Themed collection Nano-bio interactions

Tailoring nanomaterials towards global One Health: a promising nano-strategy against antibiotic resistance
Engineering nanomaterials to combat plant-associated antibiotic resistance for global One Health.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 1801-1808
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00854E
Metalloenzyme-inspired approach to the design and applications of phosphatase-mimetic nanozymes. Bridging the inorganic and organic worlds
Both nanozymes (cerium oxide) and natural enzymes can destroy toxic organophosphates (pesticide paraoxon ethyl) using analogous reaction mechanisms.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3268-3285
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00144C
Modern materials provoke ancient behavior: bacterial resistance to metal nanomaterials
Engineered nanomaterials are increasingly being used in a range of applications; it is important to characterize bacterial response to these novel materials.
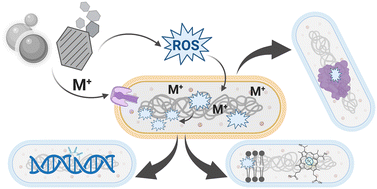
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 483-493
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00420A
The intersection of nanotechnology and urban agriculture: applications of carbon dots
Amidst the ongoing urbanization process, the significance of urban agriculture has garnered increasing attention.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 48-66
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00709C
Biologically synthesized Fe0-based nanoparticles and their application trends as catalysts in the treatment of chlorinated organic compounds: a review
Schematic representation for plant-mediated biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 1767-1788
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00843J
Nanozymes as a tool to boost agricultural production: from preparation to application
Nanozymes, as an emerging class of biomimetic enzymes, not only inherit the unique properties of nanomaterials but also endow them with catalytic functions that are similar to biological enzymes.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 98-120
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00780H
Plant nanobiotechnology: a new strategy to enhance crop photosynthesis
Primary mechanism through which nanomaterials enhance plant photosynthesis.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 4655-4665
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00520A
A critical review investigating the use of nanoparticles in cosmetic skin products
This review article focuses on current cosmetic ingredients claiming a nano nature, the unique characteristics of nanomaterials and their behaviour on the skin, how they can be suitable for natural cosmetics and nanocosmetic environmental fate.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3674-3692
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00489B
Mechanisms and applications of microbial synthesis of metal nanoparticles in agri-sectors
The synthesis method of metal nanoparticles and the form and application of microbial synthesis of metal nanoparticles.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2803-2830
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00174E
Nano-bioformulations: emerging trends and potential applications in next generation crop protection
Nano-bio-formulations for insect pest management.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2831-2860
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00263F
Mechanistic approaches for crosstalk between nanomaterials and plants: plant immunomodulation, defense mechanisms, stress resilience, toxicity, and perspectives
This review provides new insights for the development of nanomaterials with potential immunomodulatory effects in plants towards resistance against biotic and abiotic stresses.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2324-2351
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00053F
Classification, uptake, translocation, and detection methods of nanoparticles in crop plants: a review
Nanotechnology offers a viable solution to enhancing agricultural sustainability by supporting seed germination and crop growth.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1847-1870
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00059E
The nanosafety assessment of ENMs under a dermal exposure scenario: from key molecular events to in silico modeling tools
This review provides insights into key molecular events underlying ENMs toxicity under the dermal exposure scenario and the application of computational modeling tools in predicting the fate and toxicity of ENMs in nano-skin interactions.
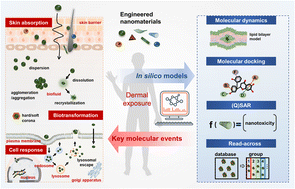
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 708-738
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00585B
A critical review on the toxicity regulation and ecological risks of zinc oxide nanoparticles to plants
This review clarifies the translocation of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) in plants, reveals the molecular mechanisms of toxicity regulation, and emphasizes the potential risks of composite systems of NPs.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 14-35
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00630A
Application of nano-agricultural technology for biotic stress management: mechanisms, optimization, and future perspectives
Nano-agricultural technology is a promising alternative for sustainable control crop biotic stress that has more economic and environmental benefits as compared with conventional analogues.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 4336-4353
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00651K
Nanomaterials for enhancing photosynthesis: interaction with plant photosystems and scope of nanobionics in agriculture
The complex process of photosynthesis requires precise arrangements of light harvesting molecules in the photosynthetic system.
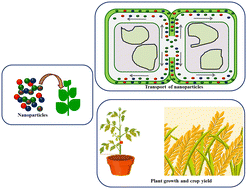
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3659-3683
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00451H
Carbon dots derived from natural sources and their biological and environmental impacts
Carbon dots derived from natural sources have drawn tremendous interest due to their superior characteristics. However, it is essential to evaluate both their biological and environmental impacts on contributions and the emerging concerns.
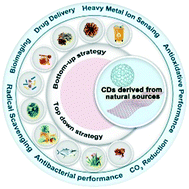
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3206-3225
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00435F
Correlation between the stability and toxicity of PFAS–nanoplastic colloids
PFAS adsorption on nanoplastics occurs in aqueous environments and the toxicity of the formed adducts increases with the colloidal stability.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 1821-1827
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00948G
Combining Trichoderma sp. and biogenic AgNPs from Trichoderma strains as a synergistic control complex to improve the growth of muskmelon and suppress Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis
The combination application of AgNPs and Trichoderma koningiopsis could control the MFW disease and improve the growth and development of muskmelon.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 2034-2049
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00760C
Nano zinc oxide activates MdCDF2 to promote DNA replication and cell proliferation in apple calli
The molecular mechanism of how ZnO NPs activate MdCDF2 to promote the growth of apple calli.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 1828-1839
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00997E
Upcycling plant waste: iron nanoparticles synthesized from Cannabis sativa enhance biomass and antioxidative properties in soybean (Glycine max)
Iron nanoparticles synthesized from hemp waste elevate the content of chlorophylls, antioxidants and polyphenols and improve the biomass of soybean.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 1669-1684
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN01018C
Effects of unmodified and amine-functionalized polystyrene nanoplastics on nitrogen removal by Pseudomonas stutzeri: strain characteristics, extracellular polymers, and transcriptomics
Schematic representation showing the mechanism underlying the differences in nitrogen removal performance of P. stutzeri caused by PS NPs and PS-NH2 NPs.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 1531-1544
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00983E
Luminous polystyrene upconverted nanoparticles to visualize the traces of nanoplastics in a vegetable plant
This study introduces a novel method for visualizing the uptake and accumulation of polystyrene nanoplastics in edible plants using luminous upconverted nanoparticles.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 1273-1287
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN01052C
Adaptive responses of Bacillus subtilis underlie differential nanoplastic toxicity with implications for root colonization
The toxicity of nanoplastics bound to plant growth-promoting bacteria strongly depends on their mode of growth, significantly limiting their ability to colonize roots.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 1477-1486
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00936C
Designing MOF-based green nanomaterials for enhanced pathogen resistance and pesticide degradation in tomato plants
Schematic representation showing the design and utilization of MOF-based green nanomaterials for enhanced pathogen resistance and pesticide degradation in tomato plants.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 1186-1201
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00966E
Synergistic effects of exogenous melatonin and zinc oxide nanoparticles in alleviating cobalt stress in Brassica napus: insights from stress-related markers and antioxidant machinery
The combined synergistic effects of exogenous melatonin (MT) and zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) in alleviating cobalt (Co) stress in Brassica napus (ZS 758).

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 368-387
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00821A
Multi-omics revealed the mechanisms of AgNP-priming enhanced rice salinity tolerance
AgNPs, as nanobiostimulants, increase the grain yield of rice grown in a saline land.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 466-480
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00685B
Salinity alters the toxicity of copper nanoparticles to anammox consortia through modulating extracellular polymeric substances and membrane permeability
Among numerous engineered nanoparticles (NPs), CuNPs have been identified as a kind of high-risk inhibitor to anammox bacteria; however, the potential effects of salinity on the toxicity of CuNPs to anammox consortia remain unclear.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 491-501
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00688G
Manganese-based nanozyme enabled efficient mitigation of Huanglongbing-induced oxidative damage in Citrus
Manganese oxide nanozymes (MONPs) facilitate the alleviation of Huanglongbing (HLB) symptoms in Citrus by mitigating oxidative stress.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2025,12, 701-715
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00519H
Biodegradable nanoparticles aid the gut microbial community in delaying antibiotic resistance emergence
The antibiotic-nanoparticle combinatorial treatment delays the rise in antibiotic resistance genes and minimizes adverse impacts on the gut microbiome compared to free antibiotics.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 4501-4512
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00382A
Antifungal profile and mechanism of bioinspired nanoscale magnesium against the agriculturally important pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum
Biogenic MgNPs suppress watermelon Fusarium wilt, caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum (Fon), through precisly targeting peroxin biogenesis-centered signaling events in Fon.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 4279-4292
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00548A
Biobased, biodegradable but not bio-neutral: about the effects of polylactic acid nanoparticles on macrophages
Macrophages treated with polylactide beads degrade them but show various responses in the meantime.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 4102-4116
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00335G
Rhizosphere regulation with cerium oxide nanomaterials promoted carrot taproot thickening
Nanomaterials (NMs) provide great potential for sustainable development by regulating rhizosphere processes to improve crop productivity.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3359-3373
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00334A
The endocrine disruptor effect of metal nanoparticles mainly depends on their capacity to release metal ions
This study compares the impact of different types of metal nanoparticles on major endocrine pathways. It shows that metal ions releasing ones such as silver nanoparticles inhibit Zn-finger dependent pathways, while rock solid nanoparticles do not.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3192-3201
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00065J
Exploring catalytic degradation of environmental fenamiphos by yeast enolase cross-linked with COOH-functionalized silver nanoparticles
This study investigated the sustainable hydrolysis of the neurotoxic organophosphate insecticide fenamiphos using enolase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae FN6-01.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3080-3091
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00052H
Iron oxide nanoparticles as enhancers of growth-promoting bacteria: a step towards developing nano-biofertilizers
Co-inoculation of IONPs and PGPB in the soybean seed treatment improves the seedling development of soybean and shows a viable alternative for use as a nano-biofertilizer or for improving the potential control of plant diseases in crops.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3053-3065
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00049H
Metal ion transport: unveiling the difference of nanoplastics and microplastics in Chiromantes dehaani glucolipid metabolism
Microplastic pollution has emerged as a prominent concern within the global environmental landscape, given its propensity for substantial accumulation in estuaries, thereby posing threats to both biodiversity and human food security.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2716-2729
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00045E
Construction of a nontoxic nano-pesticide and its co-application with natural predators for perfect cooperative pest management: an innovative strategy for pesticide reduction
The current study develops a nano-pesticide that is nontoxic toward the predatory stinkbug but with enhanced bioactivity toward the common cutworm, which proposes to co-apply the nano-pesticide with predator as an innovative pest control technique.
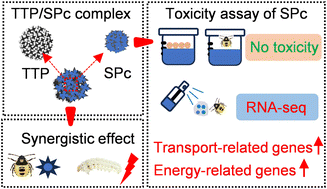
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1902-1914
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00060A
A multi-technique analysis of gelatin biodegradation on the surface of core–shell nanoparticles by Alteromonas macleodii extracellular proteases
Multi-technique characterization at the nanoscale of gelatin biodegradation on the surface of core–shell nanoparticles by extracellular proteases.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1429-1441
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00523B
Nature-derived gelatin-based antifungal nanotherapeutics for combatting Candida albicans biofilms
Biodegradable and all-natural gelatin-based nanoemulsions encapsulate and stabilize antifungal essential oils to provide efficient penetration and eradication of drug-resistant fungal biofilms without resistance generation.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 637-644
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00372H
Colloidal stabilization of hydrophobic InSe 2D nanosheets in a model environmental aqueous solution and their impact on Shewanella oneidensis MR-1
Exposure of InSe-EGCG to Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 decreases cell growth.
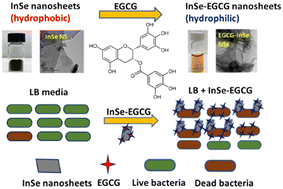
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 627-636
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00382E
Interaction of supported phospholipid bilayers with diamond nanoparticles non-covalently functionalized with a cationic polyelectrolyte
Cationic polymer-wrapped diamond nanoparticles interact with lipid bilayers to reveal the influence of phospholipid composition and surface charge on nanoparticle-membrane interactions.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 601-613
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00349C
Understanding the reaction mechanisms of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) with lithium cobalt oxide and other metal oxide nanomaterials
Biomolecules that have both redox capability and phosphate functionality undergo direct surface initiated redox with high-valent metal oxide nanoparticles, oxidizing the molecule and increasing Co release from the nanoparticles.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 518-528
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00351E
Influence of sensor composition on nanoparticle and protein interaction with supported lipid bilayers
Differences between protein adsorption to bilayers built on SiO2 or Au solid supports suggests that their behavior is affected by underlying substrate material and not just the proximal bilayer.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 561-577
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00406F
Nonmonotonic relationship between the degradation of black phosphorus and its bioactivity in suppressing the centrosome polo-like kinase 1
Molecular dynamics simulations are performed to reveal the degradation-dependent bioactivity of black phosphorus in suppressing the centrosome polo-like kinase 1.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 278-293
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00446E
Characterisation of a phosphatase-like nanozyme developed by baking cysteine and its application in reviving mung bean sprouts damaged by ash
Baked cysteine is mainly composed of cystine, a dimer with a SS bond. It acts as a nanozyme with phosphatase activity and an allosteric mechanism, repairs damage caused by ash to plant roots and germination and synergically combines with chlorophyll.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 266-277
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00415E
A dual pesticide–fertilizer silicon-base nanocomposite to synergistically control fungal disease and provide nutrition
The mixed utilization of pesticides and fertilizers plays an important role in the prevention of plant diseases and in providing nutrients for crop growth.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3462-3475
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00500C
Impact of nano-titanium dioxide extracted from food products on Caco-2 cells using three-phase digestion model
This work implicates Zn-mediated cellular processes in the mechanism of toxicological action of TiO2 nanoparticles. Improved understanding of mechanism of toxicological action will inform more proportionate and precautionary regulatory approaches.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3329-3342
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00549F
Single-cell metal–phenolic nanocoatings protect strictly anaerobic methanogens for methane production at an atmospheric oxygen level
MPN coating was formed on individual M. acetivorans surfaces by converting the TA–Fe2+ complex into TA–Fe3+ species, which reduced the contact of oxygen molecules with M. acetivorans and allowed M. acetivorans to produce methane in the presence of oxygen.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3379-3388
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00471F
Chitosan nanocarriers loaded with salicylic acid for controlling fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) and alleviating oxidative stress in maize plants
Foliar spraying with SA–CS nanocomposites (SCNs) significantly increased maize plant resistance against S. frugiperda by increasing defense compound (BX) production and anti-insect gene (Pep1, RIP2, MPI and JAR1a) expression.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3295-3306
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00532A
Reduction in insect attachment ability by biogenic and non-biogenic ZnO nanoparticles
ZnO-nanoparticles reduce the attachment ability of the green stinkbug Nezara viridula, a major pest worldwide, by aggregating on insect attachment devices. These findings can help to develop nontoxic pest-control methods that can be alternatives to insecticides.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3062-3071
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00545C
Biogenic FeS nanoparticles modulate the extracellular electron transfer and schwertmannite transformation
Iron sulfide nanoparticles (e.g., FeS NPs), which are ubiquitous in sulfate (SO42−)-rich anaerobic environments, can act as an electrical wire for long-distance extracellular electron transfer (EET) and bridge spatially discrete redox environments.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2733-2743
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00316G
DNA delivery by high aspect ratio nanomaterials to algal chloroplasts
Single walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are coated with polyethylenimine (PEI) of different molecular weight for DNA delivery into algal chloroplasts without the use of mechanical aid for understanding their impact on cell viability and function.
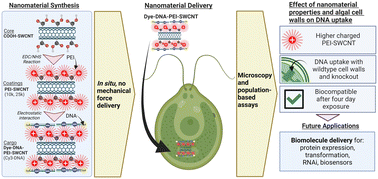
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2890-2903
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00268C
Carbon dots enhanced cold tolerance of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.): scavenging reactive oxygen species, modulating hormones and up-regulating gene expression
Herein, carbon dots (CDs) improving lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) growth and cold tolerance under low-temperature stress (4 °C) were investigated.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2849-2860
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00257H
The heterogeneous diffusion of polystyrene nanoparticles and the effect on the expression of quorum-sensing genes and EPS production as a function of particle charge and biofilm age
Biofilms are abundantly present in both natural and engineered environmental systems and will likely influence broader particle fate and transport phenomena.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2551-2565
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00219E
Comparing the inhibitory effects of CuO-rGO, CuO NPs, and CuCl2 on the oomycete Phytophthora sojae: insights from phenotypic and transcriptomic analyses
The antibacterial mechanism involves inducing oxidative stress, resulting in disruptions to the mycelial cell membrane, intracellular structure, and various metabolic processes.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2299-2311
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00363A
Silicon quantum dots promote radish resistance to root herbivores without impairing rhizosphere microenvironment health
Soil-applied silicon quantum dots (Si QDs) significantly increased radish taproot resistance against white grubs and simultaneously shaped a healthy rhizosphere microenvironment.
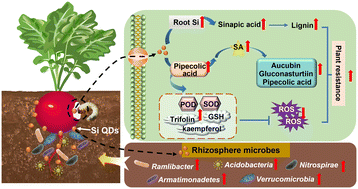
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2232-2244
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00368J
Charged nanoplastics differentially affect the conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes
The transfer of antibiotic resistance genes was influenced by the concentration and surface charge of nanoplastics. This was due to a combination of the promotion effect of ROS and the inhibition caused by nanoplastic agglomeration.
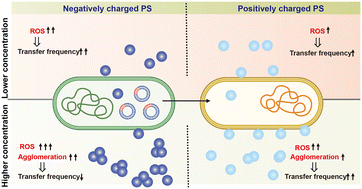
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2273-2285
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00229B
Cerium oxide nanomaterials improve cucumber flowering, fruit yield and quality: the rhizosphere effect
Cerium oxide nanomaterials improved cucumber flowering, fruit yield and quality: the rhizosphere effect.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2010-2021
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00213F
Chitosan–silica nanocomposites induced resistance in faba bean plants against aphids (Acyrthosiphon pisum)
Chitosan–silica nanocomposites enhanced faba bean plant resistance against aphids by increasing the production of anti-insect metabolites.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1966-1977
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00234A
Chronic exposure to complex metal oxide nanomaterials induces production of reactive oxygen species in bacteria
Chronic exposure of Shewanella oneidensis to nanoscale lithiated nickel manganese cobalt oxide induces ROS production in the bacteria, filamentation, vesicle formation, DNA damage, and evolution of resistance to other stressors such as antibiotics.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1978-1992
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01144A
Does the doping strategy of ferrite nanoparticles create a correlation between reactivity and toxicity?
The doping strategy of ferrite nanoparticles induced a correlation between their reactivity and toxicity. The evidence showed the induction of biological responses as a factor of their dissolution and suspension properties of ferrite nanoparticles.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1553-1569
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00076A
Emerging investigator series: differential effects of carbon nanotubes and graphene on the tomato rhizosphere microbiome
Carbon nanotube induces stronger and unique microbiome alterations in the tomato rhizosphere compared to the bulk soil, whereas graphene has a limited impact on soil microbiomes.
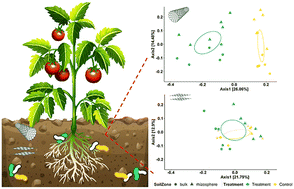
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1570-1584
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01026G
Effective control of the tomato wilt pathogen using TiO2 nanoparticles as a green nanopesticide
TiO2 NPs are a novel nanopesticide for tomato wilt pathogen control. The antibacterial mechanism of intracellular ROS production is different from traditional concepts.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1441-1452
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00059A
Polystyrene nanoplastics foster Escherichia coli O157:H7 growth and antibiotic resistance with a stimulating effect on metabolism
Exposure to nano-polystyrene has the potential to increase the risk of Escherichia coli O157:H7 contamination in aquatic environments.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1341-1351
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00982J
Nanoplastics promote the dissemination of antibiotic resistance through conjugative gene transfer: implications from oxidative stress and gene expression
S-PSNPs facilitated conjugative transfer frequency of ARGs between E. coli strains than L-PSNPs, and the mechanisms include SOS response, membrane permeability and altered related gene expression.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1329-1340
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01036D
Cellular mechanisms of transcriptional regulation of human cell lines exposed to cadmium-based quantum dots
CdS QDs activate calcium signaling and apoptosis in HepG2 human hepatocytes. CdS QDs trigger inflammatory response and autophagy in THP-1 human macrophages.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1177-1189
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01044E
Comparison of biokinetic models for non-dissolvable engineered nanomaterials in freshwater aquatic organisms
Understanding the uptake and elimination kinetics of engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) in aquatic organisms is essential for their environmental risk assessment.
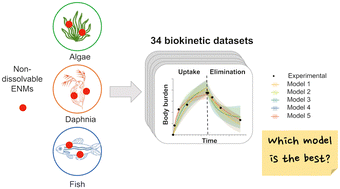
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1065-1076
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01039A
A MOF-based pH-responsive dual controlled-release system for herbicide pretilachlor and safener AD-67 delivery that enhances the herbicidal efficacy and reduces side effects
The herbicide-safener dual controlled release system AD-67@Pre@ZIF-67 was successfully prepared for the high efficiency and low toxicity of herbicide.
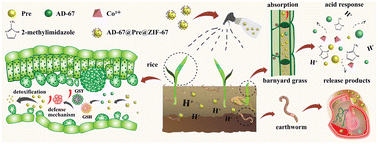
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1016-1029
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01093C
A promising approach to an environmentally friendly pest management solution: nanocarrier-delivered dsRNA towards controlling the destructive invasive pest Tuta absoluta
Nanocarrier-delivered dsRNA can be a promising environmentally friendly pest management solution.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1003-1015
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01076C
About this collection
This web collection includes research articles published in Environmental Science: Nano featuring nano-bio interactions.