Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleDevelopment and validation of the UPLC-MS method for simultaneous determination of six new psychoactive substances
Zhouhong Tanab,
Yunbo Wenb,
Kai Yangc,
Xia Zhaoa,
Xiaoli Yang*a and
Jieli He *ab
*ab
aCollege of Pharmacy, Dali University, Dali 671000, Yunnan, P. R. China. E-mail: hejieli@dali.edu.cn
bYunnan Provincial Key Laboratory of Forensic Science, Kunming, 650223, Yunnan, P. R. China
cPublic Security Bureau, Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture, Dali 671000, Yunnan, P. R. China
First published on 21st September 2022
Abstract
The combined abuse of benzodiazepines and antipsychotics has become a global problem, and to develop a highly sensitive and selective method for monitoring of benzodiazepine hypnotics and antipsychotics is urgently necessary. In this work, we established a rapid method for the simultaneous determination of benzodiazepines (diazepam, alprazolam, triazolam, and estazolam) and antipsychotic drugs (clozapine, and chlorpromazine) based on ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). The accuracy, precision, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), specificity, matrix effect and carry-over effect were verified in detail. The results of the recovery and repeat experiments proved that the proposed UPLC-MS method possessed very satisfactory accuracy and precision. The LOD and LOQ of the six psychoactive substances were as low as 0.001–0.005 and 0.005–0.01 μg L−1, respectively. The proposed method was employed to analyze urine samples which were pretreated with a protein precipitation process. The potential influences of precipitants on the analysis results were evaluated statistically, and 0.1% formic acid/acetonitrile/water was selected as the optimum precipitation agent. The detection of the targets was free from matrix and carryover effects.
1. Introduction
New psychoactive substances (NPS) as structural variants of typical illicit drugs have become the most ideal substitutes for traditional drugs. Their synthesis is based on the structural parent nuclei of illegal substances, which are slightly modified to produce effects similar to those of known illegal substances (such as cannabinoids).1 Due to subtle structural differences, most NPS were not detected by drug-detection systems, allowing criminals to evade the law.2–5 In recent years, with the continuous development of the internet network, the market of NPS has been expanding, and the abuse of NPS has become a global problem.6–8 In 2018, the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) reported that one new NPS appears per week on average.9,10 By January 2021, more than 1000 NPS had been reported.3 In response to the growing number of NPS, the EMCDDA has implemented the EU Early Warning System (EWS), which aims to monitor, analyse and report on the growth trend of NPS.11 From 2014 to 2019, the number of first identified NPS decreased from 100 to 53, and the prevalence of NPS also declined.11,12 However, seizures of NPS are very limited, and the main categories of NPS seized are synthetic stimulants such as phenylethylamine and cathinone. In addition, there are currently no guidelines regarding the threshold reference standard value of NPS in biological samples, resulting in the difficulty of monitoring.13 Moreover, because of the quick regeneration of NPS, it was probably withdrawn from the sale market before they were uncovered, resulting in possible delays in validation and notification of NPS by the EWS.1,14With increasing control of NPS, clinical psychotropic prescription drugs have become the most popular NPS substances for criminals, such as diazepam, alprazolam and barbiturates. Prescription drugs are not only easier to obtain, but also can completely avoiding drug detection system. Among them, benzodiazepine hypnotics and antipsychotics are currently the two most popular of NPS substances sold on the black market. And both of them are central nervous system depressants. Benzodiazepines are GABA-A receptors that act on the limbic system and are mainly used to treat diseases such as anxiolytics, epilepsy, insomnia, convulsions and muscle relaxation.15–17 Antipsychotic drugs (such as chlorpromazine) mainly play a role in inhibiting the central nervous system by inhibiting the transmission of dopamine for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia and agitation.18,19 In addition to their therapeutic effects, these two types of drugs have serious side effects, such as slurred speech, unresponsiveness, delirium, coma, cognitive impairment, etc., especially after overdose in normal people. Long-term use will lead to serious drug tolerance, addiction, withdrawal symptoms, extrapyramidal system and other risks.20–22 In addition, it is more serious that it will produce superimposed effect, leading to acute symptoms such as liver lung injury and even death if the two drugs are taken at the same time.23–25 As a result, two types of drugs are also often associated with various types of crime for different purposes, such as sexual assault, murder, robbery, assault, etc., posing unprecedented challenges to public health and law enforcement everywhere.17,23 Therefore, it is particularly important to be able to quantitatively monitor the content of benzodiazepines and antipsychotics in body fluids.
At present, the commonly used detection methods for NPS substances include immunoassay, colorimetry, Raman spectroscopy, electrochemical method, liquid chromatography (HPLC), etc. However, these methods have low sensitivity and are not suitable for the detection of low content substances in human body, which may lead to false positive cases.26–28 Rapid qualitative and quantitative detection of NPS substances in conventional biological matrix samples (such as hair, urine, blood, nails) with high selectivity and sensitivity has become one of the most important research topic. Such as, Elmansi29 used micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) for simultaneous detection of three types of benzodiazepines with the low detection limit of 0.7–1.5 μg mL−1. However, this technique has the disadvantages of complex and time-consuming, which is not suitable for routine drug screening in clinical and forensic toxicology. Choudhary23 developed a high performance thin layer chromatography mass spectrometry (HPTLC-MS) method with the advantage of low operating cost to detect benzodiazepines. Nevertheless, it is not able to detect multiple substances simultaneously. Jinlei30 established a method based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) for the analysis of benzodiazepines in urine with the lower limit of quantification of 0.20–5.0 μg L−1. But the sample treatment is time-consuming and requires derivatization. In comparison, the ultra-high liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) has better adaptability especially in the determination of multiple objects because of its high selectivity and sensitivity under multiple response monitoring model (MRM) and attracts much attention.31
Accurate qualitative and quantitative detection of NPS in biological samples is highly necessary. Compare with blood, urine sample can be obtained easily and collected noninvasively and rapidly, and also is easy to handle and operate. Moreover, blood sample usually clots quickly at room temperature, while urine is relatively stable. Therefore, urine is the most commonly used biological material, and it is essential to pretreat it before analysis. The currently common pretreatments are solid phase extraction (SPE), liquid liquid extraction (LLE) and protein precipitation (PP).32–35 SPE bases on the difference in partition coefficient between the solid phase and the liquid phase of the target to separate the target from urine sample. And it requires long-time extraction and complex multi-step process. LLE achieves the purpose of separation according to the different solubility of the target component in the solvent. Although it is not as complicated as SPE, a large amount of harmful volatile organic solvents is needed. PP is a method of precipitation by using organic solvents (such as methanol, ethanol, acetone, etc.) that are miscible with water to significantly reduce the solubility of protein in water. By comparison, PP has several advantages of convenient, efficient and easy to automate, and becomes the most suitable method for urine pretreatment.
Herein, we developed a rapid and simple liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technique to analyze benzodiazepines (diazepam, alprazolam, triazolam, estazolam) and antipsychotics (clozapine and chlorpromazine) simultaneously in urine sample after PP pretreatment, and provided a basis method for the quality control of NPS in clinical monitoring.
2. Experimental section
2.1 Chemicals and reagents
Diazepam (98.0%), chlorpromazine (99.0%), clozapine (99.0%), alprazolam (98.0%), triazolam (98.0%), and estazolam (99.0%) were provided by Dali State Public Security Bureau (Dali, China). Methanol was purchased from Honeywell International Company (Charlotte, USA). Formic acid was obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Massachusetts, USA). Acetonitrile was provided by Shanghai Aladdin Industrial Co., Ltd. All reagents were of chromatographic grade. Ultrapure water was purified by a pure water system (DZG-303A, Tangle Corning Technology Factory, China) for prepared needed solutions. Filtration membrane (nylon66) with a diameter of 13 mm and 0.22 μm was purchased from Tianjin Jinrong Experimental Equipment Company (Tianjin, China).The stock solutions of triazolam, estazolam, alprazolam, diazepam, and clozapine were separately prepared with a concentration of 10 μg mL−1. A series of mixed standard working solutions with concentrations of 0.01, 0.025, 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 10.0 μg L−1 were prepared for calibration, verification and analysis. Methanol was used as diluent in the preparation of the individual stock solutions. All as-prepared solutions were stored at a 4 °C.
2.2 UPLC-MS conditions
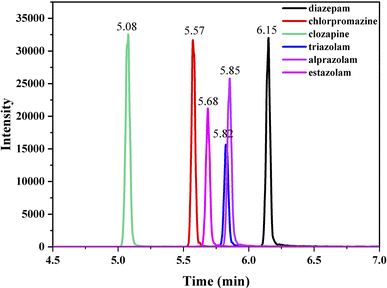
Ultimate 3000 HPLC system coupled with a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Ultimate 3000-TSQ Quantis) with an electrospray ionization source (ESI) was employed and a hypersil gold column (1.9 mm particle size, 100 mm × 2.1 mm i.d.) was thermostated at 30 °C. The mobile phase was composed of 0.05% formic acid in water (v/v, component A) and acetonitrile (component B), and the flow rate was 0.3 mL min−1. The optimized gradient elution program of solvent B was as follows: 0–0.5 min, 10%; 0.5–0.7 min, 10–26.5%; 0.7–2.0 min, 26.5–70%; 2–3.2 min, 70%; 3.2–3.5 min, 70–90%; 3.5–7 min, 90%; 7–7.5 min, 90–26.5%; 7.5–12 min, 26.5–10%. In MRM mode, the analyte standard with a concentration of 1 μg mL−1 (injection rate of 15 μL min−1) was injected into the mass spectrum, and the parent ion peak of the substance was decided by optimizing the ion source spray voltage to ensure that the response intensity was above 106. Collision energy, sheath gas and auxiliary gas flow rate were automatically optimized by the system. Under optimized conditions, two ions with highest intensity were selected as characteristic peak ions, one for quantification and another for qualitation. ESI was performed on positive ionization multi reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. ESI monitoring parameters were optimized as follows: ion source spray voltage, 3500 V; sheath gas flow rate, 25 L min−1; auxiliary gas flow rate, 5 L min−1; ion transfer tube temperature, 350 °C; atomization temperature, 300 °C. The retention time (RT) and ion parameters of the compounds studied in MRM mode are shown in Table 1, and the UPLC-MS spectra of the compounds analyzed under optimized conditions are shown in Fig. 1.| Analyte | Precursor ion | Quantification | Qualitication | RT (min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production | CE (V) | Product ion | CE (V) | |||
| Diazepam | 285.1 | 154.1 | 26.95 | 193.1 | 31.33 | 6.15 |
| Chlorpromazine | 319.1 | 214.0 | 20.25 | 86.1 | 40.13 | 5.57 |
| Clozapine | 327.0 | 192.1 | 41.27 | 270.1 | 25.13 | 5.08 |
| Triazolam | 343.1 | 315.2 | 24.59 | 308.2 | 23.24 | 5.82 |
| Alprazolam | 308.9 | 204.6 | 40.55 | 281.0 | 25.72 | 5.85 |
| Estazolam | 295.2 | 241.1 | 21.51 | 267.0 | 24.08 | 5.68 |
2.3 Methods validation
The established method was validated in accordance with the forensic toxicological methods validation protocols developed by the scientific working group on forensic toxicology (SWGTOX) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).36,37 Validation contents include linearity, accuracy, precision, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), specificity, matrix effect, and carryover effect.Calibration curves were obtained by analyzing mixture of standard solutions (containing diazepam, chlorpromazine, clozapine, alprazolam, triazolam, and estazolam) at eight concentration levels (0.01, 0.025, 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 10.0 μg L−1), and constructed by plotting the peak areas versus the concentrations of analyte with linear regression. Linearity was considered satisfactory if the R2 value was higher than 0.99. The standard serial solutions with three concentration gradients (0.1, 1.0 and 10.0 μg L−1) were prepared to examine the accuracy and repeatability. Accuracy was evaluated by a blank spiked recovery experiment in methanol (HPLC grade) and calculated as (measured value/expected value) ×100%. Accuracy was assumed satisfactory if recoveries were in the range of 80–120%. For within-run precision estimation, six replicates at three concentrations of 0.1, 1.0 and 10.0 μg L−1 were analyzed on a single day. One replicate was analyzed on 7 days for between-day precision investigation. The relative standard deviation (RSD) must less than 15%. The ratio of analyte responsesignal and background noise (S/N) ≥ 3 is considered as LOD, and S/N ≥ 10 is LOQ. Specificity of the method was assessed by analyzing blank urine samples from six different sources after adding mixing standard solution of 0.1 μg L−1. Carryover effect was evaluated by the influence of residue of high concentration sample on analysis results of blank negative sample, and the experiment was repeated for three times. Matrix effect evaluation was carried out by relative response of the standard solution and matrix sample spiked with the same concentration of analyte.
2.4 Urine sample pretreatment
Urine sample was pretreated by PP method. Total six blanks urine samples from healthy volunteers were collected and mixed. Add 35 mL of precipitant into 5 mL of the mixed urine sample, and then process for 10 min with ultrasound. After that, the urine sample was centrifuged for 10 min (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 r/min), and the supernatant was filtered by 0.22 μm membrane to obtain blank urine. The spike procedure was performed by adding some amounts of 0.5, 5.0 and 50.0 μg L−1 of mixed standard working solution into the blank urine samples, and the obtained standard addition concentrations were 0.1, 1.0, and 10.0 μg L−1 (in sextuplicate).
000 r/min), and the supernatant was filtered by 0.22 μm membrane to obtain blank urine. The spike procedure was performed by adding some amounts of 0.5, 5.0 and 50.0 μg L−1 of mixed standard working solution into the blank urine samples, and the obtained standard addition concentrations were 0.1, 1.0, and 10.0 μg L−1 (in sextuplicate).
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Methods validation
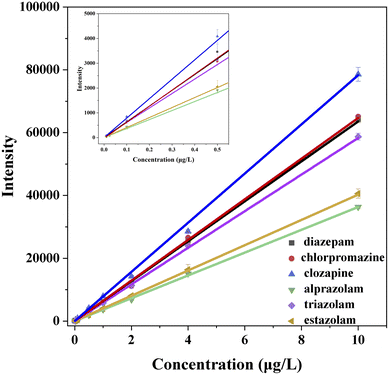
Fig. 2 shows the calibration curves of the six standard solutions at concentration of 0.01, 0.025, 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 10.0 μg L−1 measured by UPLC-MS, and their correspondingly correlation regression equations are displayed in Table 2. The coefficients of six analytes are all greater than 0.9990 in the range of 0.01–10.0 μg L−1, indicating that the correction curves fit well and have good correlation within the linear range. The corresponding LOD and LOQ values of the six analytes (Table 2) are in the range of 0.001–0.005 and 0.01–0.005 μg L−1, which are lower than that of most literature methods.38–41| Analyte | Calibration curve | R2 | Range (μg L−1) | LOD (μg L−1) | LOQ (μg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diazepam | Y = 6356.35X + 2.25 | 0.9991 | 0.01–10.0 | 0.002 | 0.005 |
| Chlorpromazine | Y = 6471.17X − 25.67 | 0.9992 | 0.01–10.0 | 0.001 | 0.005 |
| Clozapine | Y = 7830.00X + 5.51 | 0.9990 | 0.01–10.0 | 0.001 | 0.005 |
| Triazolam | Y = 5828.78X + 31.11 | 0.9992 | 0.01–10.0 | 0.002 | 0.005 |
| Alprazolam | Y = 3632.50X + 2.93 | 0.9991 | 0.01–10.0 | 0.005 | 0.01 |
| Estazolam | Y = 4027.09X + 5.25 | 0.9999 | 0.01–10.0 | 0.005 | 0.01 |
The intraday accuracy and precision of the proposed UPLC-MS method are expressed as the recovery rate and RSD correspondingly of the six analytes at three fortification levels assay (0.1, 1.0, 10.0 μg L−1). As shown in Table 3, the average recoveries of all six analytes ranged between 89.3–119.9%, 93.1–98.6% and 98.3–103.6% at the concentration of 0.1, 1.0 and 10.0 μg L−1, respectively. The RSD values were 5.59–11.83%, 3.30–5.28% and 1.44–4.54% at 0.1, 1.0 and 10.0 μg L−1, accordingly. Table 4 displays the between-day accuracy and precision. The average recoveries were between 89.5% and 108.9%, and the RSD values were < 15% for all analytes. The above results indicating the accuracy and precision of the offered method are satisfactory, especially at high concentration level.
| Analyte | 0.1 μg L−1 | 1.0 μg L−1 | 10.0 μg L−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
| Diazepam | 114.6 | 11.83 | 96.6 | 4.13 | 103.6 | 3.13 |
| Chlorpromazine | 111.6 | 10.04 | 93.1 | 5.28 | 101.8 | 1.44 |
| Clozapine | 113.5 | 6.14 | 98.6 | 3.43 | 98.5 | 2.71 |
| Triazolam | 119.9 | 6.64 | 97.8 | 3.30 | 100.7 | 4.54 |
| Alprazolam | 114.0 | 5.59 | 96.8 | 3.57 | 100.1 | 2.67 |
| Estazolam | 89.3 | 11.96 | 98.3 | 3.63 | 98.3 | 4.14 |
| Analyte | 0.1 μg L−1 | 1.0 μg L−1 | 10.0 μg L−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
| Diazepam | 103.8 | 10.40 | 90.4 | 7.28 | 93.7 | 10.63 |
| Chlorpromazine | 106.4 | 5.32 | 89.5 | 3.96 | 99.2 | 2.70 |
| Clozapine | 99.2 | 14.33 | 92.0 | 7.14 | 89.5 | 10.08 |
| Triazolam | 108.9 | 12.48 | 94.3 | 3.70 | 93.9 | 7.18 |
| Alprazolam | 99.2 | 4.76 | 92.2 | 5.05 | 93.1 | 7.54 |
| Estazolam | 94.8 | 5.81 | 96.6 | 1.72 | 97.4 | 0.95 |
3.2 Evaluation of precipitants for urine sample pretreatment
Protein precipitation method was used to pretreat the urine sample. The removal efficiency of urine protein changed with the different precipitant, which probably interfered with determination results of targets. Here, acetonitrile, methanol and acetonitrile water with 0.1% formic acid (V![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) V = 10
V = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 90) were adopted to pretreat the urine samples. Certain amounts of mixed standard solutions with the theoretical spiked concentration of 1.0 μg L−1 were added into the obtained blank urine samples, and three parallel spiked recovery results were shown in Table 5. To check the outliers, the Grubbs test was employed and a 95% confidence level was selected. The G value was calculated by eqn (1), where xq,
90) were adopted to pretreat the urine samples. Certain amounts of mixed standard solutions with the theoretical spiked concentration of 1.0 μg L−1 were added into the obtained blank urine samples, and three parallel spiked recovery results were shown in Table 5. To check the outliers, the Grubbs test was employed and a 95% confidence level was selected. The G value was calculated by eqn (1), where xq, ![[x with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0078_0304.gif) and S are are suspicious value, average value and standard deviations, respectively. The critical value of G is G0.05,3 = 1.155 (ref. 42).
and S are are suspicious value, average value and standard deviations, respectively. The critical value of G is G0.05,3 = 1.155 (ref. 42).
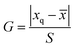 | (1) |
| Extracting agent | Analyte | Measured values (μg L−1) | Mean values (μg L−1) | S | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetonitrile | Diazepam | 0.6815 | 0.6805 | 0.5865 | 0.6495 | 0.0546 |
| Chlorpromazine | 0.7504 | 0.7380 | 0.7754 | 0.7546 | 0.0191 | |
| Clozapine | 0.6538 | 0.6056 | 0.5822 | 0.6139 | 0.0365 | |
| Triazolam | 0.9757 | 1.0285 | 1.0288 | 1.0110 | 0.0306 | |
| Alprazolam | 0.8055 | 0.7751 | 0.7252 | 0.7686 | 0.0405 | |
| Estazolam | 0.8216 | 0.7757 | 0.8529 | 0.8167 | 0.0388 | |
| Methylalcohol | Diazepam | 0.7682 | 0.7534 | 0.7085 | 0.7434 | 0.0310 |
| Chlorpromazine | 1.0066 | 1.0410 | 1.0185 | 1.0220 | 0.0175 | |
| Clozapine | 0.7550 | 0.7915 | 0.8210 | 0.7892 | 0.0331 | |
| Triazolam | 0.6932 | 0.7898 | 0.8028 | 0.7619 | 0.0599 | |
| Alprazolam | 0.6457 | 0.8945 | 0.7214 | 0.7539 | 0.1275 | |
| Estazolam | 0.8405 | 0.8199 | 0.7722 | 0.8109 | 0.0350 | |
| 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile water | Diazepam | 0.8734 | 0.8580 | 0.8917 | 0.8744 | 0.0169 |
| Chlorpromazine | 1.0212 | 0.9868 | 0.9669 | 0.9916 | 0.0275 | |
| Clozapine | 0.8882 | 0.8519 | 0.8607 | 0.8669 | 0.0189 | |
| Triazolam | 1.0403 | 0.9919 | 0.9616 | 0.9980 | 0.0397 | |
| Alprazolam | 1.0036 | 0.9878 | 1.0052 | 0.9989 | 0.0010 | |
| Estazolam | 0.9381 | 0.9704 | 0.9900 | 0.9661 | 0.0262 | |
When acetonitrile was used as the precipitant, the questionable values of diazepam, chlorpromazine, clozapine, triazolam, alprazolam, and estazolam were 0.5865, 0.7754, 0.6538, 0.9757, 0.7252, and 0.7757, and corresponding G values were 1.1538, 1.0890, 1.0932, 1.1536, 1.0716, and 1.0567, which were all lower than G0.05,3, indicating the xq values should be retained. For methanol as the precipitant, the xq values were 0.7085, 1.0410, 0.7550, 0.6932, 0.8945, 0.7722, and the calculated G values were 1.1258, 1.0857, 1.0332, 1.1469, 1.1027, and 1.1057, respectively. Therefore, all xq values should not be discarded. Similarly, 0.8917, 1.0212, 0.8882, 1.0403, 0.9878, 0.9381 were xq values when 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile water was as the precipitant. Correspondingly, the calculate G values of 1.0237, 1.0764, 1.1270, 1.0655, 1.1100, 1.0687 were also all lower than G0.05,3, and all xq values should be retained.
The significant difference in the analysis results of samples after different precipitant treatments were checked by F test. The 95% confidence level was selected in the statistical evaluation. The F value was calculated by eqn (2).
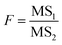 | (2) |
MS1 and MS2 represent the inter-group and the intra-group variance accordingly, where 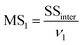 ,
, 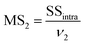 , SSinter and SSintra are the sums of squares of deviations, and ν1 and ν2 are degree of freedom of inter and intra groups (ν1 = k − 1, ν2 = N − k, where k is the number of groups and N is the total number of samples). SS, MS1, MS2 and F of the six analytes were shown in Table 6. Compare the calculated F value with the critical value F0.05,(ν1,ν2), and if F > F0.05,(ν1,ν2), it means that the results are significant different and the differences are statistically significant. Here, the critical value of F0.05,(2,6) was 6.060, and the F values of the six analytes were all greater than F0.05,(2,6). Therefore, it was concluded that the recovery results of urine samples after different precipitants treatment are significant different and the differences are statistically significant.
, SSinter and SSintra are the sums of squares of deviations, and ν1 and ν2 are degree of freedom of inter and intra groups (ν1 = k − 1, ν2 = N − k, where k is the number of groups and N is the total number of samples). SS, MS1, MS2 and F of the six analytes were shown in Table 6. Compare the calculated F value with the critical value F0.05,(ν1,ν2), and if F > F0.05,(ν1,ν2), it means that the results are significant different and the differences are statistically significant. Here, the critical value of F0.05,(2,6) was 6.060, and the F values of the six analytes were all greater than F0.05,(2,6). Therefore, it was concluded that the recovery results of urine samples after different precipitants treatment are significant different and the differences are statistically significant.
| Analyte | source of variation | SS | ν (df) | MS | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diazepam | Inter-group | 0.077 | 2 | 0.038 | 27.152 |
| Intra-group | 0.008 | 6 | 0.001 | ||
| Chlorpromazine | Inter-group | 0.129 | 2 | 0.064 | 135.256 |
| Intra-group | 0.003 | 6 | 0.000 | ||
| Clozapine | Inter-group | 0.127 | 2 | 0.063 | 32.325 |
| Intra-group | 0.012 | 6 | 0.002 | ||
| Triazolam | Inter-group | 0.118 | 2 | 0.059 | 29.000 |
| Intra-group | 0.012 | 6 | 0.002 | ||
| Alprazolam | Inter-group | 0.113 | 2 | 0.057 | 9.440 |
| Intra-group | 0.036 | 6 | 0.006 | ||
| Estazolam | Inter-group | 0.046 | 2 | 0.023 | 20.366 |
| Intra-group | 0.007 | 6 | 0.001 |
After confirming the significant differences among the three precipitants, q test should be used for pairwise comparison of the recovery rates of each group for the investigation of the best precipitants. The 95% confidence level was selected in the statistical evaluation. The q value was calculated by eqn (3).
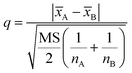 | (3) |
![[x with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0078_0304.gif) A and
A and ![[x with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0078_0304.gif) B is the respective average values of the two groups of data compared, nA and nB is corresponding detection times of the two groups of data.
B is the respective average values of the two groups of data compared, nA and nB is corresponding detection times of the two groups of data.
As shown in Table 7, the differences between every two groups of acetonitrile group, methanol group and 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile water group were significant in both diazepam and clozapine analysis. For chlorpromazine and triazolam determination, there were no significant differences between methanol and 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile water group, acetonitrile and 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile water group, respectively. For both alprazolam and estazolam testing, there were not significantly different between acetonitrile and methanol group. Combined with the recovery results which displayed in Table 5, 0.1% formic acid and acetonitrile water was chosen as the best precipitant for urine pretreatment in the following study.
| Analyte | Comparison group | |![[x with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0078_0304.gif) A − A − ![[x with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0078_0304.gif) B| B| |
MS | q |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a 1 was acetonitrile group; 2 was methanol group; 3 was 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile water group. | ||||
| Diazepam | 1 and 2 | 0.094 | 0.001 | 5.15 |
| 1 and 3 | 0.225 | 0.001 | 12.32 | |
| 2 and 3 | 0.131 | 0.001 | 7.18 | |
| Chlorpromazine | 1 and 2 | 0.267 | 0.001 | 14.62 |
| 1 and 3 | 0.237 | 0.001 | 12.98 | |
| 2 and 3 | 0.030 | 0.001 | 1.64 | |
| Clozapine | 1 and 2 | 0.175 | 0.001 | 9.59 |
| 1 and 3 | 0.253 | 0.001 | 13.86 | |
| 2 and 3 | 0.078 | 0.001 | 4.27 | |
| Triazolam | 1 and 2 | 0.249 | 0.002 | 9.64 |
| 1 and 3 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.50 | |
| 2 and 3 | 0.236 | 0.002 | 9.14 | |
| Alprazolam | 1 and 2 | 0.015 | 0.006 | 0.34 |
| 1 and 3 | 0.230 | 0.006 | 5.14 | |
| 2 and 3 | 0.245 | 0.006 | 5.48 | |
| Estazolam | 1 and 2 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.33 |
| 1 and 3 | 0.149 | 0.001 | 8.16 | |
| 2 and 3 | 0.155 | 0.001 | 8.49 | |
3.3 Validation of the proposed method to determine the urine sample
To validate the application of the proposed UPLC-MS method in real samples monitoring, it was employed to determine the spiked urine sample after pretreating by acetonitrile water with 0.1% formic acid (V![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) V = 10
V = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
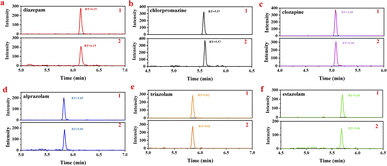
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 90). Add appropriate amounts of standard mixed working solutions into the obtained blank urine samples to get 0.1, 1.0, 10.0 μg L−1 spiked solutions, and then determine the all six analytes (in sextuplicate). The MRM chromatograms of mixed standard working solution and spiked urine sample are displayed in Fig. 3. As it shows, the impurity peaks of endogenous compounds in urine samples would not interfere with the target analytes. Compare with the standard working solution of the same concentration, the impurity peaks of endogenous compounds in urine samples would not interfere with the detection of the targets. The average recoveries and RSD values of the analytes were shown in Table 8. The recoveries of all target compounds were 81.2–104.1% with RSD of 2.44–12.01%. Together, these results suggested the proposed method for real urine sample determination is of high specificity, good precision and accuracy.
90). Add appropriate amounts of standard mixed working solutions into the obtained blank urine samples to get 0.1, 1.0, 10.0 μg L−1 spiked solutions, and then determine the all six analytes (in sextuplicate). The MRM chromatograms of mixed standard working solution and spiked urine sample are displayed in Fig. 3. As it shows, the impurity peaks of endogenous compounds in urine samples would not interfere with the target analytes. Compare with the standard working solution of the same concentration, the impurity peaks of endogenous compounds in urine samples would not interfere with the detection of the targets. The average recoveries and RSD values of the analytes were shown in Table 8. The recoveries of all target compounds were 81.2–104.1% with RSD of 2.44–12.01%. Together, these results suggested the proposed method for real urine sample determination is of high specificity, good precision and accuracy.
| Analyte | 0.1 μg L−1 | 1.0 μg L−1 | 10.0 μg L−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
| Diazepam | 87.0 | 7.57 | 87.3 | 3.99 | 97.0 | 4.99 |
| Chlorpromazine | 100.3 | 5.83 | 98.9 | 2.44 | 104.1 | 3.31 |
| Clozapine | 81.2 | 10.03 | 84.5 | 3.70 | 97.8 | 4.37 |
| Triazolam | 99.8 | 5.65 | 100.8 | 6.51 | 103.0 | 3.58 |
| Alprazolam | 83.1 | 12.01 | 96.4 | 4.09 | 101.0 | 3.39 |
| Estazolam | 81.6 | 6.74 | 97.1 | 5.67 | 96.7 | 4.84 |
Matrix effect is always an annoying problem in UPLC-MS analysis. The exogenous and endogenous impurities including salts and other matrix components in urine samples would flow out from the column with the target compounds and enter into ionization source, which might seriously affect the ionization process of the target compounds and lead to the inhibition or enhancement of ionization signals. In ESI mode, chlorpromazine and triazolam produced ion-enhancing effects, while the other four analytes (diazepam, clozapine, alprazolam and estazolam) showed different degrees of ion inhibition. To verify the influence of matrix effects in urine, the relative responses of target analytes in spiked blank urine samples and standard solutions with the same concentrations were explored for 6 parallel measurements and the results are displayed in Table 9. If values of average recovery within (100 ± 25) % and RSD < 15%, the matrix effect bears almost no influence on the method. At the concentrations of 1.0 and 10.0 μg L−1, the average recovery and RSD values of all six analytes were in the range of 85.8–106.3% and 2.23–5.94%, respectively. Even as low as 0.1 μg L−1, the matrix effect also could be ignored in all but clozapine analysis.
| Analyte | 0.1 μg L−1 | 1.0 μg L−1 | 10.0 μg L−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
| Diazepam | 76.0 | 7.54 | 90.0 | 3.64 | 93.6 | 4.56 |
| Chlorpromazine | 89.1 | 6.07 | 106.3 | 2.23 | 102.2 | 3.02 |
| Clozapine | 71.7 | 9.94 | 85.8 | 3.37 | 99.3 | 3.99 |
| Triazolam | 79.4 | 5.60 | 103.0 | 5.94 | 102.2 | 3.27 |
| Alprazolam | 108.5 | 11.29 | 99.6 | 3.71 | 101.0 | 3.09 |
| Estazolam | 91.6 | 6.64 | 98.8 | 5.17 | 98.4 | 4.42 |
Carryover effect was also studied indetail. After injecting of high concentration of 10.0 μg L−1 spiked urine sample, the blank negative sample was analyzed immediately. The corresponding response signals of negative sample for three repeated experiments were all lower than the detection limit, implying the carryover effect was mostly negligible.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the UPLC-MS method with good specificity, accuracy and high precision was developed for qualitative and quantitative analysis of six new psychotropic substances (diazepam, chlorpromazine, clozapine, triazolam, alprazolam and estazolam). Under optimized chromatographic conditions and positive ionization mode of UPLC-MS technology, all substances show good linearity in the range of 0.01–10 μg L−1. The detection and quantification limits can reach 0.001 and 0.005 μg L−1, respectively. The matrix and carry-over had no effects on the results of detection, and could be ignored. Further more, the protein precipitation method was used to pretreat the urine samples, and effects of precipitants were analyzed statistically and evaluated. The 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile water was chosen as the optimal precipitant. In summary, the established method is sensitive, specific, simple and rapid, which can be applied in clinical and forensic toxicological analysis.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Opening Foundation of Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory of Forensic Science (No. 2020SKF02) and scholarship for Academic Leader of Yunnan Province (No.2018HB003).Notes and references
- E. Y. Chung, H. J. Cha, H. K. Min and J. Yun, Arch. Pharmacal Res., 2021, 44, 402 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. F. da Cunha, K. D. Oliveira, M. A. Huestis and J. L. Costa, J. Anal. Toxicol., 2020, 44, 697 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. K. Nzekoue, M. Agostini, M. Verboni, C. Renzoni, L. Alfieri, S. Barocci, M. Ricciutelli, G. Caprioli and S. Lucarini, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2021, 205, 114310 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Pettersson Bergstrand, M. R. Meyer, O. Beck and A. Helander, Drug Test. Anal., 2018, 10, 496 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Y. Simão, M. Antunes, H. Marques, T. Rosado, S. Soares, J. Gonçalves, M. Barroso, M. Andraus and E. Gallardo, Bioanalysis, 2020, 12, 1557 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Vardal, G. Wong, A. M. L. Oiestad, S. Pedersen-Bjergaard, A. Gjelstad and E. L. Oiestad, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2018, 410, 4967 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Garcia, N. B. Tiscione, D. T. Yeatman and L. Richards-Waugh, J. Anal. Toxicol., 2021, 45, 462 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Dunlop, K. Hayes, P. Leavy, D. Cusack and R. Maguire, J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2017, 1064, 22 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. F. da Cunha, K. D. Oliveira, M. S. Cardoso, A. C. F. Arantes, P. H. P. Coser, L. N. Lima, A. C. S. Maluf, M. A. C. Comis, M. A. Huestis and J. L. Costa, Drug Alcohol Depend., 2021, 227, 108962 CrossRef.
- L. Orsolini, S. Chiappini, J. M. Corkery, A. Guirguis, D. Papanti and F. Schifano, Expert Rev. Neurother., 2019, 19, 1253 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Castiglioni, N. Salgueiro-Gonzalez, L. Bijlsma, A. Celma, E. Gracia-Lor, M. S. Beldean-Galea, T. Mackulak, E. Emke, E. Heath, B. Kasprzyk-Hordern, A. Petkovic, F. Poretti, J. Rangelov, M. M. Santos, M. Sremacki, K. Styszko, F. Hernandez and E. Zuccato, Water Res., 2021, 195, 116983 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. E. Grafinger, W. Bernhard and W. Weinmann, Sci. Justice, 2019, 59, 459 CrossRef.
- A. Peacock, R. Bruno, N. Gisev, L. Degenhardt, W. Hall, R. Sedefov, J. White, K. V. Thomas, M. Farrell and P. Griffiths, Lancet, 2019, 394, 1668 CrossRef.
- F. Pantano, S. Graziano, R. Pacifici, F. P. Busardò and S. Pichini, Curr. Neuropharmacol., 2019, 17, 818 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. G. Kang and H. R. Lin, J. Anal. Toxicol., 2019, 43, 96–103 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Garcez, C. Fernandes, F. Barbosa, M. R. Pereira, C. Silveira, J. Marques-Teixeira and A. R. Goncalves, Psychopharmacol., 2020, 237, 1 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Banaszkiewicz, M. K. Wozniak, M. Kata, E. Domagalska, M. Wiergowski, B. Szpiech and A. Kot-Wasik, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2020, 191, 113569 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Choi, M. E. Barra, K. Newman and J. H. Sin, J. Intensive Care Med., 2020, 35, 1118 CrossRef.
- Y. Cao, F. Zhao, J. Chen, T. Huang, J. Zeng, L. Wang, X. Sun, Y. Miao, S. Wang and C. Chen, J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2020, 1147, 122129 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Atkin, S. Comai and G. Gobbi, Pharmacol. Rev., 2018, 70, 197 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. L. Li, Z. Y. Zhang, T. W. Zhao, C. Y. Meng, Q. Y. Zhang and M. M. Wang, Mikrochim. Acta, 2020, 187, 540 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Takeuchi, N. E. MacKenzie, D. Samaroo, O. Agid, G. Remington and S. Leucht, Schizophr. Bull., 2020, 46, 1439 CrossRef.
- P. Choudhary, S. Bansal and K. L. Verma, J. Planar Chromatogr. - Mod. TLC., 2020, 33, 523 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Y. Cheng, W. Y. Chen, H. C. Liu, T. W. Yang, C. H. Pan, S. Y. Yang and C. J. Kuo, Psychopharmacol., 2018, 235, 3329 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Morgan, N. Martucci, A. Kozlowska, W. Gamal, F. Brzeszczynski, P. Treskes, K. Samuel, P. Hayes, L. Nelson, P. Bagnaninchi, J. Brzeszczynska and J. Plevris, Biomed. Pharmacother., 2019, 111, 1408 CrossRef CAS.
- S. M. Ahmad and J. M. F. Nogueira, Talanta, 2019, 199, 195 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Pettersson Bergstrand, A. Helander, T. Hansson and O. Beck, Drug Test. Anal., 2017, 9, 640 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Shafi, A. J. Berry, H. Sumnall, D. M. Wood and D. K. Tracy, Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol., 2020, 10, 2045125320967197 Search PubMed.
- H. Elmansi and F. Belal, Microchem. J., 2019, 145, 330 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Jinlei, A. Wurita, W. Xuejun, Y. Hongkun, G. Jie and C. Liqin, Leg. Med., 2021, 48, 101822 CrossRef.
- S. Lehmann, T. Kieliba, J. Beike, M. Thevis and K. Mercer-Chalmers-Bender, J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2017, 1064, 124 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Lopez-Garcia, N. Mastroianni, C. Postigo, D. Barcelo and M. Lopez de Alda, J. Chromatogr. A, 2018, 1576, 80 CrossRef CAS.
- C. de Paula, M. Jurisch, E. Piccin and R. Augusti, Drug Test. Anal., 2018, 10, 1348 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. De Boeck, L. Moreels, W. Dehaen, J. Tytgat and E. Cuypers, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2019, 164, 57 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Furugen, A. Nishimura, M. Kobayashi, T. Umazume, K. Narumi and K. Iseki, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2019, 168, 83 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Scientific Working, Group for Forensic, J. Anal. Toxicol., 2013, 37, 452 CrossRef.
- S. M. R. Wille, W. Coucke, T. De Baere and F. T. Peters, Curr. Pharm. Des., 2017, 23, 5442 CAS.
- M. Cobo-Golpe, A. de-Castro-Rios, A. Cruz, M. Paramo, M. Lopez-Rivadulla and E. Lendoiro, Forensic Sci. Int., 2021, 326, 110935 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Orfanidis, H. Gika, O. Mastrogianni, A. Krokos, G. Theodoridis, E. Zaggelidou and N. Raikos, Forensic Sci. Int., 2018, 290, 137 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. De Boeck, S. Missotten, W. Dehaen, J. Tytgat and E. Cuypers, Forensic Sci. Int., 2017, 274, 44 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, Y. Zhuo, X. Tang, H. Qiang, W. Liu, H. Wu, P. Xiang, G. Duan and M. Shen, Drug Test. Anal., 2020, 12, 472 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Li, H. Zhao and Y. Chai, Analytical Chemistry, People's Medical Publishing House, Beijing, China, 2011 Search PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |