Themed collection Analytical Toxicology of Nanoparticles

Editorial – Analytical Toxicology of Nanoparticles
This Editorial introduces Analyst's themed collection on the Analytical Toxicology of Nanoparticles, guest edited by Christy L. Haynes.

Analyst, 2014,139, 868-869
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN90114A
Chip based single cell analysis for nanotoxicity assessment
A microfluidic CoC system was developed for nanotoxicity assessment at single and multiple cell levels which can measure and compare the microscopic and macroscopic effects of nanoparticles interaction with cells, without interference from neighbor cells' cues and also overall integrative effects produced by nanoparticles and cell–cell communication.

Analyst, 2014,139, 2088-2098
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN02280C
ATR-FTIR spectroscopy as a tool to probe surface adsorption on nanoparticles at the liquid–solid interface in environmentally and biologically relevant media
Given the importance of nanoparticle surface composition in nanotoxicology, analytical tools that can probe nanoparticle surfaces in aqueous media are crucial but remain limited.

Analyst, 2014,139, 870-881
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01684F
Molecular interactions of nanomaterials and organisms: defining biomarkers for toxicity and high-throughput screening using traditional and next-generation sequencing approaches
The expression of molecular pathways in an organism provides a clue as to the potential impacts of exposure to nanomaterials.

Analyst, 2014,139, 882-895
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01644G
Proteomic evaluation of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles toxicity in Daphnia magna
Using a redox-proteomics approach, this study demonstrates that silver nanoparticles and AgNO3 affect the proteome differently, indicating different biological impacts.
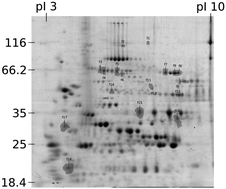
Analyst, 2014,139, 1678-1686
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN02160B
Using citrate-functionalized TiO2 nanoparticles to study the effect of particle size on zebrafish embryo toxicity
TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) are photoactive, potentially producing toxicity in vivo in the presence of sunlight.
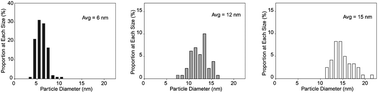
Analyst, 2014,139, 964-972
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01966G
Centrifugation-based assay for examining nanoparticle–lipid membrane binding and disruption
A simple but effective assay is described where nanoparticle binding to model cell membranes can be quickly assessed as a function of nanoparticle surface chemistry and membrane composition.

Analyst, 2014,139, 973-981
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01601C
Integrated approach to evaluating the toxicity of novel cysteine-capped silver nanoparticles to Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
The toxicity of cysteine capped Ag nanoparticles to E. coli and P. aeruginosa was evaluated using an integrated approach that measured particle dissolution, bacterial growth, and effects on cell membranes.
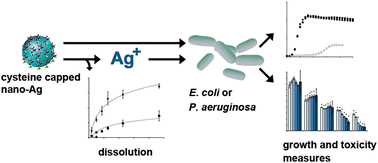
Analyst, 2014,139, 954-963
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01648J
On-chip evaluation of platelet adhesion and aggregation upon exposure to mesoporous silica nanoparticles
Schematic of on-chip platelet adhesion/aggregation assay platform.

Analyst, 2014,139, 906-913
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01679J
Association rule mining of cellular responses induced by metal and metal oxide nanoparticles
Relationships among different cellular response types, induced by exposure to metal and metal–oxide nanoparticles, were identified via association rule mining.
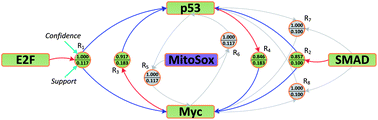
Analyst, 2014,139, 943-953
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01409F
Paracrine signalling of inflammatory cytokines from an in vitro blood brain barrier model upon exposure to polymeric nanoparticles
Nanoparticles can cause a signalling response across an in vitro blood-brain barrier model.
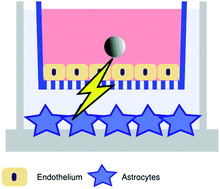
Analyst, 2014,139, 923-930
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01621H
Mid-infrared spectroscopic assessment of nanotoxicity in Gram-negative vs. Gram-positive bacteria
Vibrational spectroscopy provides a spectral fingerprint identifying the effects of carbon-based nanoparticles in bacterial cells.

Analyst, 2014,139, 896-905
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01649H
Reprotoxicity of gold, silver, and gold–silver alloy nanoparticles on mammalian gametes
The influence of metal and alloy nanoparticles on the functionality and viability of farm animal derived oocytes and sperm was examined to increase our understanding of nanoparticle reprotoxicity.
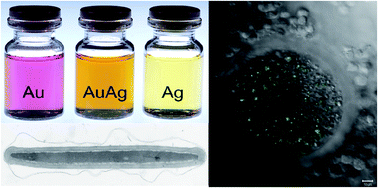
Analyst, 2014,139, 931-942
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01463K
Detection and characterization of silver nanoparticles and dissolved species of silver in culture medium and cells by AsFlFFF-UV-Vis-ICPMS: application to nanotoxicity tests
A methodology based on asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation coupled with UV-Vis absorption spectrometry and ICP mass spectrometry has been applied to the study of silver nanoparticles and dissolved species in cytotoxicity tests.
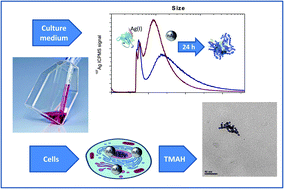
Analyst, 2014,139, 914-922
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01443F
About this collection
This collection of papers highlights the analytical challenges in nanoparticle research with papers coming from a wide variety of disciplines including analytical chemistry, surface science, soil science, and freshwater biology. The collection is Guest Edited by Christy Haynes. New articles will be added to this collection as they are published.