Direct electrochemical extraction increases microbial succinic acid production from spent sulphite liquor†
Abstract
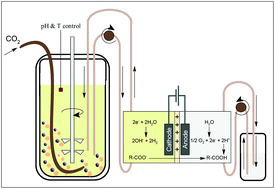
The fermentative production of succinic acid leads to increasing toxicity over time, and requires base addition to counteract acidification. Here we integrated a fed-batch Basfia succiniciproducens succinic acid fermentation with membrane electrolysis. This approach brings the broth in direct contact with an OH− and H2 producing cathode, and enables in situ extraction of succinate towards the low volume H+ and O2 producing anode compartment. In the latter, the succinate is acidified to succinic acid and precipitated. The key advantage of the cathodic process is the production of base maintaining fermentation pH with limited external base addition. The bacterial cells are recycled through the cathode compartment of the electrochemical cell, and exposed to H2, creating biological reducing power. Fermentations were executed with glucose, xylose and ultrafiltered spent sulphite liquor (SSL), the side stream generated via acidic sulphite pulping of Eucalyptus globulus wood. The membrane was not permeable to cells, color and solids, which resulted in combined succinate extraction, clarification, acidification and concentration in a single unit operation. The succinic acid to by-product ratio increased, favoring the production of succinic acid over lactic, formic and acetic acids, with up to 15% higher total sugars to succinic acid conversion yield. The OH− production due to water reduction resulted in lower NaOH usage (up to 33% less) for maintaining the pH during fermentation. The maximum productivity also increased by 30% to a rate of 0.41 g L−1 h−1 with the electrochemical system, with 1.65 kW h per kg succinic acid extracted in the case of SSL and 2.4 and 1.9 kW h per kg succinic acid extracted in the case of glucose and xylose, respectively. Considering the aforementioned advantages, this integrated system could evolve into a breakthrough technology in sustainable industrial succinic acid production from crude industrial side streams.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Green Biorefinery Technologies based on Waste Biomass


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...