Themed collection Bioinspired systems in supramolecular chemistry and nanotechnology

Bioinspired systems in supramolecular chemistry and nanotechnology – introducing the SupraBio themed issue
Welcome to this issue of New Journal of Chemistry featuring the themed issue “Bioinspired systems in supramolecular chemistry and nanotechnology”.
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5120-5121
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ90041C
Cationic liposome–nucleic acid complexes for gene delivery and gene silencing
The evolution of liposomes highlighting surface functionalization: from naked and PEGylated liposomes to PEGylated cationic liposome–nucleic acid nanoparticles for therapeutics.
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5164-5172
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ01314J
Bioinspired nanoarchitectonics as emerging drug delivery systems
Bioinspired nanoarchitectonics opens a new era for designing drug delivery systems.
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5149-5163
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00864B
Supramolecular immobilization of bio-entities for bioelectrochemical applications
Supramolecular systems based on host-guest, electrostatic, or metal-ligand interaction and their use in bioelectrochemical applications are reviewed.
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5173-5180
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00755G
Self-assembly of fatty acids: from foams to protocell vesicles
Stable aqueous dispersions of fatty acids can now be obtained and yield multiple applications.
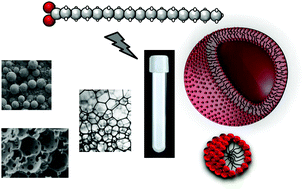
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5142-5148
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00914B
Compartmentalised chemistry: from studies on the origin of life to engineered biochemical systems
Splitting chemical reactions into microscale compartments is one of the greatest inventions of chemical evolution.
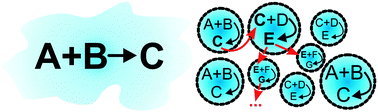
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5135-5141
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00894D
A hybrid lipid oligonucleotide: a versatile tool for supramolecular chemistry
Lipid oligonucleotides (LONs) self-assemble into supramolecular structures. This property has an impact on the biological effects of the oligonucleotide sequences.
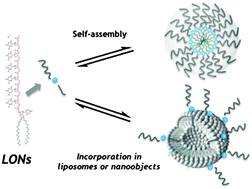
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5129-5134
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00850B
Guanosine and isoguanosine derivatives for supramolecular devices
Guanosine (G) and isoguanosine (isoG) derivatives can self-assemble, yielding supramolecules that have found broad applications in diverse fields.
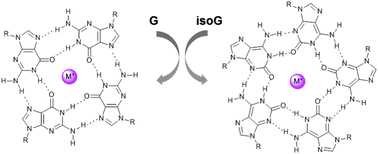
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5122-5128
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00665H
A reversible supramolecular assembly containing ionic interactions and disulfide linkages
A reversible ionic supramolecular assembly is described which can be disrupted and reformed by application of either a heating–cooling cycle or a mild redox reaction.
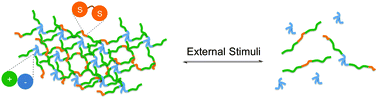
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5186-5189
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00895B
DNA-controlled aggregation of virus like particles – mimicking a tetherin-like mechanism
Lipophilic DNA with two α-tocopherol anchors, mimicking tetherin, a cell protein reducing spreading of viruses, induces aggregation of virus-like particles.
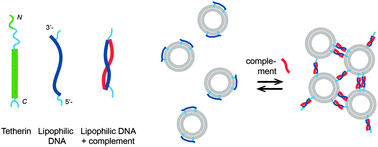
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5181-5185
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00724G
Diastereoselective self-assembly of clofarabine lipids
Clofarabine lipids form superstructures via diastereoselective self-assembly.
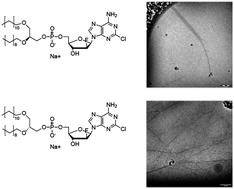
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5247-5253
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00856A
EPR based distance measurement in Cu-porphyrin–DNA
Measurement of EPR spectra of Cu-porphyrin–DNA reveals intermolecular interactions between the DNA strands with average distances of 6.5–8.9 Å.
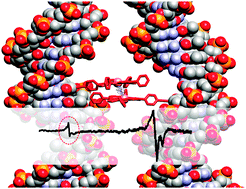
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5254-5259
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00673A
Cyclodextrin-scaffolded amphiphilic aminoglucoside clusters: self-assembling and gene delivery capabilities
The self-assembling and gene transfer capabilities of monodisperse amphiphilic aminoglucoside–cyclodextrin conjugates depend on the amino disposition at the glycationic head.
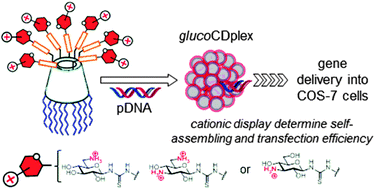
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5215-5225
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00700J
A releasable disulfide carbonate linker for polyethyleneimine (PEI)-based gene vectors
In the present research study, we used a releasable disulfide carbonate linker to construct polyethyleneimine-based gene vectors with regulated DNA release.
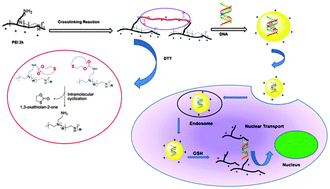
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5207-5214
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00699B
Efficient synthesis of small-sized phosphonated dendrons: potential organic coatings of iron oxide nanoparticles
Small-sized dendritic phosphonic acids are ideal coatings for iron oxide nanoparticles to be used in vivo.
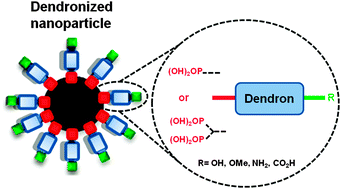
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5226-5239
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00654B
Nucleolipids as building blocks for the synthesis of 99mTc-labeled nanoparticles functionalized with folic acid
Nucleoside-lipids are efficient bio-inspired amphiphiles for the construction of nanoparticles for image-guided therapy applications.
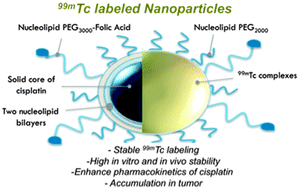
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5240-5246
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00559G
The impact of two –GlyProGly– motifs on formation of di-copper complexes by His4-cyclopeptides
The interactions of copper(II) ions with the macrocyclic peptide, c(HKHGPG)2, were investigated in aqueous solution as a function of pH by potentiometric titration, spectroscopic (UV-Vis, CD, and EPR) and mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) measurements.
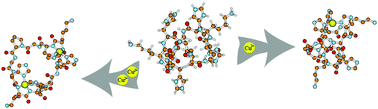
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5198-5206
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00689E
Lipidic spherulites as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents
Paramagnetic spherulites were successfully obtained following 3 grafting strategies of gadolinium chelate. Grafting onto lipid bilayers gave the best relaxivity results.
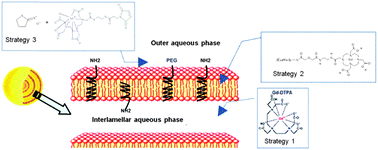
New J. Chem., 2014,38, 5190-5197
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00571F
About this collection
This themed collection, consisting of 7 review articles and 10 original research papers, covers various types of supramolecular systems at the biological interface: lipids, nucleic acids, peptides, DNA and also various hybrid systems and nanoparticles. Some of the contributions are oriented towards gaining deeper insights into a particular system (self-assembly properties, spectroscopy, intermolecular interactions). Other contributions are focused on applications, particularly in medicine (imaging contrast agents, gene delivery and gene silencing systems, drug delivery).