Themed collection Green Biorefinery Technologies based on Waste Biomass

Green biorefinery technologies based on waste biomass
This themed issue includes a collection of articles on green biorefinery technologies based on waste biomass.
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1168-1170
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC90021G
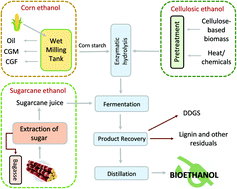
Emerging techniques in bioethanol production: from distillation to waste valorization
Ethanol production from biomass, especially waste biomass, and the use of such ethanol as fuel can reduce fossil fuel consumption and ameliorate the hidden costs of burning fossil fuels such as its environmental impact.
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1171-1185
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC02698J
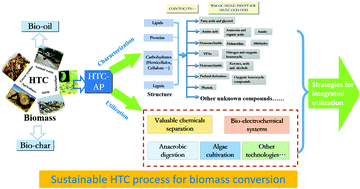
Characterization and utilization of aqueous products from hydrothermal conversion of biomass for bio-oil and hydro-char production: a review
Hydrothermal conversion (HTC), including hydrothermal liquefaction and hydrothermal carbonization, is a promising thermochemical technology for biomass utilization.
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1553-1572
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03957G
From waste biomass to chemicals and energy via microwave-assisted processes
Lignocellulosic waste material serves as a considerable renewable feedstock that could be used to replace oil refineries with biorefineries.

Green Chem., 2019,21, 1202-1235
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03908A
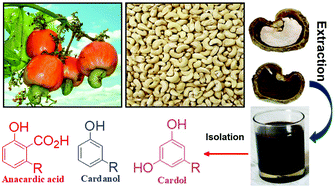
Cashew nut shell: a potential bio-resource for the production of bio-sourced chemicals, materials and fuels
Cashew nut shells, agro-waste generated from cashew nut factories, are rich in valuable bio-based green and renewable materials.
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1186-1201
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC02972E
Visible light-mediated and water-assisted selective hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived guaiacol to cyclohexanol
Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived guaiacol is achieved by magnetically separable bimetallic AgPd supported on carbon nitride using formic acid as H2 source; nitride support is obtainable via calcination of chitosan, a marine-derived renewable waste material.
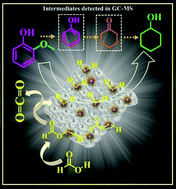
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1253-1257
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03951H
Synergetic conversion of microalgae and CO2 into value-added chemicals under hydrothermal conditions
CO2 (or HCO3−) is selectively reduced into formate with microalgae as the reductant, and simultaneously HCO3− significantly enhances the conversion of microalgae into organic acids and N-substituted lactam as the oxidant.
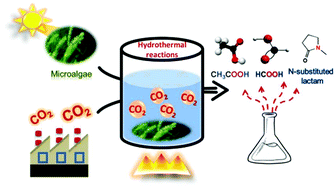
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1247-1252
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03645D
Ultrasound assisted ZnO coating in a microflow based photoreactor for selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde
Heterogeneous photocatalysis in a microflow system for generation of value added chemicals is a novel green chemistry approach requiring the understanding of photocatalysis, microfluidics and reactor design.
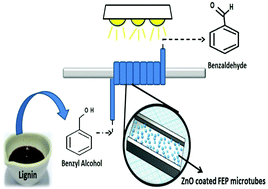
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1241-1246
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03131B
Using in vivo nickel to direct the pyrolysis of hyperaccumulator plant biomass
The effects of naturally occurring nickel in hyperaccumulator plants used for phytoremediation of contaminated soils on the microwave (MW) biomass pyrolysis are described for the first time.
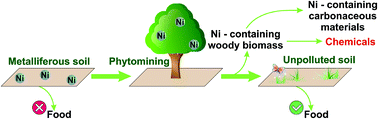
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1236-1240
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03015D
Functionalized chitosan adsorbents allow recovery of palladium and platinum from acidic aqueous solutions
Chitosan biosorbents for the recovery of palladium and platinum from aqueous waste streams.

Green Chem., 2019,21, 2295-2306
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC00166B
Direct electrochemical extraction increases microbial succinic acid production from spent sulphite liquor
The fermentative production of succinic acid leads to increasing toxicity over time, and requires continuous succinic acid removal from the broth to improve fermentation efficiency.
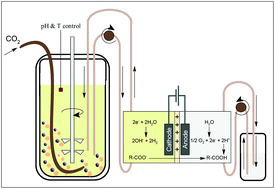
Green Chem., 2019,21, 2401-2411
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC00361D
Water-assisted selective hydrodeoxygenation of phenol to benzene over the Ru composite catalyst in the biphasic process
Schematic illustration of HDO of phenol to benzene in the biphasic catalytic process.
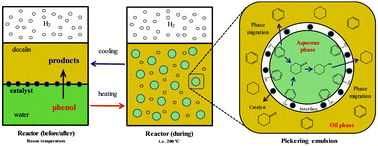
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1668-1679
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC04017F
Funneling aromatic products of chemically depolymerized lignin into 2-pyrone-4-6-dicarboxylic acid with Novosphingobium aromaticivorans
Lignin is an aromatic heteropolymer found in plant biomass.
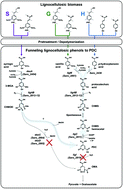
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1340-1350
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03504K
Granular fermentation enables high rate caproic acid production from solid-free thin stillage
Disc shaped microbial aggregates enriched in Ruminococcaceae and lactic acid bacteria produced caproic acid from solid-free thin stillage.
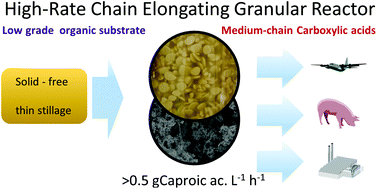
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1330-1339
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03648A
Aromatics from lignin through ultrafast reactions in water
Nowadays, the valorization of lignin, the major natural source of aromatics, is a challenge for the scientific community.
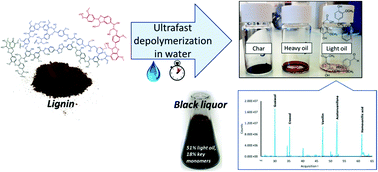
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1351-1360
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC03989E
Anaerobic conversion of the hydrothermal liquefaction aqueous phase: fate of organics and intensification with granule activated carbon/ozone pretreatment
Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) is considered to be a promising route for biofuel production from wet biomass.
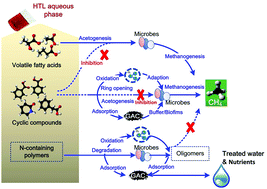
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1305-1318
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC02907E
Development of a waste-derived lignin-porphyrin bio-polymer with enhanced photoluminescence at high water fraction with wide pH range and heavy metal sensitivity investigations
A new lignin-porphyrin bio-polymer (AL-CTPP) for potential bio-imaging and heavy metals sensing.
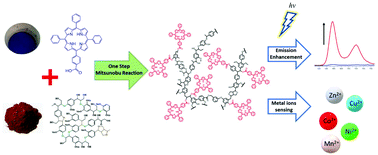
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1319-1329
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC02904K
Microbial electrochemical treatment of biorefinery black liquor and resource recovery
A microbial electrochemical process for energy-effective biorefinery black liquor treatment and in situ value-added product recovery.
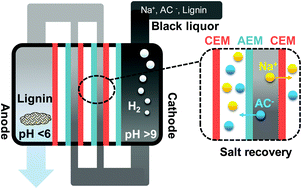
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1258-1266
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC02909A
Combining steam distillation with microwave-assisted pyrolysis to maximise direct production of levoglucosenone from agricultural wastes
The favourable impact of using a wet waste stream of agricultural residues in a biorefinery was studied through a combination of pyrolysis and self-induced steam distillation of hemicellulose depleted barley straw.
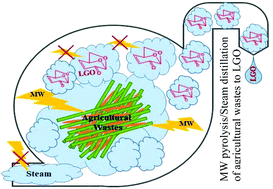
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1282-1291
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC02994F
An efficient magnetic carbon-based solid acid treatment for corncob saccharification with high selectivity for xylose and enhanced enzymatic digestibility
An efficient magnetic carbon-based solid acid treatment for corncob saccharification.
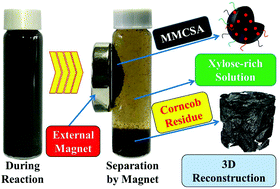
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1292-1304
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC02854K
Aluminium-biochar composites as sustainable heterogeneous catalysts for glucose isomerisation in a biorefinery
Novel and sustainable aluminium-biochar composite carries amorphous Al-oxygen species, providing Lewis acidity to catalyse isomerisation of glucose to fructose.
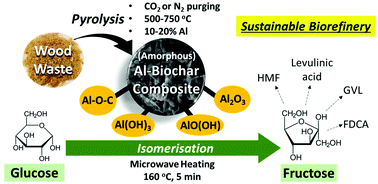
Green Chem., 2019,21, 1267-1281
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC02466A
About this collection
Biomass waste is rich in biodegradable organic matter and available in large quantities worldwide. The utilisation of biomass waste helps reduce pollution but can also provide renewable energy and bio-based chemicals for future society. Therefore, biomass waste resource utilisation has attracted increasing attention in scientific, industrial and government communities. Anaerobic digestion is an established technology widely applied in the utilisation of waste biomass but the (bio)gas produced from this process is of low value and the costs of pre-treatment reduce the cost-effectiveness; the chemical potential of the bio-resource is also lost. An increasing amount of new research is focused on the application of different technologies (including fermentation, hydrothermal conversion, pyrolysis, and microwave treatment) to make high value chemicals from biomass waste and thus improve resource utilisation. However, these technologies can suffer from high costs and secondary pollution. There is also a concern about separation steps since these can represent up to 80% of the total costs of many common chemical processes and this is likely to increase for bio-biomass based processes. The combination and ultimately integration of green technologies is crucial to realise the full potential of bio-wastes as chemical and energy resources.
The theme of this special issue, is to explore the status and development of chemical and biological technologies for waste biomass resource utilisation and with separations as a major theme.
Guest Edited by James H Clark (University of York), Vania Zuin (Federal University of São Carlos), Shicheng Zhang (Fudan University), Carol Sze Ki Lin (City University of Hong Kong), Buxing Han (Chinese Academy of Sciences), Christopher J. Chuck (University of Bath), Changwei Hu (Sichuan University), Christian Stevens (Ghent University) and Jiajun Fan (University of York).