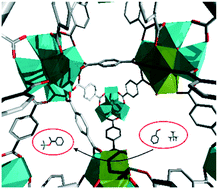
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4137-4141
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00224F
An in situ investigation of the water-induced phase transformation of UTSA-74 to MOF-74(Zn)
In water, UTSA-74 transforms through a dissolution–recrystallization process to its polymorph MOF-74(Zn).
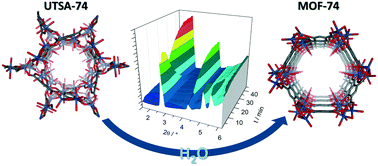
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4152-4156
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00094D
Nanostructured ZnO as a structural template for the growth of ZIF-8 with tunable hierarchical porosity for CO2 conversion
We report a new approach to introduce hierarchical porosity into ZIF-8 by using three-dimensional nanostructured porous ZnO as a structural template.
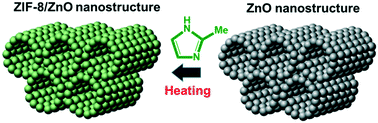
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4147-4151
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CE02549H
Synthesis of vanillin via a catalytically active Cu(II)-metal organic polyhedron
Crystalline Cu (II)-MOP 1 was employed for the first time in the catalytic conversion of trans-ferulic acid to vanillin.
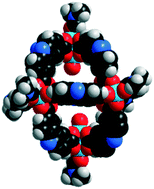
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4142-4146
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CE02621D
Improved catalytic performance of porous metal–organic frameworks for the ring opening of styrene oxide
An emerging strategy to improve the performance of porous metal–organic framework (MOF) materials as heterogeneous catalysts is reported.
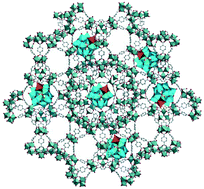
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4219-4226
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00528H
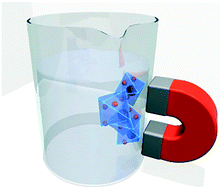
Fe3O4@HKUST-1 and Pd/Fe3O4@HKUST-1 as magnetically recyclable catalysts prepared via conversion from a Cu-based ceramic
A Fe3O4/Cu- ceramic system converted into a magnetic HKUST-1 composite was used as a recyclable catalyst for one-pot cascade and hydrogenation reactions.
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4201-4210
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00390K
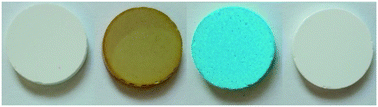
Systematic study of the impact of MOF densification into tablets on textural and mechanical properties
Densification process of MOF powders (HKUST-1, UiO-66, UiO-66-NH2, and UiO-67) into mechanically resistant pellets with maintained microporosity and enhanced volumetric uptake.
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4211-4218
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00338B
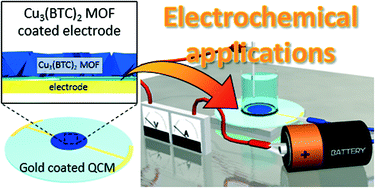
Electrochemical sensing and catalysis using Cu3(BTC)2 coating electrodes from Cu(OH)2 films
Metal–organic framework (MOF) coatings were prepared on gold electrodes through the conversion from Cu(OH)2 nanobelts to Cu3(BTC)2 MOFs.
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4194-4200
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CE00416H
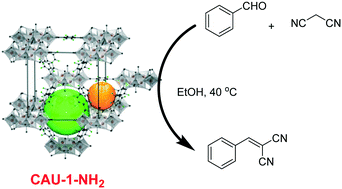
Knoevenagel condensation reaction catalysed by Al-MOFs with CAU-1 and CAU-10-type structures
This manuscript reports the Knoevenagel condensation reaction between benzaldehyde and malononitrile using CAU-1-NH2 as a reusable heterogeneous catalyst under mild reaction conditions.
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4187-4193
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CE02664H
Pd(0) loaded Zn2(azoBDC)2(dabco) as a heterogeneous catalyst
A new metal–organic framework Zn2(azoBDC)2(dabco) is used as a palladium(0) carrier and its application as a heterogeneous catalyst is demonstrated.
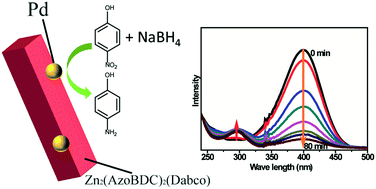
CrystEngComm, 2017,19, 4182-4186
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CE02447E