Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleOrganocatalytic asymmetric formal oxidative coupling for the construction of all-aryl quaternary stereocenters†
Zhiyang
Li
 ac,
Yichen
Li
ac,
Yichen
Li
 b,
Xingguang
Li
b,
Xingguang
Li
 ad,
Mandi
Wu
ad,
Mandi
Wu
 b,
Ming-Liang
He
b,
Ming-Liang
He
 *b and
Jianwei
Sun
*b and
Jianwei
Sun
 *acd
*acd
aDepartment of Chemistry, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), Clear Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong SAR, China. E-mail: sunjw@ust.hk
bDepartment of Biomedical Sciences, City University of Hong Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong SAR, China. E-mail: minglihe@cityu.edu.hk
cShenzhen Bay Laboratory, Shenzhen 518107, China
dShenzhen Research Institute, HKUST, No. 9 Yuexing 1st Rd, Shenzhen 518057, China
First published on 29th July 2021
Abstract
A new catalytic asymmetric formal cross dehydrogenative coupling process for the construction of all-aryl quaternary stereocenters is disclosed, which provides access to rarely explored chiral tetraarylmethanes with excellent enantioselectivity. The suitable oxidation conditions and the hydrogen-bond-based organocatalysis have enabled efficient intermolecular C–C bond formation in an overwhelmingly crowded environment under mild conditions. para-Quinone methides bearing an ortho-directing group serve as the key intermediate. The precise loading of DDQ is critical to the high enantioselectivity. The chiral products have also been demonstrated as promising antiviral agents.
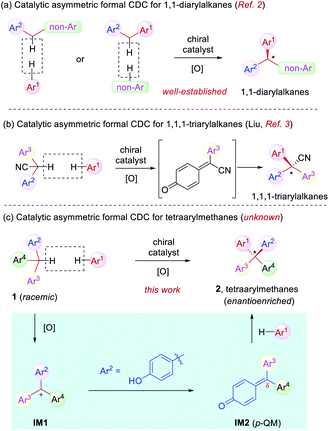
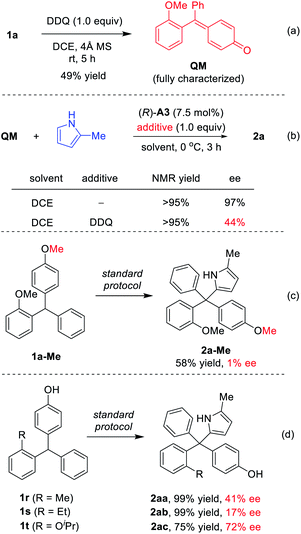
Cross dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) is a powerful tool to forge intermolecular C–C bonds from two C–H bonds without prefunctionalization.1 Specifically, the benzylic C–H bond is relatively prone to oxidation and thus it has evolved into a versatile arena for the implementation of this reaction, leading to efficient construction of various benzylic stereogenic centers. As a result, CDC has proved to be useful for the establishment of a wide range of 1,1-diaryl stereocenters (Scheme 1a).2 Recently, Liu and coworkers reported a elegant synthesis of enantioenriched triarylacetonitriles via in situ oxidation of α-diarylacetonitriles to para-quinone methides (p-QMs) followed by asymmetric nucleophilic addition with stereocontrol induced by a chiral phosphoric acid catalyst. This represents a rare example of formal CDC for the synthesis of 1,1,1-triarylalkanes (Scheme 1b).3 However, the establishment of tetraaryl-substituted carbon stereocenters by this approach remains unknown (Scheme 1c).
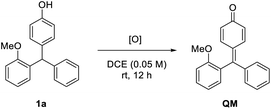
Distinct from the asymmetric synthesis of triaryl-substituted stereocenters,4 substantial steric hindrance in establishing tetraaryl-substituted quaternary stereocenters poses significant synthetic challenges.5–8 Indeed, even racemic or achiral syntheses of tetraarylmethanes have been an elusive topic of investigation in organic synthesis.6 In this context and in continuation of our effort in the studies of asymmetric reactions of para-quinone methides (p-QMs)9,10 as well as the synthesis of chiral tetraarylmethanes,8 we envisioned that suitable oxidation of racemic triarylmethane 1 is expected to generate triarylmethyl cation IM1 (Scheme 1c). With one aryl group as para-hydroxyphenyl, this cation could be stabilized in the form of p-QM IM2. Subsequent asymmetric nucleophilic addition by another electron-rich arene to the p-QM intermediate is expected to generate chiral tetraarylmethanes 2. The challenges associated with this one-pot process mainly include the compatibility problem between the oxidative condition and the catalytic asymmetric system in order to achieve both high efficiency and enantioselectivity.
We commenced our study with racemic triarylmethane 1a as the model substrate. The initial study was directed to the search for a suitable oxidant to mildly generate the p-QM intermediate (Table 1).11 At room temperature, the use of superstoichiometric amounts of Ag2O or benzoquinone was completely ineffective (entries 1 and 2). Similarly, the reaction did not proceed using oxygen as the oxidant in combination with catalyst Mn(acac)3 (entry 3). Subsequently, considerable efforts were devoted to screening many other oxidation systems, almost all of which were completely incapable for this oxidation (entries 4–8). However, eventually we were delighted to identify DDQ as the superior oxidant, leading to complete and clean conversion to the desired QM at room temperature (entry 9). In contrast, a combination of catalytic DDQ with 5 equivalents of MnO2 gave only 60% conversion (entry 10).
| Entry | [O] | Conv. (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ag2O (5.0 equiv.) | 0 |
| 2 | Benzoquinone (1.5 equiv.) | 0 |
| 3 | Mn(acac)3 (10 mol%), O2 (1 atm) | 0 |
| 4 | KBr (1.2 equiv.), Oxone (1.2 equiv.) | 0 |
| 5 | K3Fe(CN)6 (1.5 equiv.) | 0 |
| 6 | AIBN (0.5 equiv.), TBHP (3.0 equiv.) | 0 |
| 7 | FeCl3 (10 mol%), TBHP (3.0 equiv.) | 0 |
| 8 | TEMPO (3.0 equiv.) | 0 |
| 9 | DDQ (1.0 equiv.) | 100 |
| 10 | DDQ (20 mol%), MnO2 (5.0 equiv.) | 60 |
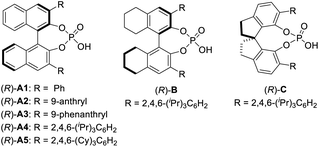
We next set out to evaluate the key C–C bond formation step (Table 2). 2-Methylpyrrole was employed as the nucleophile. Chiral phosphoric acids were used as catalysts in view of their exceptional performance in the asymmetric reactions of QMs.12,13 After oxidation, the nucleophile and catalyst were added to the reaction mixture. The reaction with catalyst (R)-A1 proceeded smoothly at room temperature to form the desired product 2a in 90% yield, but unfortunately in a racemic form (entry 1). Next, a range of chiral phosphoric acids were screened. To our delight, the BINOL-derived TRIP catalyst, (R)-A4, provided excellent enantioselectivity (93% ee, entry 4). However, those with H8BINOL- and SPINOL-derived catalysts (B and C) bearing the same 2,4,6-triisopropylphenyl substituents proved to be inferior. Finally, a slightly modified acid A5 was found to be the best (95% ee, entry 7). Decreasing the temperature to 0 °C improved the result (97% ee, entry 8). However, no further improvement was observed at a lower temperature. While DCM was comparable to DCE, other solvents (e.g., EtOAc and Et2O) significantly affected the enantioselectivity. Varying the concentration led to no improvement (entries 9–13). Finally, the catalyst loading could be reduced to 7.5 mol% without erosion in yield or enantioselectivity (entry 14). Notably, during the course of our study, the enantioselectivity was found to be sensitive to the amount of DDQ when it was used in excess. For example, with 1.5 equivalents of DDQ (entry 15), the enantioselectivity decreased to 51% ee. However, with 0.8 equivalents, the selectivity remained excellent, albeit with reduced yield. These results suggest that the excessive DDQ might be detrimental to stereocontrol. Unfortunately, this feature also prevented the two-step protocol from merging into one operation. The catalyst has to be added after complete consumption of DDQ to ensure high enantioselectivity (entry 17). Moreover, although the oxidation step was relatively fast (∼30 min) based on TLC analysis, keeping this mixture under stirring for an additional 4 h before adding the acid catalyst was critical to achieve high enantioselectivity, which is likely to ensure complete consumption of DDQ or precipitation of its reduced form DDQH2 from the solution (entry 18).
| Entry | CPA | Temp. | Yield 2a (%) | ee (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Reaction conditions: 1a (0.025 mmol), 3a (0.05 mmol), catalyst (10 mol%), DCE (0.5 mL). Yield is based on analysis of the 1H NMR spectroscopy of the crude reaction mixture using CH2Br2 as an internal standard. | ||||
| 1 | (R)-A1 | rt | 90 | 0 |
| 2 | (R)-A2 | rt | 95 | 47 |
| 3 | (R)-A3 | rt | 92 | 49 |
| 4 | (R)-A4 | rt | 96 | 93 |
| 5 | (R)-B | rt | 93 | 65 |
| 6 | (R)-C | rt | 91 | 9 |
| 7 | (R)-A5 | rt | 95 | 95 |
| 8 | (R)-A5 | 0 °C | 95 | 97 |
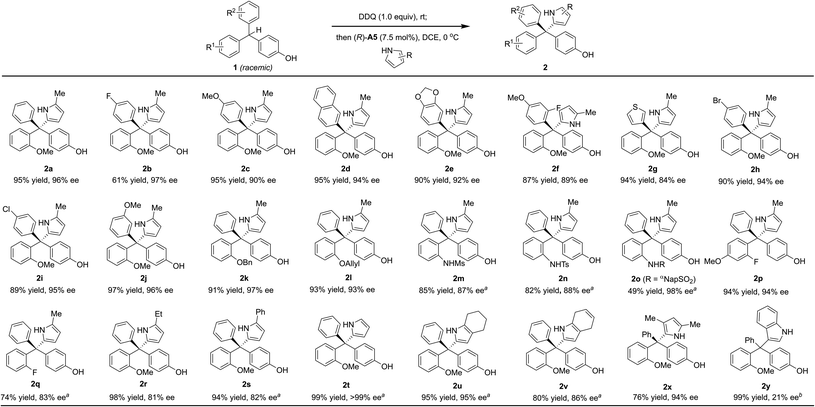
With the optimized conditions (entry 14, Table 2), we examined the reaction scope (Scheme 2). A wide range of diversely-substituted triarylmethanes participated in this process with good to excellent efficiency and enantioselectivity. In addition to OMe, other alkoxy groups (e.g., OBn and OAllyl, 2k–l), protected amine groups (e.g., sulfonamides, 2m–o), and even fluorine (2p–q) can serve as an effective directing group when they are present at the ortho position. Moreover, as shown in the case of 2f, the observed good enantioselectivity indicated that the directing ability of alkoxy and fluorine groups is remarkably different. The incorporation of a heterocycle, such as thiophene (2g), did not interfere with the reactivity or enantiocontrol. Some other pyrroles, including 2,4-dimethyl pyrrole (2x), were also good nucleophiles. 4,7-Dihydro-1H-indole also reacted smoothly to form the product 2v. Subsequent oxidation by DDQ could easily afford the indole-substituted tetraarylmethane 2weqn (1). Unfortunately, pyrroles with carbonyl substituents and other electron-rich arenes, such as indole, furan, 2-naphthol, and 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene, were not reactive under the standard conditions (0 °C). At room temperature, indole could react to form the desired product 2y, but in only 21% ee, while the others remain unreactive.
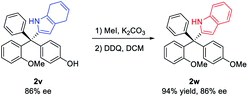 | (1) |
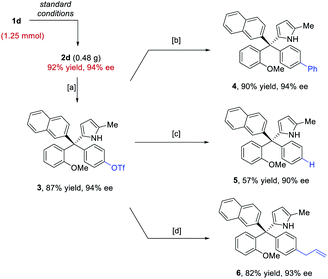
The standard protocol could be scaled to 1.25 mmol without erosion in efficiency or enantiocontrol (Scheme 3). Moreover, the directing groups, such as the para-hydroxy group, could be easily converted or removed. For example, after triflation of the phenol unit in 2d, the triflate 3 could easily participate in coupling reactions to form the arylation, reduction, and allylation products 4–6. The high enantiopurity remained essentially intact.
To understand the reaction mechanism, we carried out some control experiments. First, the intermediate QM, though unstable and easy to undergo addition, was obtained by careful isolation from the oxidation step in the presence of molecular sieves (Scheme 4a). Next, in the absence of DDQ, the standard reaction between QM and 2-methylpyrrole proceeded with high efficiency and excellent enantioselectivity (97% ee, Scheme 4b). However, with DDQ as an additive, the enantioselectivity decreased to 44% ee, which confirmed that it is detrimental to enantiocontrol.14 The methylated substrate 1a-Me was also examined. The desired tetraarylmethane 2a-Me was successfully formed, but in an almost racemic form (Scheme 4c). In this case, the corresponding oxonium cation served as an activated intermediate, rather than p-QM. This result indicated that the free hydroxyl group in the standard substrates is not necessary for DDQ oxidation, but the resulting p-QM intermediate is essential for excellent enantiocontrol.
Finally, the substrates bearing other ortho-substituents in place of the ortho-methoxyl group were examined. With ortho-methyl and ethyl groups (1r–s), low enantioselectivies were obtained in spite of excellent yields. In particular, the ethyl group has a similar size to the methoxyl group, but does not provide hydrogen bonding interactions. The dramatically low ee (17% ee) for this case provided strong evidence that steric hindrance is not key to the excellent asymmetric induction for 1a. Furthermore, substrate 1t (with ortho-OiPr) also provided a lower ee (72% ee) than 1a. These results suggested that it is the hydrogen bonding interaction with the ortho-directing group, not the steric or electronic effect, that leads to the excellent enantiocontrol in the standard protocol.8
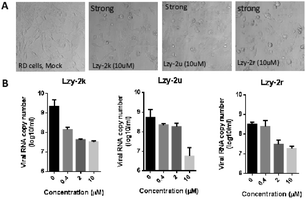
We also randomly selected a few of our products to test their potential antiviral activities in Rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cells, which are commonly used to investigate enterovirus A71 (EV-A71) infections. Our compounds showed relatively high CC50 measured by MTT assay, indicating low cell toxicity (Table 3). Their protection from cytopathic effects (CPE) from EV-A71 infection was then studied. EV-A71 infection could cause strong CPE and cell death. However, almost complete CPE protection was observed when these cells were treated with our products at 10 μM concentration (Fig. 1). Quantitation of viral genome RNA in the secreted virions showed potent inhibition of virus replication with IC50 ranging from 0.20 to 1.24 μM, indicating a high selectivity index (Table 3). The virus yield was reduced by 121.6, 89.7, and 16.9 fold upon treatment of 2k, 2u and 2r, respectively. These results clearly indicated the great potential of these compounds as antiviral agents.
| Compound | CC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | Selectivity indexb |
|---|---|---|---|
| a CC50, 50% cytotoxic concentration measured by viability assay (without virus infection); IC50, the viral RNA copies were reduced by 50% compared with the control (without compound treatment) in the secreted virions. b A selectivity index (CC50/IC50) of >10 is considered to have good potential for drug development. | |||
| 2k | 29.3 | 0.20 | 148.5 |
| 2u | 33.2 | 0.24 | 138.3 |
| 2r | 28.2 | 1.24 | 22.7 |
In conclusion, we have developed the first catalytic asymmetric formal cross dehydrogenative coupling for the efficient synthesis of enantioenriched chiral tetraarylmethanes, a family of challenging molecules to synthesize. Enabled by a one-pot oxidation and nucleophilic addition protocol, the intermolecular C–C bond was efficiently forged from two C–H bonds with high enantioselectivity under mild conditions, which benefitted from successful understanding and addressing the key compatibility issue between the DDQ oxidant and resulting DDQH2 with the catalytic asymmetric system. Finally, these new products have been demonstrated as promising antiviral agents.
Data availability
Details of experimental procedures, characterizations, and copy of NMR spectra as well as HPLC traces are provided in the ESI.†Author contributions
Z. L. and X. L. performed the synthetic experiments and wrote the paper. Y. L. and M. W. performed the antiviral experiments. M. H. directed the antiviral study and wrote the paper. J. S. conceived and directed this work and wrote the paper. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91956114 and 81671995), the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (16302617, 16302318, and 16303420) and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee (JCYJ20170818113708560, JCYJ20180507181627057, and JCYJ20200109141408054). We thank Dr. Herman H. Y. Sung for help with structure elucidation.References
- Reviews of CDC reactions: (a) C.-J. Li, Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, 42, 335–344 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. S. Yeung and V. M. Dong, Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 1215–1292 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. A. Girard, T. Knauber and C.-J. Li, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 74–100 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Selected examples of catalytic asymmetric formal CDCs for the synthesis of 1,1-diarylalkanes: (a) H. Wu, Y.-P. He, L. Xu, D.-Y. Zhang and L.-Z. Gong, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 3466–3469 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. Guo, J. Song, S.-W. Luo and L.-Z. Gong, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 5558–5562 CrossRef CAS; (c) E. Larionov, M. M. Mastandrea and M. A. Pericàs, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 7008–7013 CrossRef CAS; (d) F. Benfatti, M. G. Capdevila, L. Zoli, E. Benedetto and P. G. Cozzi, Chem. Commun., 2009, 5919–5921 RSC.
- Z. Wang, Y. Zhu, X. Pan, G. Wang and L. Liu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 3053–3057 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For reviews (a and b) and selected examples (c–j) of asymmetric synthesis of chiral triarylmethanes: (a) M. Nambo and C. M. Crudden, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 4734–4742 CrossRef CAS; (b) R. Kshatriya, V. P. Jejurkar and S. Saha, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2019, 3818–3841 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. Mondal, D. Roy and G. Panda, ChemCatChem, 2018, 10, 1941–1967 CrossRef CAS; (d) S. C. Matthew, B. W. Glasspoole, P. Eisenberger and C. M. Crudden, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 5828–5831 CrossRef CAS; (e) Y. Huang and T. Hayashi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 7556–7559 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) T. Pan, P. Shi, B. Chen, D.-G. Zhou, Y.-L. Zeng, W.-D. Chu, L. He, Q.-Z. Liu and C.-A. Fan, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 6397–6402 CrossRef PubMed; (g) B.-F. Shi, N. Maugel, Y.-H. Zhang and J.-Q. Yu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 4882–4886 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) Y. Lou, P. Cao, T. Jia, Y. Zhang, M. Wang and J. Liao, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 12134–12138 CrossRef CAS; (i) S. Saha, S. K. Alamsetti and C. Schneider, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 1461–1464 RSC; (j) J. H. Kim, S. Greßies, M. Boultadakis-Arapinis, C. Daniliuc and F. Glorius, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 7652–7656 CrossRef CAS; (k) M. R. Franklin, Biochem. Pharmacol., 1993, 46, 683–689 CrossRef CAS.
- Construction of quaternary stereocenters is a longstanding challenge in organic synthesis, for selected reviews: (a) K. Quasdorf and W. L. E. Overman, Nature, 2014, 516, 181–191 CrossRef CAS; (b) J. Prakash and I. Marek, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 4593–4623 RSC.
- For selected recent examples of racemic or achiral synthesis of tetraarylmethanes: (a) M. Nambo, M. Yar, J. D. Smith and C. M. Crudden, Org. Lett., 2015, 17, 50–53 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. Nambo, J. C.-H. Yim, K. G. Gowler and C. M. Crudden, Synlett, 2017, 28, 2936–2940 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. Zhang, B.-S. Kim, C. Wu, J. Mao and P. J. Walsh, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 14641–14648 CrossRef; (d) D. Roy and G. Panda, Tetrahedron, 2018, 74, 6270–6277 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Tsuchida, Y. Senda, K. Nakajima and Y. Nishibayashi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 9728–9732 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, M. Duan, Z. Deng, Q. Shao, M. Chen, G. Zhu, K. N. Houk and J. Sun, Nat. Catal., 2020, 3, 1010–1019 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) Z. Wang, F. Ai, Z. Wang, W. Zhao, G. Zhu, Z. Lin and J. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 383–389 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Z. Wang, Y. F. Wong and J. Sun, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 13711–13714 CrossRef CAS; (c) Y. F. Wong, Z. Wang and J. Sun, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016, 14, 5751–5754 RSC; (d) D. Qian, L. Wu, Z. Lin and J. Sun, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 567 CrossRef PubMed; (e) J. Yan, M. Chen, H. H.-Y. Sung, I. D. Williams and J. Sun, Chem.–Asian J., 2018, 13, 2440–2444 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Reviews of asymmetric reactions of quinone methides: (a) Z. Wang and J. Sun, Synthesis, 2015, 47, 3629–3644 CrossRef; (b) W. Li, X. Xu, P. Zhang and P. Li, Chem.–Asian J., 2018, 13, 2350–2359 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For examples of in situ oxidative generation of QMs for asymmetric synthesis: (a) K. Gebauer, F. Reuß, M. Spanka and C. Schneider, Org. Lett., 2017, 19, 4588–4591 CrossRef CAS; (b) Y. Mao, Z. Wang, G. Wang, R. Zhao, L. Kan, X. Pan and L. Liu, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 7785–7791 CrossRef CAS.
- Pioneering studies and recent reviews of CPA-related catalysis: (a) T. Akiyama, J. Itoh, J. K. Yokota and K. Fuchibe, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 1566–1568 CrossRef CAS; (b) D. Uraguchi and M. Terada, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 5356–5357 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) D. Parmar, E. Sugiono, S. Raja and M. Rueping, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 9047–9153 CrossRef CAS; (d) T. Akiyama and K. Mori, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 9277–9306 CrossRef CAS; (e) T. James, M. van Gemmeren and B. List, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 9388–9409 CrossRef CAS.
- Selected early examples of asymmetric reactions of QMs catalyzed by chiral phosphoric acids: (a) O. El-Sepelgy, S. Haseloff, S. K. Alamsetti and C. Schneider, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 7923–7927 CrossRef CAS; (b) C.-C. Hsiao, H.-H. Liao and M. Rueping, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 13258–13263 CrossRef CAS; (c) Z. Wang, Y. F. Wong and J. Sun, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 13711–13714 CrossRef CAS; (d) J.-J. Zhao, S.-B. Sun, S.-H. He, Q. Wu and F. Shi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 5460–5464 CrossRef CAS; (e) Y. Xie and B. List, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 4936–4940 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) While it is unclear how DDQ influences the enantiocontrol, its interference with the hydrogen bond network in the enantiodetermining transition state might be a possible reason.; (b) DDQH2 was also tested as an additive, but it was not soluble and did not influence the enantioselectivity..
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d1sc03324g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |