Flexible and adhesive liquid-free ionic conductive elastomers toward human–machine interaction†
Zhenyu
Xu
ab,
Rui
Li
a,
Huijing
Li
ab,
Guorong
Gao
 *ab and
Tao
Chen
*ab and
Tao
Chen
 *ab
*ab
aKey Laboratory of Marine Materials and Related Technologies, Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Marine Materials and Protective Technologies, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo 315201, China. E-mail: gaogr@nimte.ac.cn; tao.chen@nimte.ac.cn
bSchool of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
First published on 26th August 2022
Abstract
Based on the demand for flexible human–machine interaction devices, it is urgent to develop high-performance stretchable ionic conductive materials. However, most gel-based ionic conductive materials are composed of crosslinked polymer networks that contain liquids, and suffer from limitations of solvent volatilization and leakage, and the cross-linking restricts the movement and diffusion of polymer chains, making it difficult for them to achieve adhesion. Here, we introduce flexible and adhesive liquid-free ionic conductive elastomers (ICE) with salt using a non-crosslinked polymer strategy. The ICE show a transparency of 89.5%, Tg of −51.2 °C, negligible weight loss at 200 °C, a tensile fracture strain of 289.5%, and an initial modulus of 45.7 kPa, and is adhesive to various solid surfaces with an interfacial toughness of 11.4 to 41.4 J m−2. Moreover, the ICE exhibit stable electrical conductivity under ambient conditions. Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) were assembled on an electrical shell surface with the adhesive ICE as an electrostatic induction layer and were displayed for use as human–machine interactive keyboards. This approach opens a route to making adhesive and stable polymer ionic conductors for human–machine interaction.
1 Introduction
With the rapid development of human–machine interaction technology, there is an urgent need for the development of flexible stretchable electronic materials.1,2 In the early stage, flexible elastic conductive materials were mainly polymer composites that were filled with metals, carbons, and conjugated polymers.3,4 It was hard for them to achieve transparency and high conductivity at the same time. Recently, ionic conductors that conduct electricity using ions, including hydrogels5 and ionic liquid gels,6 have attracted wide research interest. These materials are composed of stretchable polymer networks and absorbed with aqueous electrolytes or ionic liquids, allowing a broad range of applications. The combination of conductivity,7 stretchability,8 transparency,8 adhesiveness,9,10 and self-healing11 properties makes them ideal materials for ionotronic devices, including artificial skins,12–14 artificial axons,15 artificial muscles,16 artificial tongues,17 deformable touch panels,18 generators,19,20 and diodes.21 However, these devices suffer from limitations inherent to the liquid-containing materials. The hydrogels dehydrate rapidly under ambient conditions due to evaporation. By introducing hygroscopic components such as LiCl22 and glycerin,23 durable moisturizing hydrogels can be obtained, but their water contents vary significantly with temperature and humidity. A hydrogel sealed in a hydrophobic elastomer can keep its water content, but there is a hassle of interfacial separation24,25 while ionic liquid gels suffer from liquid leakage upon deformation.26 It is still urgent to develop ionic conductive materials with durability and stability for human–machine interactive devices.More recently, ionic conductive elastomers (ICE) have been developed, which consist of polymer networks and mobile ions, but contain no liquid.27–34 Because they are liquid-free, ICE have no weight or performance loss in air, thus achieving durability and performance stability that are extremely difficult or even impossible to realize by hydrogels and ionic liquid gels. Such advantages enable ICE to be demonstrated for making flexible and stable transistors,35 sensors,36 electroluminescent devices,37 and triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs).38 In human–machine interaction scenarios, ICE are always integrated with machines or human bodies. However, chemical crosslinking restricts the movements of polymer segments, thereby preventing the continuous molecular interaction between polymers and the contacted substrates, thus making the ICE difficult to achieve adhesion. Therefore, it needs to be fixed to the target surface with glue or tape. A key challenge for an ICE ionotronic device toward human–machine interaction is to develop a liquid-free material system that combines flexibility, self-adhesiveness, conductivity, transparency, high-temperature resistance, anti-drying, and anti-freezing.
In this study, we developed a novel flexible and adhesive liquid-free ICE toward human–machine interaction. The ICE are synthesized through a strategy of one-step free radical polymerization of liquid acrylate monomers containing dissolved solid lithium salts. The material is soft with an initial tensile modulus of 45.7 kPa and stretchable with a fracture strain of 289.5%. As the acrylate polymers are commonly used as adhesives due to the strong hydrogen bonding ability of ester groups,39 the ICE generate adhesiveness to various solid substrates. We investigate the effects of lithium salt dosage and the type of polymer side group on the electrical conductivity and the obtained ICE with a maximum electrical conductivity of 1.8 × 10−2 S m−1. The material also features optical transparency, high-temperature stability, as well as durability, and significantly higher decomposition voltage in comparison with hydrogels. We use the ICE to make strain sensors and stretchable TENGs. To demonstrate the advantages in the field of human–machine interaction, we use the flexibility and adhesion of the ICE to easily construct several TENGs on the electrical plastic shell, collect the voltage signals from TENGs, convert the signals into binary codes, and then convert them into letters and display them on a monitor.
2 Experimental section
2.1 Materials
2-Ethoxyethoxyethyl acrylate (EEEA) was obtained from J&K Scientific Co., Ltd. Ethylene glycol methyl ether acrylate (MEA), ethylene glycol phenyl ether acrylate (PEA), benzophenone (BP), lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulphonyl)imide (LiTFSI), acrylamide (AAm), N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide (MBAA), ammonium persulfate (APS) and N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) were obtained from the Aladdin Shanghai Reagent Co., Ltd. Butyl acrylate (BA) was obtained from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd. All chemicals were used as received. VHBTM 4905 tape (thickness 0.5 mm) was obtained from 3 M Corporation.2.2 Synthesis of ionic conductive elastomers (ICE)
ICE were prepared by free radical polymerization of LiTFSI/acrylate monomer mixed solution under UV irradiation. A typical example is given below. LiTFSI (0.5 g, 1.7 mmol) and BP (0.005 g, 0.027 mmol) were added to the liquid monomer EEEA (4.82 g, 25.6 mmol). The mixture was stirred for 0.5 h to obtain a transparent solution. Then, the solution was poured into a mold composed of two quartz glasses and a silicone frame with an inner size of 60 mm × 60 mm × 1 mm, subsequently polymerized under UV light (365 nm) for 6 h to generate the PEEEA ICE.2.3 Synthesis of the PAAm hydrogel ionic conductor
1.5 g AAm was dissolved in 1 M NaCl aqueous solution (10 mL) with 0.01 g MBAA as a cross-linker. APS (0.005 g) and TEMED (5 μL, 0.055 mmol) were added, subsequent by stirring for 10 min. The final solution was poured into a mold composed of two plate glasses and a silicone frame with a chamber size of 60 mm × 60 mm × 1 mm. The hydrogel was obtained after polymerizing at 40 °C for 6 h.2.4 Material tests and characterizations
2.5 Preparation of strain sensors based on ICE
A strain sensor was made by connecting both ends of a PEEEA ICE strip (25 mm × 8 mm × 1 mm) with copper wires. It was mounted on a Universal Testing System (Zwick Roell Z1.0) and stretched at 50 mm min−1. The electrochemical workstation (CHI660E) was used to apply a constant voltage of 1 V on the sensor and record the current (I) over time (t). The relative resistance (ΔR/R0) was calculated from ΔR/R0 = (R − R0)/R0 = I0/I − 1, where R0 and I0 represent the initial resistance and current, respectively.2.6 Preparation of the TENG
The TENG was prepared by sandwiching a layer of PEEEA ICE (30 mm × 30 mm × 1 mm) between two VHBTM 4905 elastomers and connecting to the ICE with a copper electrode. The output performances, including open-circuit voltage (Voc), short-circuit current (Isc), short-circuit charge quantity (Qsc), and power density of a TENG were recorded on an electrometer (Keithley 6514).2.7 Preparation of a human–machine interactive system
Five TENGs were connected to a Mini STM 32 demo board (Guangzhou Xingyi Electronic Technology Co., Ltd) via separate signal capture circuits. The demo board converted electrical signals into digital signals, which were encoded and converted into letters and symbols by the microcontroller.3. Results and discussion
3.1 Design and physical properties of the ionic conductive elastomer (ICE)
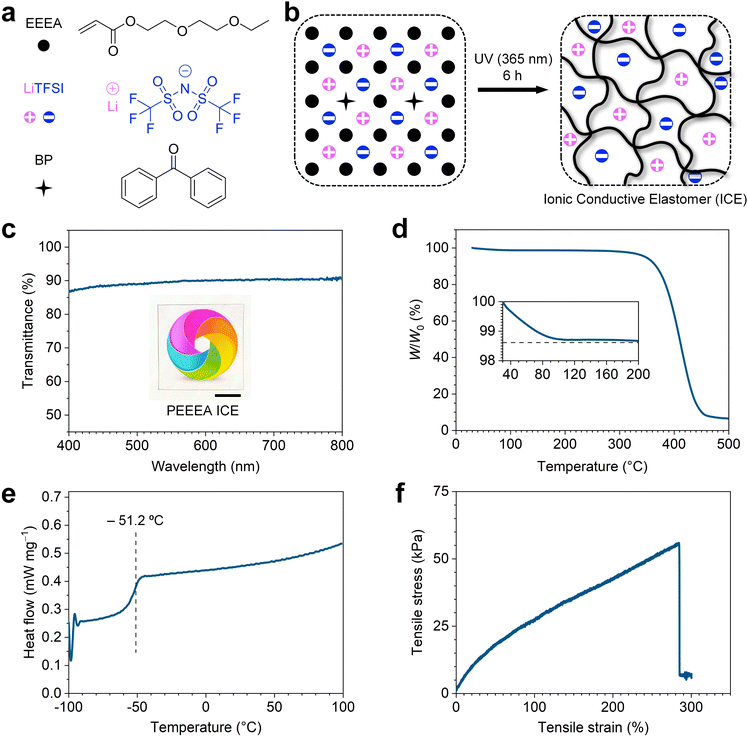
To synthesize the ICE, the electrolyte salt powder lithium bis(trifluoromethane sulfonimide) (LiTFSI) and the initiator benzophenone (BP) were dissolved in the liquid monomer 2-ethoxyethoxyethyl acrylate (EEEA) (Fig. 1a) to form a transparent solution. The molar percentage of LiTFSI to EEEA was fixed at 6.6% (molar ratio, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 15) unless otherwise stated. The ICE were then obtained by polymerization under ultraviolet light (365 nm) irradiation for 6 h (Fig. 1b). The ICE is highly transparent in the visible light region. As shown in Fig. 1c, a sample with a thickness of 1 mm showed an average transmittance of 89.5% in the wavelength range of 400–800 nm. The high transparency indicates the LiTFSI powders were thoroughly dissolved in the polymer matrix, and no phase separation occurred during polymerization.
15) unless otherwise stated. The ICE were then obtained by polymerization under ultraviolet light (365 nm) irradiation for 6 h (Fig. 1b). The ICE is highly transparent in the visible light region. As shown in Fig. 1c, a sample with a thickness of 1 mm showed an average transmittance of 89.5% in the wavelength range of 400–800 nm. The high transparency indicates the LiTFSI powders were thoroughly dissolved in the polymer matrix, and no phase separation occurred during polymerization.
The liquid-free ICE exhibits high thermal stability and a wide operating temperature window. From the TGA curve in Fig. 1d, the ICE shows a slight weight loss of 1.4% when the temperature increases from 30 to 200 °C. From the DSC curve in Fig. 1e, the ICE show a glass transition (Tg) temperature of −51.2 °C, above which the ICE are flexible elastomers. Thus, the operating temperature of ICE can range from −51.2 to 200 °C. The weight loss before 200 °C (Fig. 1d) may be related to the water evaporation from the ICE, as the Li+ in the ICE have the hygroscopic ability.40 In sharp contrast, the PAAm hydrogel ionic conductor showed 60.1% weight loss when the temperature reached 100 °C in thermogravimetric analysis (Fig. S1, ESI†). Furthermore, the ICE is quite stable at high temperature. When stored in an oven at 80 °C, the naked ICE remained 98% of the initial mass after 2 h, which almost unchanged after another 10 h (Fig. S2, ESI†).
The ICE possesses good stretchability, with a fracture strain of 289.5% ± 32.6%, fracture stress of 56 ± 8.9 kPa, and initial modulus (E) of 45.7 ± 4.8 kPa. Fig. 1f shows the typical tensile stress–strain curve of the ICE. It also shows good resilience. In ten consecutive cyclic tensile tests with a maximum tensile strain of 150%, the strain always recovered to 4% after unloading at each cycle (Fig. S3, ESI†). The effect of polymer side groups on the mechanical properties of the ICE were investigated. Different types of ICE were synthesized by replacing EEEA with monomer ethylene glycol phenyl ether acrylate (PEA), butyl acrylate (BA), and ethylene glycol methyl ether acrylate (MEA) (Fig. S4a, ESI†), respectively. Typical tensile stress–strain curves of PPEA, PBA, and PMEA ICE are shown in Fig. S4b (ESI†). The fracture strain was 96.5% ± 4.5%, 522.3% ± 45.1%, and 450.3% ± 20.5% for PPEA, PBA, and PMEA ICE, respectively (Fig. S4c, ESI†) while the fracture stress was 603.9 ± 16.9 kPa, 199.7 ± 13 kPa, and 152.8 ± 4 kPa (Fig. S4c, ESI†), and the E was 875.4 ± 70.2 kPa, 134.7 ± 9.3 kPa, and 129.1 ± 5.5 kPa for PPEA, PBA, and PMEA ICE, respectively (Fig. S4d, ESI†). These results suggest that the tensile properties of ICE can be regulated by side groups. Polymers with rigid side groups, such as benzene rings, will restrict the activity of chain segments, and improve the strength and modulus of the ICE. Increasing the repeat units (such as ethoxy) of flexible side groups will improve the flexibility of polymers, and lead to reduced strength and modulus of the ICE. These results were consistent with DSC analysis, and the Tg was −5, −39.9, and −40 °C for PPEA, PBA, and PMEA, respectively (Fig. S4e, ESI†).
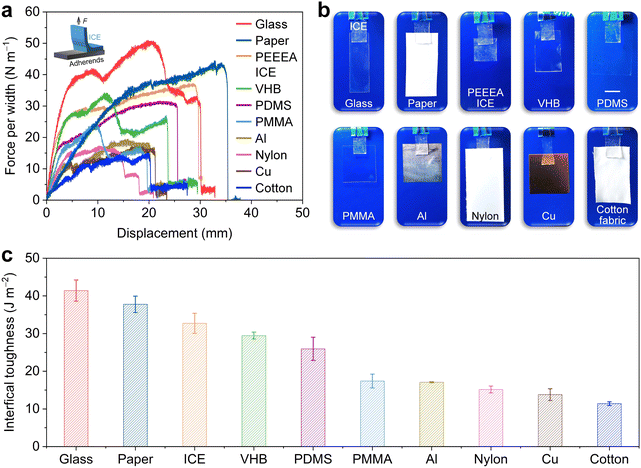
3.2 Adhesion properties of the ICE
The ICE is adhesive to various solid materials. Fig. 2a shows that the ICE pieces adhere to a piece of glass, paper, ICE, VHB tape, PDMS, PMMA, aluminum (Al), Nylon, copper (Cu), and cotton fabric. These adherends are dangling from ICE without shedding. The adhesion properties were evaluated through 90° peeling-off tests (Fig. 2b). The interfacial toughness of ICE adhered to the glass, paper, ICE, VHB, PDMS, PMMA, Al, Nylon, Cu, and cotton fabric is 41.4 ± 2.8, 37.8 ± 2.2, 32.7 ± 2.7, 29.5 ± 0.9, 26 ± 3, 17.4 ± 1.8, 17.1 ± 0.2, 15.2 ± 0.9, 13.8 ± 1.6, and 11.4 ± 0.5 J m−2, respectively (Fig. 2c).Adhesion is a complicated physical and chemical process, and the adhesion strength depends on the chemical interactions between interfaces and surface topology. Polyacrylates are commonly used to make solvent-free pressure-sensitive adhesives.39 The forces acting between surfaces of non-polar polyacrylates and adherends can be classified as van der Waals interactions, which drop to an insignificant magnitude when the distance between the two bodies is greater than 0.5 nm.41 The oxygen atoms on ester and ether groups from PEEEA easily form hydrogen bonds with hydroxyl or amino groups from the adherends.42 On the other hand, the adhesion properties are affected by chemical cross-linking, which restricts the movement of polymer chains. Our PEEEA ICE was synthesized without chemical cross-linkers, and thus the polymer chains can diffuse across the surface of the target substrate to generate intimate contact on a molecular scale.43
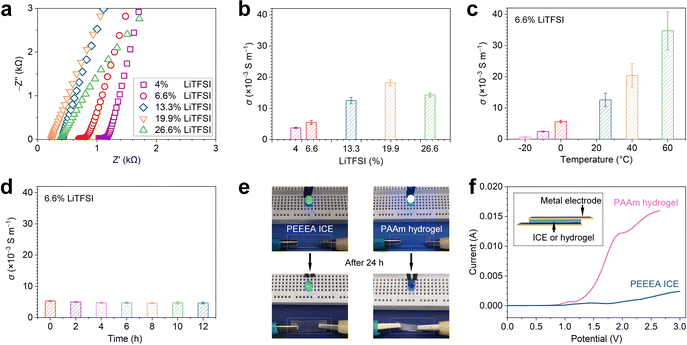
3.3 Electrical conductivity of the ICE
The ICE has good ionic conductivity. Fig. 3a shows the Nyquist plots of the ICE, which were prepared from various LiTFSI/monomer molar ratios. We calculated the conductivities (σ) by σ = d/AR, where d is equal to the thickness, A equal to the area of an ICE sample, and R is equal to the Z’ value at the intersection point of the curve, and the Z′ axis. The σ of the ICE with 4%, 6.6%, 13.3%, 19.9%, and 26.6% LiTFSI is 3.7 × 10−3 ± 1.6 × 10−4, 5.7 × 10−3 ± 6.1 × 10−4, 1.2 × 10−2 ± 1 × 10−3, 1.8 × 10−2 ± 9.3 × 10−4, and 1.4 × 10−2 ± 6.4 × 10−4 S m−1, respectively (Fig. 3b). The σ first increased by increasing the LiTFSI ratio, then decreased when exceeding 19.9%. We propose that the σ of the ICE is affected by the synergistic effects of LiTFSI concentration and polymer segment motion ability. The mobile ions increase with the LiTFSI content, leading to the increase of σ. On the other hand, the coordination between Li+ and carbonyl groups in polyacrylates reduces the flexibility of polymer chains.44 It was confirmed by the linear rheological behavior of the PEEEA ICE and PEEEA polymer without LiTFSI (Fig. S5, ESI†). In a wide frequency range (0.1–100 Hz), the dynamic shear modulus, including storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G′′) of the PEEEA ICE are both significantly bigger than that of the PEEEA polymer. The combined effect is that the σ of the ICE reaches a maximum value when the molar ratio of LiTFSI to monomer is 19.9%. Moreover, with the same LiTFSI/monomer molar ratio of 6.6%, the σ sequence of three kinds of ICE is PPEA (6 × 10−6 ± 4.3 × 10−7) < PBA (5.3 × 10−4 ± 3.4 × 10−5) < PMEA ICE (3.4 × 10−3 ± 8.16 × 10−4) (Fig. S6, ESI†), which is consistent with the reverse order of Tg of these ICE (Fig. S4e, ESI†). These results prove that the σ of the ICE decreases with the reduction of polymer chain activity. The σ of the ICE increases monotonously with increasing temperature (Fig. 3c), as higher temperature leads to greater chain activity thus facilitating ion mobility.The ICE are stable in ambient conditions. Fig. 3d shows when being exposed to the atmosphere at room temperature, the σ of ICE decreased from 5.3 × 10−3 to 4.7 × 10−3 in the first 4 h, probably due to the absorption of water from the air, and then remained at 4.7 × 10−3 until 12 h. When a piece of ICE was used as a wire in a direct current circuit, the indicator bulb remained bright after 24 h. In contrast, with an ionic hydrogel wire, the bright light bulb completely went out after 24 h. Fig. 3f shows the linear-sweep-voltammetry curves of ICE and PAAm hydrogel that conduct on a CHI660E electrochemical workstation, the scan rate was 1 mV S−1 at the range of 0–3 V. The curve of hydrogel rose steeply when voltage exceeded 0.8 V, indicating the electrolysis of water. The curve of ICE was flat until 1 V voltage, indicating that a higher voltage can be applied to the ICE. The resistances of the ICE samples increased by tensile (Fig. S7a, ESI†) or gradual tensile tests with a strain increment of 20% at each step (Fig. S7b, ESI†) when 1 V voltage was applied, and thus the ICE could be used as strain sensors.3,4
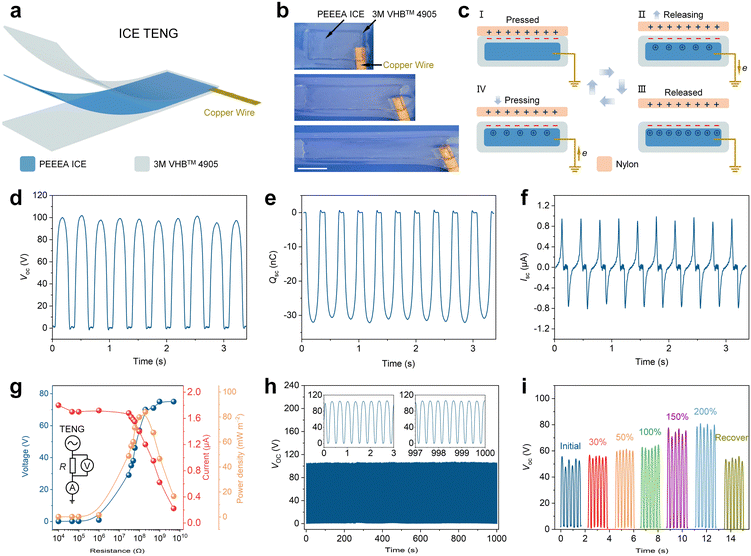
3.4 Mechanism and characterization of the stretchable ICE TENG
A single-electrode mode TENG is prepared with the ICE as the flexible interlayer electrode and VHBTM 4905 tape as the surface layer electrification material (Fig. 4a). Fig. 4b shows an ICE TENG stretched to a strain of 170%. The TENG produces alternating current based on the coupling effect of contact electrification and electrostatic induction (Fig. 4c). Briefly, in step I of Fig. 4c, contact electrification occurs at the interface when a contact material, such as a Nylon plate, contacts the electrification layer, due to the difference in electron affinity between the two materials. In step II of Fig. 4c, as the Nylon plate moves away, the negative charges in the VHB layer induce the directed migration of the positive ions, thus electrons flow from the copper electrode to the ground, until an electrostatic equilibrium is established in step III of Fig. 4c. In step IV of Fig. 4c, as the Nylon plate turns back, electrons flow back from the ground. Thus, the alternating current is detected.To evaluate the output performance of the TENG, a reciprocating motor with a Nylon plate at the top was used to provide contact-separation motion relative to an ICE TENG (size, 3 cm × 3 cm) at a frequency of 3 Hz. The peak open-circuit voltage (Voc) is 98 V (Fig. 4d), the short-circuit charge quantity (Qsc) is 32 nC (Fig. 4e), and the peak to peak short-circuit current (Isc) is 1.8 μA (Fig. 4f). The output power density was further evaluated by varying the external resistance (R) (Fig. 4g). The voltage applied to the R increases, while the current in the circuit decreases as the R increases from 104 to 5 × 109 Ω (Fig. 4g). The maximum power density is 84 mW m−2 at R of 200 MΩ. The durability of the ICE TENG is evaluated by tapping it for 3000 cycles. Fig. 4h shows the peak Voc is almost unchanged at 102 V in the whole process. The ICE TENG could also generate electricity after stretching. A TENG with an initial size of 1 cm × 2 cm was stretched to 30%, 50%, 100%, 150%, 200%, then recovered to 0, the corresponding Voc was 56, 61, 62.5, 76, 80 V, which then recovered to 52 V (Fig. 4i). The improvement of Voc could be attributed to the increase in surface area of TENG, as the amounts of charges in the contact electrification step increase with the contact area.
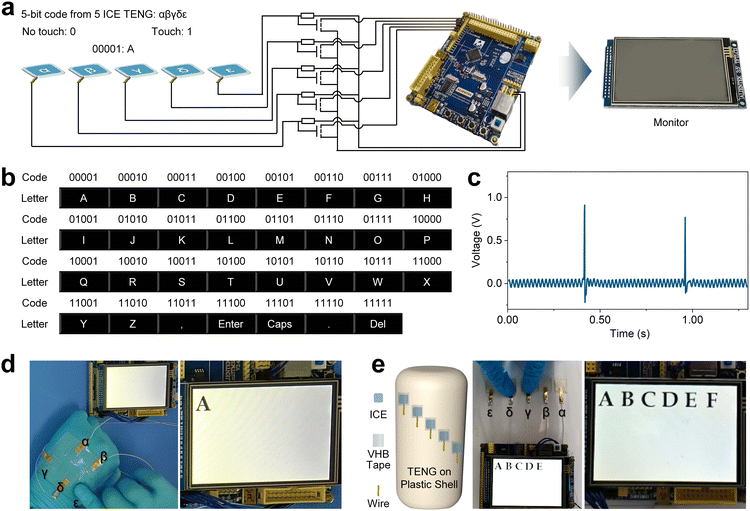
3.5 Flexible and adhesive ICE-based TENG toward human–machine interaction
We developed a flexible and adhesive human–machine interaction system based on ICE TENG (Fig. 5a). Five TENGs were connected to five field-effect transistors (FETs), which are used as analog switches and were connected to a demo board through five circuits (Fig. 5a). When a finger tapped a TENG, a voltage pulse was generated (Fig. 5b), and thus the corresponding FET was turned on. The microcontroller unit (MCU) in the demo board can distinguish between tapping or no tapping of a TENG according to the corresponding FET. Defining tapping as “1” and no tapping as “0”, there are 25 − 1 five-bit binary codes, from 00001 to 11111, which could be generated individually or simultaneously by tapping the five TENGs. We imparted each binary code a specific meaning, such as a letter, punctuation, or function key (Fig. 5c) that could be read from the monitor on the demo board (Fig. 5a), thus demonstrating the ICE TENG can be used as flexible and wearable human–machine interaction “keyboard”. For example, “A” appeared on the monitor by tapping the fifth (ε, Fig. 5d) TENG, and “B” appeared by taping the fourth (δ, Movie S1, ESI†) TENG. Furthermore, we assembled the ICE TENG on an electrical plastic shell where the ICE was self-adhered to the curved shell, covered by PDMS films, and then connected with metal wires to form the TENG. Fig. 5e and Movie S2 (ESI†) show the typing of these TENG to input letters. To accommodate the novice, the MCU treated the signals within 1 s as simultaneous tapping.4 Conclusions
In summary, we have reported a flexible and adhesive liquid-free ICE that consists of long PEEEA chains and LiTFSI that are dissolved in the polymer matrix. The material with a Tg of −51.2 °C and high-temperature stability shows a fracture strain of 289.5% and an initial modulus of 45.7 kPa. The ICE is adhesive to many solid substrates including plastics, rubbers, fabrics, metals, and glasses with interfacial toughness in the range of 11.4–41.4 J m−2. The ICE can maintain the conductivity for long periods under ambient conditions, rather than losing the conductivity due to water loss as hydrogels. The ionic conductivity could be enhanced by increasing the LiTFSI concentration and the activity of polymer chains. We demonstrated the use of ICE to make TENGs, which were mechanically compliant and stretchable, and showed a Voc of 98 V, Qsc of 32 nC, Isc of 1.8 μA, and a maximum power density of 84 mW m−2. Flexible and adhesive TENGs were assembled on an electrical shell and were demonstrated to function as human–machine interactive “keyboards”. The ICE provides possibilities for key flexible electronic devices and flexible human–machine interaction.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0114900), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LD22E050008 and LY21E030013), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52073295), the Ningbo Scientific and Technological Innovation 2025 Major Project (2018B10057 and 2020Z022), the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDB-SSW-SLH036), the Sino-German Mobility Program (M-0424), and the K. C. Wong Education Foundation (GJTD-2019-13).References
- P. Rothemund, Y. Kim, R. H. Heisser, X. Zhao, R. F. Shepherd and C. Keplinger, Nat. Mater., 2021, 20, 1582–1587 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Xu, F. Zhou, H. Yan, G. Gao, H. Li, R. Li and T. Chen, Nano Energy, 2021, 90, 106614 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Li, G. Gao, Z. Xu, D. Tang and T. Chen, Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2021, 42, 2100480 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Li, Y. Liang, G. Gao, S. Wei, Y. Jian, X. Le, W. Lu, Q. Liu, J. Zhang and T. Chen, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 415, 128988 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Huang, L. Hou, T. Li, Y. Jiao and P. Wu, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2110140 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- W. Li, L. Li, S. Zheng, Z. Liu, X. Zou, Z. Sun, J. Guo and F. Yan, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2203049 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- C.-J. Lee, H. Wu, Y. Hu, M. Young, H. Wang, D. Lynch, F. Xu, H. Cong and G. Cheng, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 5845–5852 CrossRef CAS
.
- C. Keplinger, J.-Y. Sun, C. C. Foo, P. Rothemund, G. M. Whitesides and Z. Suo, Science, 2013, 341, 984–987 CrossRef CAS
.
- Y. Miao, M. Xu, J. Yu and L. Zhang, Sens. Actuators, B, 2021, 327, 128916 CrossRef CAS
.
- Y. Miao, M. Xu and L. Zhang, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2102308 CrossRef CAS
.
- G. Gao, F. Yang, F. Zhou, J. He, W. Lu, P. Xiao, H. Yan, C. Pan, T. Chen and Z. L. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2004290 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Lei, W. Zhu, X. Zhang, X. Wang and P. Wu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2008020 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. Wen, J. Tang, H. Ning, N. Hu, Y. Zhu, Y. Gong, C. Xu, Q. Zhao, X. Jiang, X. Hu, L. Lei, D. Wu and T. Huang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2011176 CrossRef CAS
.
- I. You, D. G. Mackanic, N. Matsuhisa, J. Kang, J. Kwon, L. Beker, J. Mun, W. Suh, T. Y. Kim, J. B.-H. Tok, Z. Bao and U. Jeong, Science, 2020, 370, 961–965 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- D. Zhang, M. Zhang, J. Wang, H. Sun, H. Liu, L. Mi, C. Liu and C. Shen, Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater., 2022 DOI:10.1007/s42114-022-00437-y
.
- J. A. Rogers, Science, 2013, 341, 968–969 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Yeom, A. Choe, S. Lim, Y. Lee, S. Na and H. Ko, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eaba5785 CrossRef CAS
.
- C.-C. Kim, H.-H. Lee, K. H. Oh and J.-Y. Sun, Science, 2016, 353, 682–687 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- C.-G. Han, X. Qian, Q. Li, B. Deng, Y. Zhu, Z. Han, W. Zhang, W. Wang, S.-P. Feng, G. Chen and W. Liu, Science, 2020, 368, 1091–1098 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Liu, Z. L. Wang, K. Fukuda and T. Someya, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2022 DOI:10.1038/s41578-022-00441-0
.
- Y. Zhang, C. K. Jeong, J. Wang, X. Chen, K. H. Choi, L.-Q. Chen, W. Chen, Q. M. Zhang and Q. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2103056 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. Bai, B. Chen, F. Xiang, J. Zhou, H. Wang and Z. Suo, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 105, 151903 CrossRef
.
- F. Ni, N. Qiu, P. Xiao, C. Zhang, Y. Jian, Y. Liang, W. Xie, L. Yan and T. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 19237–19246 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. N. Subraveti and S. R. Raghavan, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 37645–37654 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Q. Liu, G. Nian, C. Yang, S. Qu and Z. Suo, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 846 CrossRef PubMed
.
- Z. Lei and P. Wu, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 3429 CrossRef
.
- B. B. Jing and C. M. Evans, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 18932–18937 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. Zhang, W. Guo, Z. H. Guo, Y. Ma, L. Gao, Z. Cong, X. J. Zhao, L. Qiao, X. Pu and Z. L. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2101396 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- P. Shi, Y. Wang, K. Wan, C. Zhang and T. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2112293 CrossRef CAS
.
- L. Wang, Y. Wang, S. Yang, X. Tao, Y. Zi and W. A. Daoud, Nano Energy, 2022, 91, 106611 CrossRef CAS
.
- K. Zhao, K. Zhang, R. A. Li, P. Sang, H. Hu and M. He, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 23714–23721 RSC
.
- C. Dang, F. Peng, H. Liu, X. Feng, Y. Liu, S. Hu and H. Qi, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 13115–13124 RSC
.
- X. Qu, W. Niu, R. Wang, Z. Li, Y. Guo, X. Liu and J. Sun, Mater. Horiz., 2020, 7, 2994–3004 RSC
.
- M. Wang, Z. Lai, X. Jin, T. Sun, H. Liu and H. Qi, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2101957 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. J. Kim, B. Chen, Z. Suo and R. C. Hayward, Science, 2020, 367, 773–776 CrossRef CAS
.
- L. Shi, T. Zhu, G. Gao, X. Zhang, W. Wei, W. Liu and S. Ding, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 2630 CrossRef PubMed
.
- J. Wang, C. Yan, G. Cai, M. Cui, A. Lee-Sie Eh and P. See Lee, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 4490–4496 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. Zhang, Y. Chen, Z. H. Guo, W. Guo, X. Pu and Z. L. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 1909252 CrossRef CAS
.
- Z. Czech and R. Milker, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2003, 87, 182–191 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Aleid, M. Wu, R. Li, W. Wang, C. Zhang, L. Zhang and P. Wang, ACS Mater. Lett., 2022, 4, 511–520 CrossRef CAS
.
-
M. D. Ellul, THE ROLE OF DIFFUSION IN THE ADHESION OF ELASTOMERS (ADSORPTION, BUTYL RUBBER, VISCOELASTICITY), The University of Akron, 1984 Search PubMed
.
- Y.-J. Wang, Y. He, S. Y. Zheng, Z. Xu, J. Li, Y. Zhao, L. Chen and W. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2104296 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Yan, Y. Wang, W. Shen, F. Li, G. Gao, T. Zheng, Z. Xu, S. Qian, C.-Y. Chen, C. Zhang, G. Yang and T. Chen, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2203241 CrossRef CAS
.
- B. Yiming, Y. Han, Z. Han, X. Zhang, Y. Li, W. Lian, M. Zhang, J. Yin, T. Sun, Z. Wu, T. Li, J. Fu, Z. Jia and S. Qu, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2006111 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2sm00865c |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |