Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Capture and selective release of multiple types of circulating tumor cells using smart DNAzyme probes†
Qianying
Zhang‡
 a,
Wenjing
Wang‡
a,
Wenjing
Wang‡
 c,
Shan
Huang
a,
Sha
Yu
a,
Tingting
Tan
d,
Jian-Rong
Zhang
c,
Shan
Huang
a,
Sha
Yu
a,
Tingting
Tan
d,
Jian-Rong
Zhang
 *ab and
Jun-Jie
Zhu
*ab and
Jun-Jie
Zhu
 *a
*a
aState Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China. E-mail: jrzhang@nju.edu.cn; jjzhu@nju.edu.cn
bSchool of Chemistry and Life Science, Nanjing University Jinling College, Nanjing 210089, China
cState Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Science, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
dDepartment of Laboratory Medicine, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, 210008, China
First published on 9th January 2020
Abstract
The effective capture, release and reanalysis of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are of great significance to acquire tumor information and promote the progress of tumor therapy. Particularly, the selective release of multiple types of CTCs is critical to further study; however, it is still a great challenge. To meet this challenge, we designed a smart DNAzyme probe-based platform. By combining multiple targeting aptamers and multiple metal ion responsive DNAzymes, efficient capture and selective release of multiple types CTCs were realized. Sgc8c aptamer integrated Cu2+-dependent DNAzyme and TD05 aptamer integrated Mg2+-dependent DNAzyme can capture CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells respectively on the substrate. With the addition of Cu2+ or Mg2+, CCRF-CEM cells or Ramos cells will be released from the substrate with specific selectivity. Furthermore, our platform has been successfully demonstrated in the whole blood sample. Therefore, our capture/release platform will benefit research on the molecular analysis of CTCs after release and has great potential for cancer diagnosis and individualized treatment.
Introduction
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are a class of cancer cells present in peripheral blood which cast off from the primary tumor into peripheral blood.1,2 The detection and isolation of CTCs are of vital importance for the early diagnosis of cancer, monitoring of therapeutic efficacy and evaluation of treatment.3–6 Since the amount of CTCs is extremely exiguous in patients' blood,7–9 there is an imperative demand to capture and enrich CTCs with high efficiency accordingly. In the last few years, multitudinous systems have been reported for the separation and enrichment of CTCs such as magnetic isolation technology,10–13 microfluidic technology14–17 and flow cytometry.18,19 Most of the above methods relied on a single CTC marker to capture CTC. Considering that the expression of biomarkers on the surface of CTCs would change after CTCs undergo epithelial–mesenchymal transition, a single marker-based methodology is deficient to capture all CTCs in real blood samples, hindering further clinical studies.20–23 To meet this challenge, platforms that are able to capture and identify multiple types of CTCs based on multiple surface markers are highly desired and under rapid development.24,25Aptamers are a class of functional nucleic acid molecules, which can bind a range of targets specifically, such as proteins and intact cancer cells, after forming a unique tertiary structure.26,27 Aptamers are more friendly to prepare and easy to modify due to the simple chemical structure and excellent stability.28,29 In view of these advantages, aptamers have been extensively applied to biosensing and drug-delivery therapeutics.30–35 Besides, aptamers have also been used for CTC capture and exhibit excellent capture efficiency.24,25,36
In addition to CTC capture, the following release step is also critical, because it enables further molecular characterization studies of CTCs to be performed to obtain important information of the primary tumor, which promotes the progress of individualized therapies of tumors.14,37 Methods employed to release CTCs include nuclease release,24,38,39 photothermal release,40–42 electrochemical release,43,44 enzymatic release,45 magnetic release46 or mechanosensitive release;47 however, selective release of multiple CTCs has not been reported. Considering that the cultivation and reanalysis of released CTCs are significant, it is necessary to realize the selective release of multiple CTCs captured.
DNAzymes are functional nucleic acid molecules with catalytic properties produced by in vitro selection.48–53 Based on the specific properties of recognizing metal ions and undergoing catalytic reactions of nucleic acid cleavage, DNAzymes have been widely used as sensor elements for metal ion sensing and as a cyclic signal amplification tool for biomarker identification both in vitro and in vivo.54–61 Furthermore, DNAzymes have been utilized as gate keepers to realize the encapsulation and release of molecules.62–64 Inspired by these studies, we speculate that DNAzymes can be used for selective release of multiple types of CTCs assisted by metal ions.
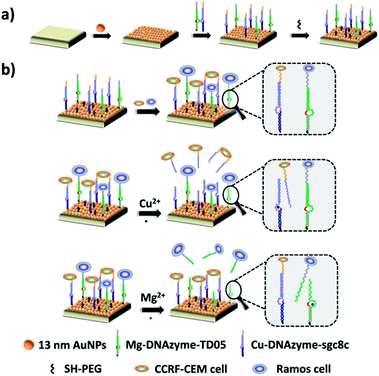
Herein, we established a platform to capture and selectively release multiple CTCs efficiently based on smart DNAzyme probes, as illustrated in Fig. 1. In our study, we used CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells as the model cells. The Sgc8c aptamer was chosen to capture CCRF-CEM cells, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cell line, while the TD05 aptamer was used to bind Ramos cells which refer to a human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line.65,66 The capture element for CCRF-CEM cells (Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c) was composed of the Cu2+-dependent DNAzyme strands and the substrate strands integrated with sgc8c aptamers. Similarly, the capture element for Ramos cells (Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05) was composed of the Mg2+-dependent DNAzyme strands and the substrate strands integrated with TD05 aptamers. CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells can be captured by sgc8c aptamers and TD05 aptamers, respectively. The addition of Cu2+ as the cofactor catalyzed the cleavage of the substrate strands of Cu2+-dependent DNAzyme, releasing CCRF-CEM cells. Similarly, the addition of Mg2+ as the cofactor catalyzed the cleavage of substrate strands of Mg2+-dependent DNAzyme, releasing Ramos cells. Consequently, this platform realizes the capture of multiple CTCs by multiple aptamers, as well as the selective release of CTCs with the addition of Cu2+ or Mg2+.
Results and discussion
Principle of the capture/release platform
The principle of our strategy to capture and selectively release multiple CTCs is shown in Fig. 1. The substrate was first modified with AuNPs, which provided more attachment sites for the capture element than the flat gold substrate. Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c and Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 were modified to capture CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells respectively. As shown in Fig. 1b, after CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells were captured, Cu2+ was used to trigger the Cu2+-dependent DNAzyme strands to catalyze the cleavage of the substrate strands to release CCRF-CEM cells, while Ramos cells cannot be released. Correspondingly, when Mg2+ was used to trigger the Mg2+-dependent DNAzyme strands to catalyze the cleavage of the substrate strands, only Ramos cells were released from the substrate. In the samples containing both CTCs and even in blood samples, our platform can capture multiple CTCs efficiently. The two captured CTCs can be released from the substrate selectively after the addition of Cu2+ or Mg2+. Compared with the methods using anti-EPCAM antibody as a single marker11,14,40,47 (Table S1†), our method can simultaneously capture multiple CTCs in blood samples, avoiding the incomplete capture due to change of CTCs' surface biomarkers after epithelial–mesenchymal transition. In addition, compared with the method to capture multiple CTCs using multiple aptamers as markers24,25 (Table S1†), selective release of multiple CTCs was achieved which makes multiple CTC typing possible and more valuable downstream molecular information of CTCs can be obtained. Our method not only captures CTCs in the blood more efficiently, but selectively releases multiple CTCs to facilitate further downstream molecular analysis of CTCs.Fabrication and characterization of the capture platform
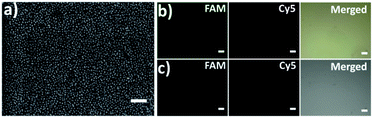
The capture platform was fabricated as shown in Fig. 1a. The AuNPs with a diameter of 13 nm were used as the supporting substrate because it can provide anchoring sites for the capture element through Au–S chemistry and has good biocompatibility for cells. The 13 nm AuNPs were fixed on the amino group modified glass surface via Au–N interaction and the modification was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). As shown in Fig. 2a, the 13 nm AuNPs were distributed uniformly and densely on the substrate. After the decoration of AuNPs on the substrate, the capture elements of Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c and Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 were immobilized on the substrate through Au–S bonds. We modified the substrate strands of Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c with FAM at the 5′ end and the substrate strands of Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 with Cy5 at the 3′ end. It can be seen that after immobilization of the thiol-modified capture elements, FAM and Cy5 fluorescence were emitted on the substrate (Fig. 2b) and when the capture elements without an –SH group were used, there was negligible fluorescence on the substrate (Fig. 2c), which suggested the successful modification of the capture elements. In order to prevent nonspecific adsorption, the substrate was further blocked with SH-PEG.44,67Cleavage verification by metal ions on the substrate
The selective release of multiple CTCs was realized via the catalytic cleavage of DNAzymes with metal ions as cofactors in our study. To verify the feasibility, gel electrophoresis was conducted to characterize this mechanism (Fig. S1†). We adopted 4 μM Cu2+ and 10 mM Mg2+ to catalyze the cleavage of the capture elements according to previous reports.68,69 As shown in Lane 2, the product of 4 μM Cu2+ catalyzed Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c probes migrated faster than Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c alone (Lane 1), indicating the successful cleavage of DNAzyme probes. Similarly, the product of 10 mM Mg2+ catalyzed Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 probes (Lane 4) migrated faster than Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 alone (Lane 3). The result demonstrates that Cu2+ and Mg2+ can be potent tools for the release of CTCs.Cell capture study
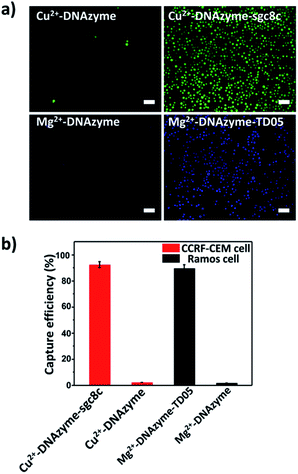
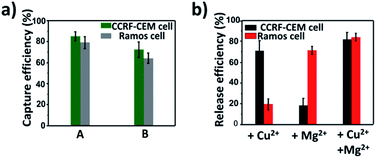
To explore the capture performance of our platform, we used CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells as the target cell lines. First, we studied the single cell type capture ability of our proposed capture platform. We prepared the Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c modified substrate and the Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 modified substrate respectively. The Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c modified substrate was incubated with CCRF-CEM cells and the Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 modified substrate was incubated with Ramos cells. In order to observe the cells clearly, CCRF-CEM cells were stained with calcein AM for 10 min while Ramos cells were stained with DAPI 15 min after incubation. As shown in Fig. 3a, the substrate without sgc8c aptamer or TD05 aptamer modification showed negligible capture of the corresponding CTCs compared to that of aptamer-containing element modified substrates. The large view of capture is shown in Fig. S2.† To optimize the capture ability of the platform, we investigated the capture time and concentration of the capture elements. As illustrated in Fig. S3,† with the increase of incubation time, the number of CTCs captured by the two capture elements all increased and reached saturation at 30 min. When the concentration of the two capture elements increased, the capture efficiency of Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c for CCRF-CEM cells and Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 for Ramos cells all increased from 0.1 to 1 μM and reached a maximum at 1 μM (Fig. S4†). The capture efficiency of Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c for CCRF-CEM cells was calculated to be 92 ± 2.4% within 30 min and the capture efficiency of Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 for Ramos cells was calculated to be 89 ± 2.8% within 30 min (Fig. 3b). In addition, the selectivity of the capture elements for CTCs was investigated. As shown in Fig. S5a,† the number of Ramos cells captured by Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c is much less than that captured by Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05. Meanwhile, the number of CCRF-CEM cells captured by Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 is much less than that captured by Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c. Moreover, we chose K562 cells which have little binding affinity to the sgc8c aptamer and TD05 aptamer to further confirm the specificity of the two capture elements. As shown in Fig. S5b,† Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c and Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 had almost no capture capability to K562 cells. Based on the above results, the binding capability between Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c and CCRF-CEM cells and Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 and Ramos cells was demonstrated to be specific.Cell release study
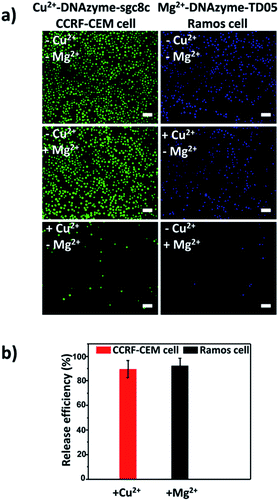
Having successfully demonstrated the specific capture, we further testified the cell release capability of our proposed platform. After the capture of CCRF-CEM cells by the Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c modified substrate, Cu2+ was added and incubated for 30 min to release CCRF-CEM cells. It can be observed that most CCRF-CEM cells were released from the substrate (Fig. 4a). In contrast, without the addition of Cu2+ or with the addition of Mg2+, only a negligible amount of CCRF-CEM cells were released from the substrate (Fig. 4a). Similarly, after the capture of Ramos cells by the Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 modified substrate, Mg2+ was added for 30 min to release Ramos cells. It can be concluded that most Ramos cells were released from the substrate only after the addition of Mg2+ (Fig. 4a). In contrast, the control samples, either without the addition of Mg2+ or with the addition of Cu2+, showed negligible Ramos cell release from the substrate (Fig. 4a). The large view of cell release is shown in Fig. S6.† Therefore, Cu2+ and Mg2+ as triggers can release CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells selectively. In order to obtain more effective release, we optimized the incubation time for the two metal ions to release the two CTCs.As shown in Fig. S7,† with the increase of the incubation time of Cu2+, the release efficiency of CCRF-CEM cells increased and reached the maximum (89 ± 6.8%) (Fig. 4b) at 30 min and with the increase of the incubation time of Mg2+, the release efficiency of Ramos cells increased and reached the maximum (92 ± 6.2%) (Fig. 4b) at 50 min. Consequently, 30 min was chosen for Cu2+ to release CCRF-CEM cells, while 50 min was chosen for Mg2+ to release Ramos cells.
Capture and selective release of multiple CTCs
After corroborating the ability of our proposed platform for the capture and selective release of the two CTCs respectively, we modified Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c and Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05 on the same substrate to study simultaneous capture and selective release of multiple CTCs. We employed the optimal capture and release conditions that are illustrated in Fig. S3, S4 and S7.† CCRF-CEM cells were pre-dyed with calcein AM for 10 min and Ramos cells were pre-dyed with DiI for 30 min. The whole process of capture and release took time that DiI was chosen which had less cytotoxicity than DAPI. As shown in Fig. 5, CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells can be captured on the substrate efficiently before the addition of metal ions. When only Cu2+ was added, the majority of CCRF-CEM cells were released, while Ramos cells were rarely released. Similarly, when only Mg2+ was added, nearly all Ramos cells were released completely, leaving most of the CCRF-CEM cells on the substrate. In the presence of Cu2+ and Mg2+, nearly all of CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells were released from the substrate. The capture and selective release of two types of CTCs in large view are shown in Fig. S8.† Based on the above results, we can conclude that our design not only achieves the efficient capture of multiple CTCs, but also selective releases the CTCs, which was worthwhile for the subsequent study.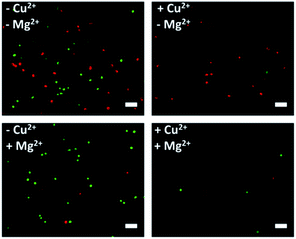 | ||
| Fig. 5 Fluorescence images of multiple CTCs after capture and selective release. The CCRF-CEM cells pre-stained with calcein AM (green) and Ramos cells pre-stained with DiI (red). Scale bars: 50 μm. | ||
Cytotoxicity of metal ions and the cell viability after release
To study the influence of metal ions on the cell viability, MTT assay was conducted. According to Fig. S9a and b,† it is clear that the viability of both CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells was maintained under 4 μM Cu2+ and 10 mM Mg2+, which was used to release CTCs, indicating that the concentration of Cu2+ and Mg2+ used in the release experiment had good biocompatibility. After the successful release of CTCs by metal ions, we explored the viability of released CTCs with live/dead cell staining with calcein AM and propidium iodide (PI). As shown in Fig. S9c and d,† almost 80% of the released CCRF-CEM cells and 90% of the released Ramos cells all showed good viability, which was essential for subsequent research of CTCs.CTC capture and release in simulated blood samples
On the basis of the above results, calcein AM-stained CCRF-CEM cells and DiI-stained Ramos cells were mixed with a buffy coat layer of healthy human blood sample at a concentration of 103 cells per mL to 102 cells per mL to investigate the practicality of our strategy in mimic clinical samples. We used a buffy coat layer of healthy human blood sample because CTCs were in the buffy coat layer and the interference of erythrocyte and most non-specific proteins in the blood sample could be avoided.70–72 As shown in Fig. 6a, when 103 CCRF-CEM cells and 103 Ramos cells were spiked into 1 mL healthy human blood, the capture efficiency using our platform was 85 ± 4.1% for CCRF-CEM cells and 79 ± 5.9% for Ramos cells respectively. In the case of 102 CCRF-CEM cells and 102 Ramos cells in 1 mL healthy human blood, 72 ± 7.5% of CCRF-CEM cells were captured and 64 ± 4.8% of Ramos cells were captured. The capture efficiency of CTCs slightly decreased as the number of CTCs in the blood reduced, which was consistent with previous reports.44,73 Besides, by means of the modification of SH-PEG, the adhesion of the blood cells on the substrate was little during the capture of CTCs (Fig. S10†). To further confirm that the captured cancer cells were CTCs, we subjected the captured CCRF-CEM cells (pre-stained with DiI) and Ramos cells (pre-stained with Calcein AM) to immunofluorescence staining with FITC-labelled anti-CD3 (a marker for T cells) and APC-labelled anti-CD19 (a marker for B cells).24 As shown in Fig. S11,† DiI-stained CCRF-CEM cells showed positive for CD3 and calcein AM-stained Ramos cells showed positive for CD19, which suggested that the captured cancer cells were CTCs. These results clearly demonstrate that our capture platform can capture CTCs efficiently even in a whole blood sample, which is a relatively complex system.Furthermore, we testified the selective release of CTCs through the addition of metal ions followed by the capture of two CTCs in a blood sample. As depicted in Fig. 6b, only in the presence of Cu2+, the release efficiency of CCRF-CEM cells was 71 ± 9.9% and the release efficiency of Ramos cells was 19 ± 5.3%. When only Mg2+ was added, the release efficiency of Ramos cells was 72 ± 3.9% and the release efficiency of CCRF-CEM cells was 18 ± 7.2%. The release of Ramos cells with the addition of Cu2+ and CCRF-CEM cells with the addition of Mg2+ came from the inevitable non-specific release caused by D-PBS flushing. In the presence of Cu2+ and Mg2+, the release efficiency was 82 ± 6.5% for CCRF-CEM cells and 85 ± 3.7% for Ramos cells respectively. These results confirmed that our work can not only provide a method to capture multiple CTCs adequately even in the blood samples but also to release CTCs selectively with high efficiency for further study.
CTC isolation from cancer patients' blood samples
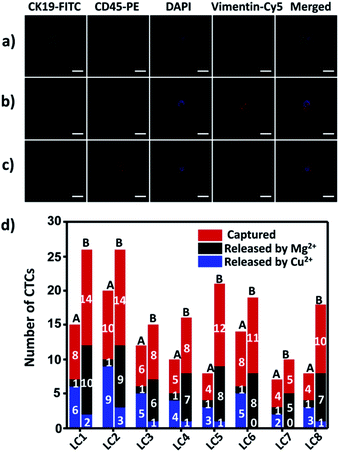
To demonstrate the suitability of our method for real clinical samples, we replaced the Sgc8c aptamer and the TD05 aptamer with the Lc-17 aptamer and the AP-1 aptamer to target two CTCs with abnormal expression of vimentin and with abnormal expression of cytokeratin (CK) respectively in lung cancer patients.38,74–76 After CTCs were captured by our platform, Cu2+ and Mg2+ were added to release CTCs successively. The released CTCs by Cu2+ or Mg2+ and unreleased CTCs were collected separately for immunofluorescence staining. As shown in Fig. 7a–c, there were vimentin-positive CTCs and CK19-positive CTCs and CD45-positive WBCs which were non-specifically captured simultaneously in a lung cancer patient blood sample. We calculated CTCs that were only positive for vimentin and CTCs that were only positive for CK19. The results summarized from 8 lung cancer patient blood samples are provided in Fig. 7d, which indicated that our strategy could perform well in real clinical samples.Experimental
Materials
All the oligonucleotides were provided by Sangon Biotechnology Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and all the sequences are shown in Table S2.† (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES) and tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride (TCEP) were purchased from Aladdin Reagent Co., Ltd. (China). BSA was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (USA). 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT), DAPI and DiI were purchased from KeyGEN BioTECH Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). Calcein AM and propidium iodide (PI) were bought from Dojindo Molecular Technologies. SH-PEG (molecular weight: 1000) was provided by Yare Biotech, Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). APC-labeled mouse anti-human CD19 (CD19-APC), FITC-labeled mouse anti-human CD3 (CD3-FITC), PE-labeled mouse anti-human CD45 (CD45-PE), mouse anti-cytokeratin 19 antibody (CK19), FITC-labeled goat anti-mouse lgG antibody, rabbit anti-vimentin antibody and Cy5-labeled goat anti-rabbit lgG antibody were purchased from Bioss (Beijing, China). Ultrapure water was used in all experiments. All chemicals were of analytical grade and used without any further purification. All experiments using human samples were performed in accordance with the Guidelines of “the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki Principles” and experiments were approved by the Ethical Committee of Medical Research, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School. Informed consents were obtained from human participants of this study.Instrumentation
Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) images were obtained on a Hitachi S-4800 scanning electron microscope (Hitachi Co., Japan). The fluorescence images were recorded on a fluorescence inversion microscope system (Nikon, TI-U). Confocal images were obtained from confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) on a Leica TCS SP8 confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems Inc., Exton, PA). The cell number was counted with a Petroff-Hausser cell counter (USA). Cell viability assay was performed on a Varioskan Flash microplate reader (ThermoFisher Scientific).Preparation of the substrate
4 mm × 4 mm glass slides were used as the substrate. First, the glass slides were immersed in piranha solution for 12 h and then rinsed with plenty of Milli-Q water. After drying with nitrogen, the glass slides were soaked in 0.5% (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES) solution for 10 h and rinsed with ethanol and Milli-Q water successively. Finally, the glass slides were grilled in a vacuum drying oven for 2 h.Fabrication of the capture platform
AuNPs with a diameter of 13 nm were prepared according to a reported method previously.77 The aminated substrate was incubated with the solution of 13 nm AuNPs for 2 hour at room temperature. Then the resulting substrate was washed with Milli-Q water and D-PBS successively. The thiolated DNAzyme strand was activated with TCEP at a molar ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 100 for 1 hour at room temperature and then mixed with the substrate strand at a molar ratio of 1
100 for 1 hour at room temperature and then mixed with the substrate strand at a molar ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 in buffer A or buffer B. Buffer A (1.5 M NaCl, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.0) was used for Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c and buffer B (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5) was used for Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05. After annealing, 80 μL of different concentrations of the mixture of the DNAzyme strand and substrate strand was incubated with the AuNP modified substrate for 2 hour at room temperature. After washing with D-PBS, the obtained substrate was incubated with 200 μL of 5 μM SH-PEG (molecular weight: 1000) for 1 hour at room temperature to block the residual nonspecific binding sites. After incubation for 1 hour, the obtained substrate was rinsed with D-PBS and employed as the capture platform. The capture elements modified with FAM or Cy5 should be protected from light during the modification process.
1 in buffer A or buffer B. Buffer A (1.5 M NaCl, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.0) was used for Cu2+-DNAzyme-sgc8c and buffer B (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5) was used for Mg2+-DNAzyme-TD05. After annealing, 80 μL of different concentrations of the mixture of the DNAzyme strand and substrate strand was incubated with the AuNP modified substrate for 2 hour at room temperature. After washing with D-PBS, the obtained substrate was incubated with 200 μL of 5 μM SH-PEG (molecular weight: 1000) for 1 hour at room temperature to block the residual nonspecific binding sites. After incubation for 1 hour, the obtained substrate was rinsed with D-PBS and employed as the capture platform. The capture elements modified with FAM or Cy5 should be protected from light during the modification process.
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
The metal ions could cleave the corresponding capture DNA, which was verified using 12% polyacrylamide gel. 10 μL of 1 μM sample was loaded onto 12% polyacrylamide gel for electrophoresis at 150 V for 45 min in 1× TBE buffer. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide and imaged with a fluorescence gel imaging system.Cell culture
Ramos cells, CCRF-CEM cells and K-562 cells were all obtained from KeyGen Biotech. Co. Ltd. (Nanjing, China). They were all cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 medium (KeyGen Biotech. Co. Ltd Nanjing, China) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (Gibco, Grand Island, NY), penicillin (100 μg mL−1) and streptomycin (100 μg mL−1) in an incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C).Cell capture
Before experiments, cells were distributed in the binding buffer (1 mg mL−1 BSA, 4.5 g L−1 glucose in D-PBS) and diluted to a concentration of 1 × 106 cells per mL. Then, cell suspensions (200 μL, 1 × 106 cells per mL) were incubated with the capture platform in an incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C) for different times. The surface of the substrate was rinsed with D-PBS gently to remove the unbound cells. CCRF-CEM cells were stained with calcein AM for 10 min while Ramos cells were stained with DAPI 15 min in an incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C). The capture results of CTCs were viewed using an inverted fluorescence microscope system. For the capture of CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells simultaneously, 200 μL of 1 × 106 cells per mL CCRF-CEM cells pre-dyed with calcein AM and Ramos cells pre-dyed with DiI were incubated with the capture platform in an incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C) for 30 min.Selective cell release by metal ions
To release the CCRF-CEM cells or Ramos cells, 4 μM Cu2+ and 50 μM ascorbate or 10 mM Mg2+ was added to the corresponding capture platform for different times in an incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C). After release, the substrate was gently washed with D-PBS for 20 s to remove the released cells and the metal ions. For the release of the two CTCs respectively, CCRF-CEM cells were stained with calcein AM for 10 min while Ramos cells were stained with DAPI 15 min finally. For the selective release of CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells simultaneously, CCRF-CEM cells were pre-dyed with calcein AM for 10 min and Ramos cells were pre-dyed with DiI for 30 min. The release results of CTCs were viewed using an inverted fluorescence microscope system.Statistics of capture efficiency and release efficiency
For calculating the capture efficiency and release efficiency, the 4 mm × 4 mm substrate was controlled using a PDMS film to complete capture and release according to the abovementioned method. The numbers of cells captured and released was counted using an inverted fluorescence microscope system.Cytotoxicity of metal ions and the cell viability after release
The cytotoxicity of metal ions was assessed using a 3-(4,5)-dimethylthiahiazo(-z-y1)-3,5-diphenytetrazoliumromide (MTT) assay using CCRF-CEM cells and Ramos cells. In short, the CCRF-CEM cells or Ramos cells (100 μL, 1 × 105 cells per mL) were seeded into a 96-well cell-culture plate, followed by the incubation of metal ions at an appropriate concentration. Then the cells were cultured for 24 h in an incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C). After discarding the supernatant by centrifugation, 100 μL of MTT (0.5 mg mL−1) was added to each well and incubated for 4 h. After 4 h, the supernatant was removed by centrifugation, and 100 μL DMSO was added to each well. Then the optical density (OD) was read at a wavelength of 490 nm. Relative cell viability was expressed as follows: % = ([OD]test/[OD]control) × 100. The viability of the released cells was assayed with live/dead cell staining with calcein AM and propidium iodide (PI). 2 μM calcein AM and 4 μM PI were incubated with the released cells for 15 min in an incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C). And then the cells were observed using an inverted fluorescence microscope system.CTC capture and release in blood samples
The buffy coat layer of the blood sample was collected carefully. After centrifugation at 450g for 10 min, the supernatant was discarded. The sediment was resuspended in 10 volumes of ACK lysis buffer (150 mM NH4Cl, 10 mM KHCO3, 0.1 mM EDTA) and incubated at 4 °C for 10 min to remove the erythrocytes. Then the mixture was centrifuged for another 10 minutes, and the cell pellets were collected carefully and resuspended in the original volume of the binding buffer. Mimic clinical samples were obtained by mixing CCRF-CEM cells pre-dyed with calcein AM and Ramos cells pre-dyed with DiI with pretreated blood sample at 103 cells per mL or 102 cells per mL. And the mimic clinical samples or cancer patient samples were incubated with the 4 mm × 4 mm capture platform controlled with a PDMS film for 30 min in an incubator (5% CO2, 37 °C). The capture results of CTCs were viewed using an inverted fluorescence microscope system. The release process followed the method mentioned earlier.Immunofluorescence staining
Cells collected in 96-well plates were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature. After washing with PBS three times by centrifugation at 2300 rpm for 10 min, the cells were blocked in D-PBS containing 5% FCS for 30 min at room temperature and washed three times with D-PBS. Then the cells were incubated with the primary antibody overnight at 4 °C. For primary antibodies with the fluorophore conjugated, the cells were washed three times with D-PBS and viewed by confocal microscopy imaging. For primary antibodies without the fluorophore conjugated, the cells were incubated with secondary antibodies for 2 h at room temperature after washing with PBS three times. Then the cells were viewed by confocal microscopy imaging after washing with D-PBS three times.Conclusions
In summary, we have reported a strategy to realize the capture and selective release of multiple CTCs using smart metal ion responsive DNAzymes probes. Our capture platform can capture multiple CTCs simultaneously with approximately 90% efficiency in buffer and with 80% efficiency in the blood sample. In addition, compared with the methods reported to capture multiple CTCs, we utilized metal ions to release CTCs that are not only more economical. Meanwhile it can achieve selective release of multiple CTCs captured with the potential to obtain downstream molecular information of a specific CTC. It has great potential to promote the development of individualized treatment of cancer.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21834004 and 21775067), the International Cooperation Foundation from Ministry of Science and Technology (2016YFE0130100), and the open research fund from State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science (Grant SKLACLS1904).Notes and references
- S. K. Arya, B. Lim and A. R. A. Rahman, Lab Chip, 2013, 13, 1995–2027 RSC.
- K. Pantel, R. H. Brakenhoff and B. Brandt, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2008, 8, 329 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. B. Smerage and D. F. Hayes, Br. J. Cancer, 2006, 94, 8–12 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Cristofanilli, G. T. Budd, M. J. Ellis, A. Stopeck, J. Matera, M. C. Miller, J. M. Reuben, G. V. Doyle, W. J. Allard, L. W. M. M. Terstappen and D. F. Hayes, N. Engl. J. Med., 2004, 351, 781–791 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. Liu, P. G. Shields, R. D. Warren, P. Cohen, M. Wilkinson, Y. L. Ottaviano, S. B. Rao, J. Eng-Wong, F. Seillier-Moiseiwitsch, A.-M. Noone and C. Isaacs, J. Clin. Oncol., 2009, 27, 5153–5159 CrossRef.
- S. Mao, Q. Zhang, H. Li, W. Zhang, Q. Huang, M. Khan and J.-M. Lin, Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 7694–7699 RSC.
- W. J. Allard, J. Matera, M. C. Miller, M. Repollet, M. C. Connelly, C. Rao, A. G. J. Tibbe, J. W. Uhr and L. W. M. M. Terstappen, Clin. Cancer Res., 2004, 10, 6897–6904 CrossRef.
- E. Racila, D. Euhus, A. J. Weiss, C. Rao, J. McConnell, L. W. M. M. Terstappen and J. W. Uhr, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1998, 95, 4589–4594 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Wang, H. Wang, J. Jiao, K.-J. Chen, G. E. Owens, K.-i. Kamei, J. Sun, D. J. Sherman, C. P. Behrenbruch, H. Wu and H.-R. Tseng, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 8970–8973 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C.-H. Wu, Y.-Y. Huang, P. Chen, K. Hoshino, H. Liu, E. P. Frenkel, J. X. J. Zhang and K. V. Sokolov, ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 8816–8823 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C.-Y. Wen, L.-L. Wu, Z.-L. Zhang, Y.-L. Liu, S.-Z. Wei, J. Hu, M. Tang, E.-Z. Sun, Y.-P. Gong, J. Yu and D.-W. Pang, ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 941–949 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhu, K. Kekalo, C. NDong, Y.-Y. Huang, F. Shubitidze, K. E. Griswold, I. Baker and J. X. J. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26, 3953–3972 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Li, G. Wang, Y. Shen, N. Guo and N. Ma, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1707152 CrossRef.
- M.-H. Park, E. Reátegui, W. Li, S. N. Tessier, K. H. K. Wong, A. E. Jensen, V. Thapar, D. Ting, M. Toner, S. L. Stott and P. T. Hammond, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 2741–2749 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Xu, J. A. Phillips, J. Yan, Q. Li, Z. H. Fan and W. Tan, Anal. Chem., 2009, 81, 7436–7442 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. A. Adams, P. I. Okagbare, J. Feng, M. L. Hupert, D. Patterson, J. Göttert, R. L. McCarley, D. Nikitopoulos, M. C. Murphy and S. A. Soper, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 8633–8641 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. L. Stott, C.-H. Hsu, D. I. Tsukrov, M. Yu, D. T. Miyamoto, B. A. Waltman, S. M. Rothenberg, A. M. Shah, M. E. Smas, G. K. Korir, F. P. Floyd, A. J. Gilman, J. B. Lord, D. Winokur, S. Springer, D. Irimia, S. Nagrath, L. V. Sequist, R. J. Lee, K. J. Isselbacher, S. Maheswaran, D. A. Haber and M. Toner, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2010, 107, 18392–18397 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. D. Jennings and K. A. Foon, Blood, 1997, 90, 2863–2892 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. L. Halo, K. M. McMahon, N. L. Angeloni, Y. Xu, W. Wang, A. B. Chinen, D. Malin, E. Strekalova, V. L. Cryns, C. Cheng, C. A. Mirkin and C. S. Thaxton, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2014, 111, 17104–17109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. J. W. van Denderen and E. W. Thompson, Nature, 2013, 493, 487 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. H. Tsai, J. L. Donaher, D. A. Murphy, S. Chau and J. Yang, Cancer Cell, 2012, 22, 725–736 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Sarrió, S. M. Rodriguez-Pinilla, D. Hardisson, A. Cano, G. Moreno-Bueno and J. Palacios, Cancer Res., 2008, 68, 989–997 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Yu, A. Bardia, B. S. Wittner, S. L. Stott, M. E. Smas, D. T. Ting, S. J. Isakoff, J. C. Ciciliano, M. N. Wells, A. M. Shah, K. F. Concannon, M. C. Donaldson, L. V. Sequist, E. Brachtel, D. Sgroi, J. Baselga, S. Ramaswamy, M. Toner, D. A. Haber and S. Maheswaran, Science, 2013, 339, 580–584 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zheng, Y. Cheng, J. Wang, J. Lu, B. Zhang, Y. Zhao and Z. Gu, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 7333–7338 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. P. Viraka Nellore, R. Kanchanapally, A. Pramanik, S. S. Sinha, S. R. Chavva, A. Hamme and P. C. Ray, Bioconjugate Chem., 2015, 26, 235–242 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Stoltenburg, C. Reinemann and B. Strehlitz, Biomol. Eng., 2007, 24, 381–403 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Kuai, Z. Zhao, L. Mo, H. Liu, X. Hu, T. Fu, X. Zhang and W. Tan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 9128–9131 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. German, D. D. Buchanan and R. T. Kennedy, Anal. Chem., 1998, 70, 4540–4545 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. B. Iliuk, L. Hu and W. A. Tao, Anal. Chem., 2011, 83, 4440–4452 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Famulok, J. S. Hartig and G. Mayer, Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 3715–3743 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Liang, Z. Yao, J. Ding, Q. Min, L. Jiang and J.-J. Zhu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 34050–34059 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Hong, X. Zhang, R. J. Lake, G. T. Pawel, Z. Guo, R. Pei and Y. Lu, Chem. Sci., 2020 10.1039/C9SC04773E.
- L. Yang, L. Meng, J. Song, Y. Xiao, R. Wang, H. Kang and D. Han, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 7466–7471 RSC.
- Z.-M. Ying, Y.-Y. Yuan, B. Tu, L.-J. Tang, R.-Q. Yu and J.-H. Jiang, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 4828–4833 RSC.
- Y. Liu, W. Hou, L. Xia, C. Cui, S. Wan, Y. Jiang, Y. Yang, Q. Wu, L. Qiu and W. Tan, Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 7505–7509 RSC.
- Y. Song, T. Tian, Y. Shi, W. Liu, Y. Zou, T. Khajvand, S. Wang, Z. Zhu and C. Yang, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 1736–1751 RSC.
- E. Obermayr, D. C. Castillo-Tong, D. Pils, P. Speiser, I. Braicu, T. Van Gorp, S. Mahner, J. Sehouli, I. Vergote and R. Zeillinger, Gynecol. Oncol., 2013, 128, 15–21 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Shen, L. Xu, L. Zhao, D. Wu, Y. Fan, Y. Zhou, W.-H. OuYang, X. Xu, Z. Zhang, M. Song, T. Lee, M. A. Garcia, B. Xiong, S. Hou, H.-R. Tseng and X. Fang, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 2368–2373 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Chen, X. Liu, B. Su, J. Li, L. Jiang, D. Han and S. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 4376–4380 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S.-W. Lv, J. Wang, M. Xie, N.-N. Lu, Z. Li, X.-W. Yan, S.-L. Cai, P.-A. Zhang, W.-G. Dong and W.-H. Huang, Chem. Sci., 2015, 6, 6432–6438 RSC.
- S.-W. Lv, Y. Liu, M. Xie, J. Wang, X.-W. Yan, Z. Li, W.-G. Dong and W.-H. Huang, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 6201–6210 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Li, J. Wang, J. Ren and X. Qu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 2248–2251 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhu, J. Yan and A. Revzin, Colloids Surf., B, 2008, 64, 260–268 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T.-T. Zhai, D. Ye, Q.-W. Zhang, Z.-Q. Wu and X.-H. Xia, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 34706–34714 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Yoshihara, R. Sekine, T. Ueki, Y. Kondo, Y. Sunaga, T. Nakaji-Hirabayashi, Y. Teramura and M. Takai, Acta Biomater., 2018, 67, 32–41 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Yu, R. He, S. Li, B. Cai, L. Zhao, L. Liao, W. Liu, Q. Zeng, H. Wang, S.-S. Guo and X.-Z. Zhao, Small, 2013, 9, 3895–3901 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Reátegui, N. Aceto, E. J. Lim, J. P. Sullivan, A. E. Jensen, M. Zeinali, J. M. Martel, A. J. Aranyosi, W. Li, S. Castleberry, A. Bardia, L. V. Sequist, D. A. Haber, S. Maheswaran, P. T. Hammond, M. Toner and S. L. Stott, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 1593–1599 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. R. Breaker and G. F. Joyce, Chem. Biol., 1994, 1, 223–229 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu, Z. Cao and Y. Lu, Chem. Rev., 2009, 109, 1948–1998 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, A. Niazov-Elkan, F. Wang and I. Willner, Nano Lett., 2013, 13, 219–225 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. K. Silverman, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2004, 2, 2701–2706 RSC.
- S. K. Silverman, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 7180–7201 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. Ali, S. D. Aguirre, H. Lazim and Y. Li, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 3751–3754 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wang, J. H. Lee and Y. Lu, Adv. Mater., 2008, 20, 3263–3267 CrossRef CAS.
- B.-C. Yin, B.-C. Ye, W. Tan, H. Wang and C.-C. Xie, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 14624–14625 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Xiao, V. Pavlov, T. Niazov, A. Dishon, M. Kotler and I. Willner, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 7430–7431 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu and Y. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 12677–12683 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Niazov, V. Pavlov, Y. Xiao, R. Gill and I. Willner, Nano Lett., 2004, 4, 1683–1687 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Peng, X.-F. Li, H. Zhang and X. C. Le, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 14378 CrossRef.
- W. Wang, N. S. R. Satyavolu, Z. Wu, J.-R. Zhang, J.-J. Zhu and Y. Lu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 6798–6802 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Meng, K. Zhang, W. Dai, Y. Cao, F. Yang, H. Dong and X. Zhang, Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 7419–7425 RSC.
- J. Elbaz, O. Lioubashevski, F. Wang, F. Remacle, R. D. Levine and I. Willner, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2010, 5, 417 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, D. Balogh, F. Wang and I. Willner, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 1934–1940 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-H. Chen, X. Yu, A. Cecconello, Y. S. Sohn, R. Nechushtai and I. Willner, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 5769–5780 RSC.
- X. Fang and W. Tan, Acc. Chem. Res., 2010, 43, 48–57 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Lou, Z. Zhou, Y. Du and S. Dong, Electrochem. Commun., 2015, 59, 64–67 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-Y. Wang, L.-X. Lü, J.-C. Shi, H.-F. Wang, Z.-D. Xiao and N.-P. Huang, Biomacromolecules, 2011, 12, 551–559 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Fan, Z. Zhao, G. Yan, X. Zhang, C. Yang, H. Meng, Z. Chen, H. Liu and W. Tan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 4801–4805 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu and Y. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 9838–9839 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. J. Lee, H.-Y. Cho, J. H. Oh, K. Namkoong, J. G. Lee, J.-M. Park, S. S. Lee, N. Huh and J.-W. Choi, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2013, 47, 508–514 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Gu, C. Ju, Y. Li, Z. Shang, Y. Wu, Y. Jia and Y. Niu, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 66, 24–31 CrossRef CAS.
- J. H. Myung, M. Roengvoraphoj, K. A. Tam, T. Ma, V. A. Memoli, E. Dmitrovsky, S. J. Freemantle and S. Hong, Anal. Chem., 2015, 87, 10096–10102 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. C. Gach, P. J. Attayek, R. L. Whittlesey, J. J. Yeh and N. L. Allbritton, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 54, 476–483 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Gao, H. Yuan, F. Jing, S. Wu, H. Zhou, H.-J. Mao, Q. Jin, Z. Jianlong, H. Cong and C. Jia, Oncotarget, 2017, 8, 12917–12928 Search PubMed.
- D. D. Dickey and P. H. Giangrande, Methods, 2016, 97, 94–103 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. S. Zamay, O. S. Kolovskaya, T. N. Zamay, Y. E. Glazyrin, A. V. Krat, O. Zubkova, E. Spivak, M. Wehbe, A. Gargaun, D. Muharemagic, M. Komarova, V. Grigorieva, A. Savchenko, A. A. Modestov, M. V. Berezovski and A. S. Zamay, Mol. Ther., 2015, 23, 1486–1496 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liu and Y. Lu, Nat. Protoc., 2006, 1, 246 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Sequences of oligonucleotides used in the study, fluorescence images of CTCs captured by the capture elements and released by metal ions in large view, selectivity study of the capture elements, optimization of capture and release time, MTT assay, live/dead cell staining, and merged image of the captured CTCs on the substrate in blood sample. See DOI: 10.1039/c9sc04309h |
| ‡ Q. Z. and W. W. contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |