Themed collection Biomedical Polymer Materials

Introduction to “Biomedical Polymer Materials”
Xuesi Chen and Huayu Tian introduce the Biomaterials Science and Journal of Materials Chemistry B cross-journal themed collection on Biomedical Polymer Materials.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 4273-4274
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM90054E
Polyprodrugs for tumor chemotherapy: from molecular structure to drug release performance
The structure–property relationship of polyprodrugs was explored from the perspective of molecular structure, by discussing the effects of the conjugations and linkers on their drug content and drug releasing performance.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 9565-9571
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01700A
Natural products applied in acute kidney injury treatment: polymer matters
The applications of renal-targeting natural polymers and polymer-delivered natural drugs for the treatment of lethal acute kidney injury are summarized.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 621-633
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01772A
Application of biomaterials in the treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage
In this review, the application of nanomaterials and hydrogels in the treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage is summarized. In addition, the potential challenges and prospects of these biomaterials for clinical translation are discussed.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 4065-4082
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00630E
Recent progress in nanomaterials for bacteria-related tumor therapy
Recent progress in nanomaterials for bacteria-related tumor therapy in terms of chemotherapy, immunotherapy and synergistic therapy is summarized in this review in order to provide some insights into this emerging and rapidly growing research area.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1965-1980
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01952G
Blood–brain barrier-crossing dendrimers for glioma theranostics
Blood–brain barrier-crossing dendrimers for glioma imaging diagnostics, chemotherapy, gene therapy, or imaging-guided therapy have been concisely reviewed with perspectives briefly discussed.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1346-1356
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00043A
Renal-clearable nanoprobes for optical imaging and early diagnosis of diseases
We summarize the advancements of renal-clearable organic nanoprobes for optical imaging and remote urinalysis. The versatile design strategies are discussed along with their challenges and perspectives for the development of next-generation renal-clearable nanoprobes.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1357-1370
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01776A
Organic–inorganic composite hydrogels: compositions, properties, and applications in regenerative medicine
Organic–inorganic composite hydrogels, with its polymeric networks interacting with inorganic fillers via different modes, provide a versatile platform for regenerative medicine.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1079-1114
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01766D
Hydroxyl-rich branched polycations for nucleic acid delivery
Amine-epoxide ring-opening polymerization was carried out to construct a hydroxyl-rich branched polycation and based on a one-pot strategy for the flexible introduction and multifunctional modification of responsive molecules.
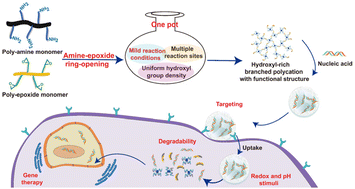
Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 581-595
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01394D
Thiol-containing hyperbranched polysiloxane for scavenging reactive oxygen species
Thiol-containing hyperbranched polysiloxane, a unconventional luminescent polymer, for scavenging intracellular reactive oxygen species.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024,12, 10584-10592
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TB01567C
Preparation of viromimetic rod-like nanoparticle vaccines (RLNVax) and study of their humoral immune activation efficacy
Antigen proteins were modified onto the surfaces of nanoparticles with various shapes. This study investigates the effect of structural anisotropy on the efficacy of humoral immune activation by nanoparticle vaccines.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 5115-5122
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00827H
ROS-responsive thermosensitive polypeptide hydrogels for localized drug delivery and improved tumor chemoimmunotherapy
A ROS-responsive hydrogel was developed as a platform for co-delivery of a chemotherapeutic drug (DOX), an immunological adjuvant (R848) and an ICB antibody (aPD-1) for combination tumor therapy and prevention of post-operative tumor recurrence.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 3100-3111
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00241E
Developing an in vitro model of haematoma for study of intracerebral haemorrhage
Intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) is a devastating neurovascular attack with limited treatment options.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 2885-2898
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00039K
The effect of charge and albumin on cellular uptake of supramolecular polymer nanostructures
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) regulates cellular internalization of charged ureido-pyrimidinone (UPy)-assembly. The BSA-bond UPy-assembly can be internalized and co-localizes with mitochondria. Without BSA, the UPy-assembly anchors to the cell membrane.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2024,12, 4854-4866
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB02631K
A mitochondria-targeting heptamethine cyanine-chlorambucil formulated polymeric nanoparticle to potentiate native tumor chemotherapeutic efficacy
Facile conjugation of chlorambucil with IR775 chloride can afford IR775-Cbl with mitochondria-targeting potency for tumor cells, exhibiting distinct “1 + 1 > 2” tumor inhibition.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 2614-2625
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00003J
Enhancing the tumor penetration of multiarm polymers by collagenase modification
Col modification significantly enhanced the tumor penetration and therapy efficacy of multiarm polymer-based nanomedicines.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 2302-2311
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM02123H
Optimization of lipid assisted polymeric nanoparticles for siRNA delivery and cancer immunotherapy
A siRNA delivery system was developed using clinically approved mPEG-b-PLGA, cationic lipid and ionizable lipid for siRNA delivery and cancer immunotherapy.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 2057-2066
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM02071A
A highly tuneable inverse emulsion polymerization for the synthesis of stimuli-responsive nanoparticles for biomedical applications
This article demonstrates an inverse emulsion scheme to polymerize a variety of ionizable and non-ionizable monomers to form stimuli-responsive nanoparticles with potential applications in biomaterials science.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1707-1715
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01765F
Preparation of glycopeptide-modified pH-sensitive liposomes for promoting antigen cross-presentation and induction of antigen-specific cellular immunity
Soybean agglutinin-derived glycopeptide-introduced pH-responsive polysaccharide-modified liposomes promote the cross-presentation and induction of antigen-specific cellular immune responses.
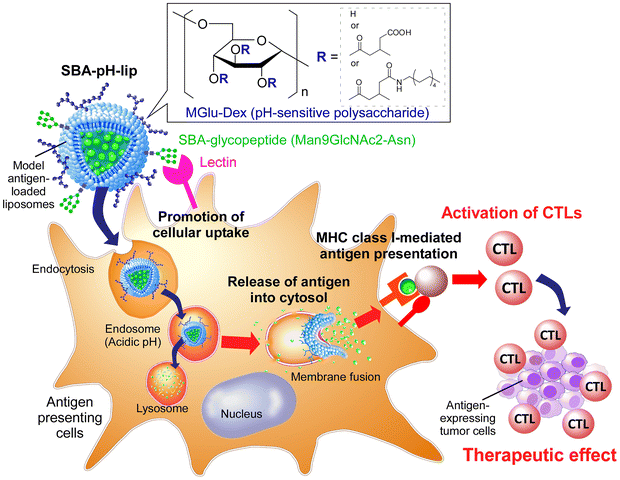
Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1490-1501
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01746J
Nitric oxide-scavenging hyaluronic acid nanoparticles for osteoarthritis treatment
This study presents a novel hyaluronic acid (HA)-based nanoparticles with dual effects for osteoarthritis (OA) treatment, combining anti-inflammatory effects through nitric oxide (NO) scavenging and lubrication effect provided by HA.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1477-1489
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01918G
A quaternary ammonium-based nanosystem enables delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 for cancer therapy
Chol-PEG and Qua-PLL were self-assembled with a Cas9/PLK1 sgRNA ribonucleoprotein to form a ternary nanoparticle QNP/RNPPLK1 for efficient cancer therapy.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1197-1210
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01629C
Wound microenvironment regulatory poly(L-glutamic acid) composite hydrogels containing metal ion-coordinated nanoparticles for effective hemostasis and wound healing
A wound microenvironment regulatory poly(L-glutamic acid) composite hydrogel can promote cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis, alleviate inflammation and polarize pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages into pro-healing M2 macrophages, thus accelerating wound healing.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1211-1227
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01978K
Quaternary ammonium-tethered hyperbranched polyurea nanoassembly synergized with antibiotics for enhanced antimicrobial efficacy
The rifampicin-loaded HPUs-QA nanoassembly (HPUs-Rif/QA) demonstrated a synergistic antimicrobial effect in killing planktonic bacteria and eradicating the corresponding biofilms.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1185-1196
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01519J
Fibrous capsule-resistant, controllably degradable and functionalizable zwitterion-albumin hybrid hydrogels
We present a biocompatible, controllably degradable, and functionalizable zwitterion-albumin hybrid hydrogel with long-term resistance against foreign body responses.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 468-478
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01783D
Nano-in-nano enteric protein delivery system: coaxial Eudragit® L100-55 fibers containing poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) nanogels
Novel nano-in-nano coaxial platform for enteric protein delivery.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 335-345
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01422C
A transdermal drug delivery system based on dissolving microneedles for boron neutron capture therapy of melanoma
A transdermal drug delivery system based on PVA/F-BPA microneedles for BNCT of melanoma.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 7568-7578
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01262J
Phosphorus core–shell tecto dendrimers for enhanced tumor imaging: the rigidity of the backbone matters
Phosphorus core–shell tecto dendrimers with rigid cores enable enhanced fluorescence/SPECT dual-mode tumor imaging likely through an amplified enhanced permeability and retention effect.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 7387-7396
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01198D
Adhesive and biodegradable polymer mixture composed of high -biosafety pharmaceutical excipients as non-setting periodontal dressing
A soft, non-setting and degradable periodontal dressing with biodegradability was developed using sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, Eudragit S 100 and povidone K30. The periodontal dressings could promote mucosal wound healing.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 7067-7076
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01314F
Surface chemistry mediates the tumor entrance of nanoparticles probed using single-molecule dual-imaging nanodots
We develop single-molecule dual-imaging nanodots by divergent growth for fluorescence and MR imaging of surface chemistry-dependent tumor entrance. The results show that the surface chemistry of nanoparticles can dominate the ways of tumor entrance.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 7051-7061
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01171B
The role of Eudragit® as a component of hydrogel formulations for medical devices
A systematic analysis is presented, highlighting the unique properties of Eudragits as additive in mucoadhesive hydrogels for ocular protein delivery.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2023,11, 9276-9289
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01579C
Biodegradable covalent organic frameworks achieving tumor micro-environment responsive drug release and antitumor treatment
A biodegradable COF was constructed to break in response to tumors, enhancing the therapeutic effect on tumors.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 6524-6536
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01088K
About this collection
Biomedical polymer materials, as materials for diagnosis, treatment and organ regeneration, have the mission of prolonging patients' lives and improving their quality of life. Their research occupies a very important position in the fields of biotechnology, life sciences and medicine, and different fields of biomedicine have different requirements for biomedical materials. Thus, in order to promote the development of the medical field, the synthesis of new biomaterials is of great significance. This themed collection across Journal of Materials Chemistry B and Biomaterials Science is Guest Edited by Professors Huayu Tian (0000-0002-2482-3744) and Xuesi Chen (0000-0001-7355-6446) (Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences) and features some of the recent articles surrounding the topic of biomedical polymer materials. We hope that this collection will give readers an overview of some of the most recent work concerning the materials chemistry and applications of novel biomedical polymer materials and will help to further exciting research in the field.