Themed collection Tuberculosis

Physicochemical properties and Mycobacterium tuberculosis transporters: keys to efficacious antitubercular drugs?
The physicochemical properties of TB drugs are compared oral drugs and antibiotics, which support likely roles for transporters contributing to their efficacy.
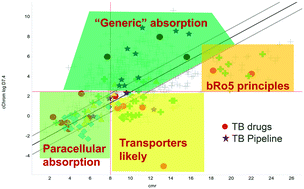
RSC Med. Chem., 2021,12, 43-56
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00265H
Mycobacterial drug discovery
Innovations in mycobacterial drug discovery to accelerate the identification of new drug candidates with confirmed targets and whole cell activity.
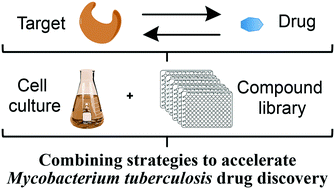
RSC Med. Chem., 2020,11, 1354-1365
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00261E
Elevated serum antibody responses to synthetic mycobacterial lipid antigens among UK farmers: an indication of exposure to environmental mycobacteria?
Antibody binding to trehalose mycolates, such as that shown, was evaluated in ELISA. Median responses with the serum of individuals with no known mycobacterial infection were low; some were very high, the majority from Welsh farmers older than 55.

RSC Med. Chem., 2021,12, 213-221
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00325E
Structure guided generation of thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-amine Mycobacterium tuberculosis bd oxidase inhibitors
Screening for inhibitors of Cyt-bd in Mycobacterium bovis BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis revealed thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine (7) which through SAR efforts resulted in an improved analogue (19) of this scaffold.
![Graphical abstract: Structure guided generation of thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-amine Mycobacterium tuberculosis bd oxidase inhibitors](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=D0MD00398K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2021)
RSC Med. Chem., 2021,12, 73-77
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00398K
Hydride-induced Meisenheimer complex formation reflects activity of nitro aromatic anti-tuberculosis compounds
The formation efficiency of hydride-induced Meisenheimer complexes of nitroaromatic compounds is consistent with their anti-TB activities exemplied by MDL860 and benzothiazol N-oxide (BTO) analogs.

RSC Med. Chem., 2021,12, 62-72
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00390E
Identification of P218 as a potent inhibitor of Mycobacterium ulcerans DHFR
P218 is a potent inhibitor of M. ulcerans DHFR (Ki 3.2 nM).

RSC Med. Chem., 2021,12, 103-109
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00303D
Itaconate is a covalent inhibitor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis isocitrate lyase
Mycobacterium tuberculosis isocitrate lyases (ICLs) form a covalent adduct with itaconate through their catalytic cysteine residue. These results reveal atomic details of itaconate inhibition and provide insights into the catalytic mechanism of ICLs.
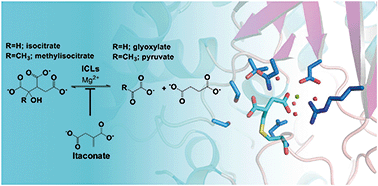
RSC Med. Chem., 2021,12, 57-61
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00301H
Structure–activity relationship studies on 2,5,6-trisubstituted benzimidazoles targeting Mtb-FtsZ as antitubercular agents
Filamenting temperature sensitive protein Z (FtsZ) is an essential bacterial cell division protein and a promising target for the development of new antibacterial therapeutics.
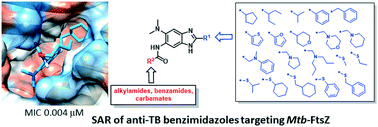
RSC Med. Chem., 2021,12, 78-94
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00256A
New insights into ethionamide metabolism: influence of oxidized methionine on its degradation path
Ethionamide (ETH) is a commercial drug, used as a second-line resource to neutralize Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections.
RSC Med. Chem., 2020,11, 1423-1428
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00253D
Meridianin D analogues possess antibiofilm activity against Mycobacterium smegmatis
This study identifies analogues of the natural product meridianin D that display increased ability to inhibit and disperse Mycobacterium smegmatis biofilms.
RSC Med. Chem., 2020,11, 92-97
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00466A
About this collection
Guest edited by Professor Sylvie Garneau-Tsodikova (University of Kentucky ) and Dr. Carlos Alemparte (GSK), this collection aims to highlight the exciting research and ongoing global efforts against Tuberculosis. New articles will be added to the collection upon publication.
Please return to this page frequently to see the collection grow.