Themed collection Mechanical Bond and Dynamic Covalent Bond

Mechanical bonds and dynamic covalent bonds
Jishan Wu and Fraser Stoddart introduce the Materials Chemistry Frontiers themed collection on mechanical bonds and dynamic covalent bonds.
Mater. Chem. Front., 2020,4, 1553-1553
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0QM90014A
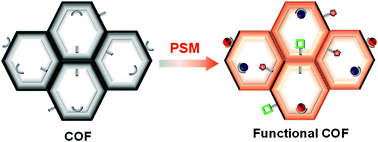
Tailored covalent organic frameworks by post-synthetic modification
This review describes recent advances and scientific challenges in the area of post-synthetic methodologies to tailor the functionalities and properties of COFs.
Mater. Chem. Front., 2020,4, 113-127
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00555B
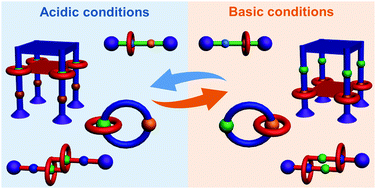
pH-Controlled motions in mechanically interlocked molecules
This review summarizes pH-controlled mechanical motions including translocation in rotaxanes, circumrotation in catenanes and other motions in more sophisticated mechanomolecules.
Mater. Chem. Front., 2020,4, 12-28
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00546C
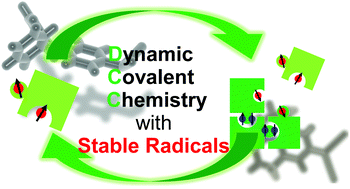
Dynamic covalent bonds: approaches from stable radical species
Dynamic covalent bonds by stable radical species are ideal platforms for simple, facile, and clean rearrangements of chemical bonds without the need for catalysts and the formation of byproducts.
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2270-2282
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00488B
Stimuli-responsive dynamic pseudorotaxane crystals
This review summarizes recent advances in dynamic pseudorotaxane crystals with response to external stimuli, such as light and/or heat.
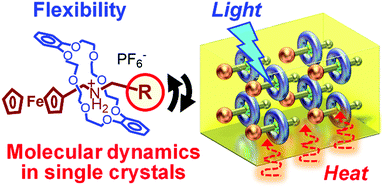
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2258-2269
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00483A
A dual-mode orthogonally tunable fluorescent system covering the whole white light region
This research revealed a distinct manipulation manner of a molecular emissive system, that is an orthogonally tunable dual-pathway mode, enabling a multi-color fluorescent system covering the whole white-light region.
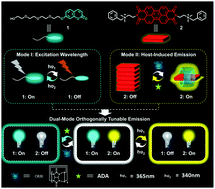
Mater. Chem. Front., 2020,4, 532-536
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00610A
Mechanofluorescent polymer/silsesquioxane composites based on tetraarylsuccinonitrile
Mechanofluorescent polymer/silsesquioxane composites were prepared by introducing tetraarylsuccinonitrile derivatives, which are mechanically cleaved to generate the corresponding pink carbon-centred radicals that exhibit yellow fluorescence.
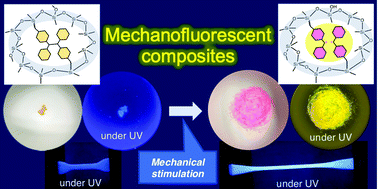
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2681-2685
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00535H
Supramolecular polymerization and cyclization of dioxynaphthalene motif bridged bifunctional UPys: minor variations in the molecular skeleton and drastic differences in self-assembly
Dramatic differences were disclosed in the supramolecular polymerizability of dioxynaphthalene motif bridged bifunctional ureidopyrimidinone isomers and their different host–guest behaviors with a blue-box.
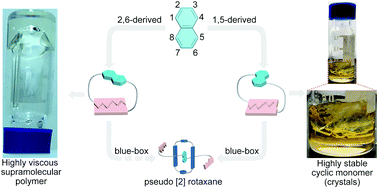
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2738-2745
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00595A
Push–pull type quinoidal perylene showing solvent polarity dependent diradical character and negative solvatochromism
A push–pull perylene dye shows solvent dependent diradical character and negative solvatochromism.
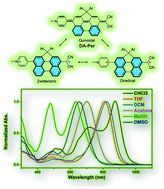
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2668-2672
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00566H
Synthesis of a cyclic poly(methyl acrylate) via topological transformation of a [1]rotaxane
Effective linear-to-cyclic polymer topology transformation of poly(methyl acrylate) (PMA) utilizing the translocation property of the introduced [1]rotaxane unit.
![Graphical abstract: Synthesis of a cyclic poly(methyl acrylate) via topological transformation of a [1]rotaxane](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C9QM00563C&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2019)
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2716-2720
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00563C
Ring size affects the kinetic and thermodynamic formation of [2]rotaxanes featuring an unsymmetric bis-crown ether component
Kinetically and thermodynamically favored [2]rotaxanes, with an axle component positioned within a large and small ring, respectively, were provided by bridging of a [2]pseudorotaxane formed from an unsymmetric mono-crown ether and the ammonium salt.
![Graphical abstract: Ring size affects the kinetic and thermodynamic formation of [2]rotaxanes featuring an unsymmetric bis-crown ether component](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C9QM00441F&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2019)
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2702-2706
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00441F
Water-compatible fluorescent [2]rotaxanes for Au3+ detection and bioimaging
Rotaxanes were studied for their selective sensing to trivalent metal ions and Au3+ with turn-on fluorescence and for bioimaging.
![Graphical abstract: Water-compatible fluorescent [2]rotaxanes for Au3+ detection and bioimaging](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C9QM00476A&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2019)
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2388-2396
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00476A
Molecular design to increase the photosensitivity of photochromic phenoxyl–imidazolyl radical complexes
An efficient strategy to increase the photosensitivity of a fast photochromic molecule is demonstrated by introducing aryl groups as sensitizers.
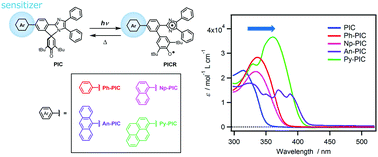
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2380-2387
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00468H
Facile synthesis of diverse rotaxanes via successive supramolecular transformations
Facile synthesis of diverse rotaxanes was successfully realized through a simple and efficient supramolecular transformation strategy.

Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 2397-2402
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00430K
Folic acid functionalized hollow nanoparticles for selective photodynamic therapy of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Folic acid conjugated hollow silica nanocarriers loaded with zinc phthalocyanine are employed for selective photodynamic therapy of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
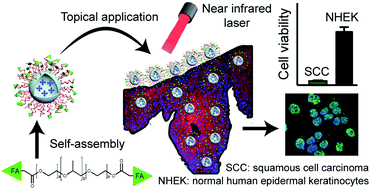
Mater. Chem. Front., 2019,3, 1113-1122
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QM00144A
About this collection
Welcome to Materials Chemistry Frontiers themed collection on “Mechanical Bond and Dynamic Covalent Bond”.
This themed collection covers the development of molecular structures and materials that are built on mechanical bond and dynamical covalent bond, including mechanically interlocked structures (catenanes, rotaxanes, molecular knots), molecular cages, covalent organic frameworks, responsive systems, etc.
Guest Editors: Jishan Wu (National University of Singapore) and Sir Fraser Stoddart (Northwestern University)
More articles will be added as soon as they are published.