Themed collection Plant responses to UV

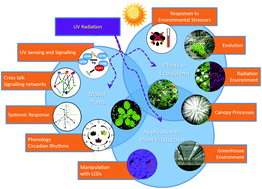
A perspective on ecologically relevant plant-UV research and its practical application
Plant UV research is at a juncture, whereby mechanistic knowledge of UV photoreceptor responses needs to be applied to ecologically relevant scenarios and put to practical use in plant production.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 970-988
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00526E
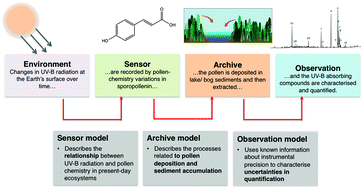
Fossil pollen and spores as a tool for reconstructing ancient solar-ultraviolet irradiance received by plants: an assessment of prospects and challenges using proxy-system modelling
A systematic evaluation of the uncertainties limiting the application of UV-B-absorbing compounds in pollen and spores to reconstruct UV-B irradiance.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 275-294
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00490K
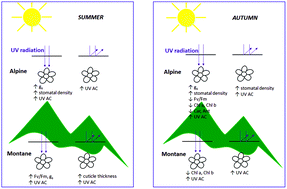
Effect of UV radiation and altitude characteristics on the functional traits and leaf optical properties in Saxifraga hostii at the alpine and montane sites in the Slovenian Alps
UV radiation affects the biochemical, physiological and morphological responses of plants.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2020,19, 180-192
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9PP00032A
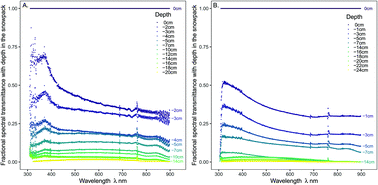
Transmission of ultraviolet, visible and near-infrared solar radiation to plants within a seasonal snow pack
Ultraviolet radiation is transmitted better than longer wavelengths through the upper centimetres of a seasonal snowpack, where about 10% of the incident photosynthetically active radiation reaches 7 cm depth.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 1963-1971
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9PP00197B
No evidence of a protective or cumulative negative effect of UV-B on growth inhibition induced by gamma radiation in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) seedlings
No protective or cummulative negative effect of UV-B on gamma radiation-induced growth inhibition in Scots pine seedlings in spite of additional DNA damage in response to UV-B.
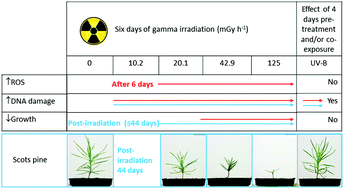
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 1945-1962
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00491A
Regulation of Arabidopsis gene expression by low fluence rate UV-B independently of UVR8 and stress signaling
Exposure of Arabidopsis to a low fluence rate of UV-B regulates a set of genes independently of UVR8 and stress signaling.
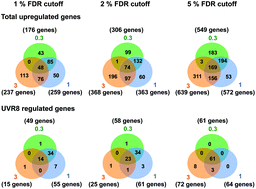
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 1675-1684
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9PP00151D
Different irradiances of UV and PAR in the same ratios alter the flavonoid profiles of Arabidopsis thaliana wild types and UV-signalling pathway mutants
UVR8, COP1 and HY5 all play an important role in the accumulation of flavonoids as a response to UV irradiation.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 1685-1699
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00496J
Hydroxycinnamic acids in sunflower leaves serve as UV-A screening pigments
Despite the weak absorption of hydroxycinnamic acids in the UV-A region, we found evidence that these compounds protect against damage induced by UV-A radiation in sunflowers.
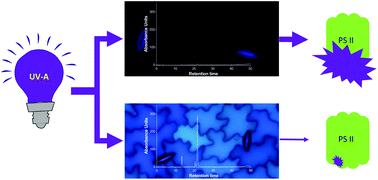
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 1649-1659
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00440D
UV-B exposure reduces the activity of several cell wall-dismantling enzymes and affects the expression of their biosynthetic genes in peach fruit (Prunus persica L., cv. Fairtime, melting phenotype)
UV-B radiation reduces the softening of peach fruit, thus improving their quality and shelf-life.
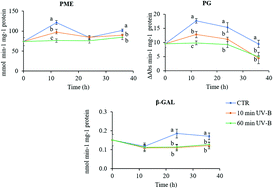
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 1280-1289
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00505B
UVR8-dependent reporters reveal spatial characteristics of signal spreading in plant tissues
We demonstrate the identification and application of molecular reporters and phenotypic traits to monitor the dynamics of the still largely unknown UVR8-dependent signalling pathways.

Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 1030-1045
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00492G
Responses of flavonoid profile and associated gene expression to solar blue and UV radiation in two accessions of Vicia faba L. from contrasting UV environments
The responses of growth, physiological traits, flavonoid profiles and gene expressions to solar blue and UV radiation differed in two accessions Aurora and ILB938 of Vicia faba.
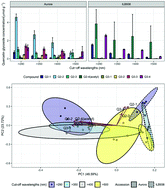
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 434-447
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00567B
Photosynthetically-active radiation, UV-A and UV-B, causes both common and specific damage and photoprotective responses in the model liverwort Marchantia polymorpha subsp. ruderalis
Damage caused by high PAR and UV-B was balanced by protection mechanisms induced by the same radiations.
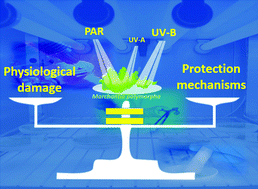
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 400-412
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00421H
UV regulates the expression of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis genes in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) in an organ and spectrum dependent manner
A combination of a substantial number of cis-acting regulatory elements (MREs, ACEs, and G-boxes) is present in promoters of copies of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis genes that show strongly enhanced expression under UV-B-containing light in Cucumis sativus.
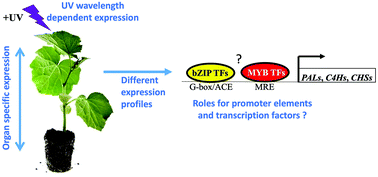
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 424-433
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00480C
Effects of water availability and UV radiation on silicon accumulation in the C4 crop proso millet
In proso millet, water shortage reduced leaf silicon, calcium, phosphorus, and sulphur levels, and ambient ultraviolet radiation reinforced this effect.
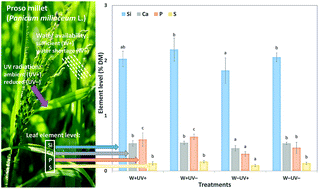
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 375-386
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00517F
UV-A screening in Cladophora sp. lowers internal UV-A availability and photoreactivation as compared to non-UV screening in Ulva intestinalis
UV-A screening reduces UV-A-driven photoreactivation of UV-B-induced DNA damage in the green macroalga Cladophora sp.
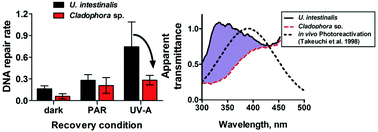
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 413-423
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00432C
A FRET method for investigating dimer/monomer status and conformation of the UVR8 photoreceptor
A Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) method is used to monitor dimer/monomer status and conformation of both wild-type and mutant variants of the UV-B photoreceptor UVR8 in vivo.
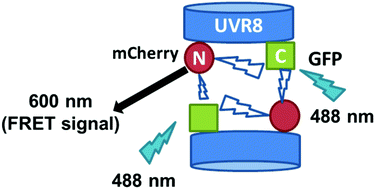
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 367-374
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00489G
Single-dose β-aminobutyric acid treatment modifies tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) leaf acclimation to consecutive UV-B treatment
β-Aminobutyric acid (BABA) pre-treatment affects acclimative plant responses to UV-B including leaf antioxidant capacities.
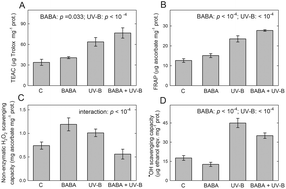
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 359-366
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00437D
Elevated air humidity increases UV mediated leaf and DNA damage in pea (Pisum sativum) due to reduced flavonoid content and antioxidant power
Growth in high relative air humidity causes diminished response to stomatal closing signals and increases susceptibility to UV-induced damage.
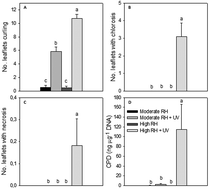
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 387-399
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00401C
About this collection
This collection highlights the breadth of research being undertaken to understand how plants respond to UV radiation in the environment. Some articles focus on the mechanisms of UV perception and the consequent regulation of gene expression and downstream responses, while others are concerned with ecological perspectives and applications in crop production.
The themed issue is based substantially on presentations given at the 2018 Network Meeting of UV4Plants, the international association for plant UV research, held in Bled, Slovenia. The meeting included workshop sessions involving researchers with diverse interests in plant UV research, which resulted in an extensive perspective article (see T. M. Robson et al.) integrating the broad spectrum of plant UV research and highlighting areas where future research could be directed.
Gareth I. Jenkins (Guest Editor)