Themed collection Soft Robotics

Introduction to Soft Robotics
Anand Kumar Mishra, Zhihong Nie, Jamie Paik and Robert Shepherd introduce the Soft Matter themed issue on Soft Robotics.

Soft Matter, 2024,20, 5271-5272
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SM90099E
Soft robot-enabled controlled release of oral drug formulations
The creation of highly effective oral drug delivery systems (ODDSs) has long been the main objective of pharmaceutical research.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 1269-1281
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM01624A
Recent advances in biomimetic soft robotics: fabrication approaches, driven strategies and applications
Compared to traditional rigid-bodied robots, soft robots are constructed using physically flexible/elastic bodies and electronics to mimic nature and enable novel applications in industry, healthcare, aviation, military, etc.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7699-7734
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM01067D
Multicomponent and multifunctional integrated miniature soft robots
The seamless integration of multiple units greatly enhances the functionalities and adaptability of miniature soft robots. This review delivers the recent progress in multicomponent and multifunctional integrated miniature soft robots.
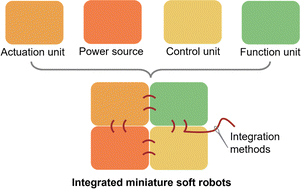
Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7464-7485
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00891B
Electrically driven liquid crystal network actuators
Electrically driven liquid crystal network (LCN) actuators, combining the merits of electrical modulation and the great actuation properties of LCN, have been advanced towards practical applications, new robotic functions and advanced motion control.
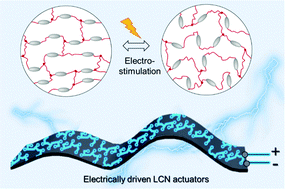
Soft Matter, 2022,18, 4850-4867
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00544A
Harnessing osmotic swelling stress for robust hydrogel actuators
The swelling of a hydrogel can exert enormous osmotic swelling stress, which can be harnessed to achieve robust hydrogel actuators. A hydrogel jack that can lift a weight 2000 times its own weight is demonstrated.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 5177-5184
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00591C
3D printable adhesive elastomers with dynamic covalent bond rearrangement
Soft 3D-printable adhesive elastomers with self-healing capabilities were formulated. These materials were 3D printed into complex structures and used to modify soft robots for shape-selective lifting.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 4964-4971
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00394A
Sensorless force and displacement estimation in soft actuators
We propose a novel sensorless estimation method for soft pneumatic actuators through injecting pressure oscillations and monitoring pressure response. We demonstrate this approach by sensing force and displacement without use of dedicated sensors.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 2554-2563
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM01197B
Magnetically induced stiffening for soft robotics
Stiffness modulation is paramount in the design of soft robotics and magnetorheological jamming beams, which combine magnetorheological fluid with scaffolding material, providing a novel method for achieving magnetically tunable stiffening ranges.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 2623-2636
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM01390H
Amorphous entangled active matter
Examining the properties of amorphous entangled systems through in silico simulations and in living aggregates of worm blobs, large-amplitude changes of the particle's shape improve the entanglement and tensile strength of the collective.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 1952-1965
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM01573K
Learning 3D shape proprioception for continuum soft robots with multiple magnetic sensors
We propose a neural architecture to make sense of the nonlinear relationship between the perceived intensity of the magnetic field and the shape of a continuum soft robot and improve efficiency by injecting priori knowledge from a kinematic model.

Soft Matter, 2023,19, 44-56
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00914E
Soft electrochemical bubble actuator with liquid metal electrode using an embodied hydrogel pneumatic source
Here, we report soft electrochemical systems that could enable pump-free pneumatic actuation. Besides, the electrochemical approach requires only a few volts to actuate, unlike dielectric actuators, which require ∼kV.
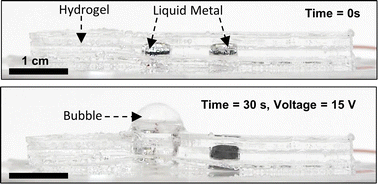
Soft Matter, 2022,18, 9291-9298
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00874B
Stretchable and conformable variable stiffness device through an electrorheological fluid
A thin, fully-soft, and stretchable variable stiffness device through electrorheological fluid was proposed, which could conform to complex surfaces in its inactive state, hang on it in its active state, and detach when the electric field is removed.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 9163-9171
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM01362B
Modelling the compression of a soft ellipsoid fingertip
This paper describes an analytical formulation of the deformation of an ellipsoid soft membrane, applied to a purely mechanically driven haptic feedback system, in particular, to the membrane of the fingertip sensor.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 9076-9085
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00763K
Effects of AC frequency on the capacitance measurement of hybrid response pressure sensors
E-skins consisting of soft pressure sensors are enabling technology for soft robots, bio-integrated devices, and deformable touch panels.
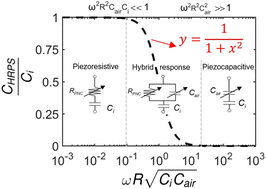
Soft Matter, 2022,18, 8476-8485
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM01250B
Motorized, untethered soft robots via 3D printed auxetics
We present a method of 3D printing handed shearing auxetics for scalable, motorized soft robotic actuators. The auxetics are assembled into multi-degree-of-freedom legs that enable fast, untethered locomotion over long operation times.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 8229-8237
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00779G
Plasticized liquid crystal networks and chemical motors for the active control of power transmission in mechanical devices
Orthogonal actuation for power and control in untethered small-scale machines is achieved with self-powered protein chemical motors and plasticized liquid crystal networks.
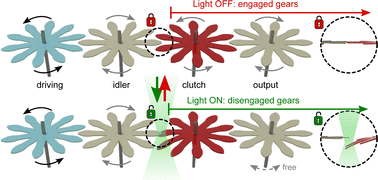
Soft Matter, 2022,18, 8063-8070
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00826B
A 3D printed hydrostatic skeleton for an earthworm-inspired soft burrowing robot
An earthworm-inspired soft-burrowing robot with a 3D-printed artificial hydrostatic skeleton.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7990-7997
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00882C
X-ray scattering as an effective tool for characterizing liquid metal composite morphology
Liquid metal soft composite morphology is quantified through X-ray scattering and real-space image analysis, providing global-averaged particle size and size distributions for material design.
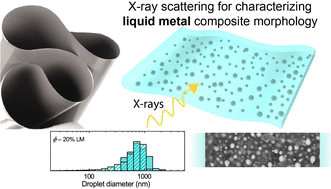
Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7762-7772
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00796G
Stretchable reflective coating for soft optical waveguides and sensors
TiO2 particles are added into silicone matrices to develop highly reflective composite coatings. Coated soft optical waveguides and strain sensors demonstrate superior environmental light shielding, and tolerance to bending, folding, and indentation.
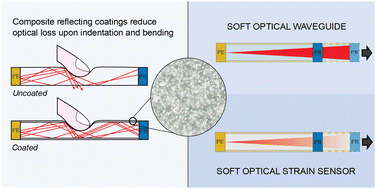
Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7827-7837
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00869F
Magnetic vitrimer-based soft robotics
We have developed a magnetic vitrimer-based soft robot that can pass through a confined space, dramatically change its configuration, self-heal without any contact, catch, secure and release a fast-moving object, and move along a planned path.
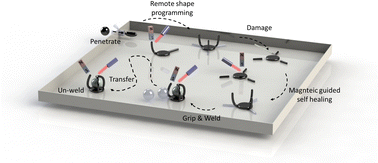
Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7604-7611
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00893A
Direct ink writing of tough, stretchable silicone composites
In this work, we report 3D printable soft composites that are simultaneously stretchable and tough.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7341-7347
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00923D
3D printing of soft fluidic actuators with graded porosity
The InFoam method combines liquid rope coiling and regular plotting to fabricate structures softer than their original material and with graded porosity. This combination can be used to realize soft robotics structures such as soft fluidic actuators.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7269-7279
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00524G
Flexible and adhesive liquid-free ionic conductive elastomers toward human–machine interaction
The stretchable and adhesive liquid-free ionic conductive elastomers were developed and assembled into triboelectric nanogenerators for use as human–machine interactive keyboards.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7103-7111
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00865C
Real time high voltage capacitance for rapid evaluation of dielectric elastomer actuators
Dielectric elastomer actuators (DEAs) are soft electromechanical transducers for robotic applications. We report a method to continuously monitor high voltage capacitance during DEA actuation to directly measure the electrical energy consumption.

Soft Matter, 2022,18, 7123-7130
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00690A
3D printed linear soft multi-mode actuators expanding robotic applications
A new soft 3D printable elastomer allows for improvements to soft pneumatic actuators that can both expand and contract under different pressures. The actuators exhibit excellent performance metrics and are shown to be viable in soft mobile robots.
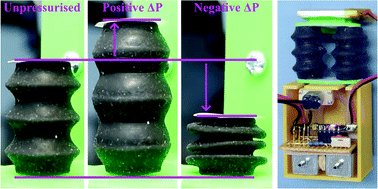
Soft Matter, 2022,18, 1911-1919
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SM00050D
About this collection
After decades of intensive research, soft robotics is not only pushing the boundary of conventional robotics but also accelerating the innovation of associated technologies. Soft robotic systems can closely mimic the complex and continuum motions of natural organisms with less manufacturing and control complexity than traditional robotics. Specifically, they show at least the following advantages over traditional robotics, including simplicity, lightweight and high compactness, infinite passive degrees of freedom, and high dexterity, agility, and adaptability, etc.
Before soft robotics become commonplace in our life, many challenges still remain. Typical ones include new material design, high-precision sensing and actuation, manufacturing, system reliability, and costs. To bring soft robots to the next level of performance, we need a tactical approach towards a well-stated goal. Guest Edited by Anand Mishra (Cornell University), Zhihong Nie (Fudan University), Jamie Paik (EPFL) and Rob Shepherd (Cornell University), this collection encompasses review and research articles relevant to the design, fabrication, and operation of soft robots.