Synthesis and biological evaluation of pyrazolo–triazole hybrids as cytotoxic and apoptosis inducing agents†
Abstract
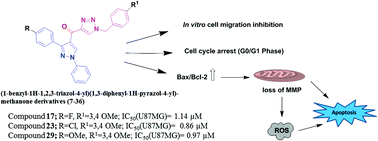
A series of pyrazolo–triazole hybrids were designed and synthesized by combining the 1,3-diphenyl pyrazole and triazole scaffolds to obtain (1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methanones. All the synthesized compounds were screened for their anticancer activity against four tumor cell lines, viz. HT-29 (colon), PC-3 (prostate), A549 (lung), and U87MG (glioblastoma) cells. Most of the tested compounds showed moderate to potent cell growth inhibition on different cancer cells, in particular, the compounds 17, 23, and 29 exhibited promising cytotoxicity against these cell lines with the IC50 values in the range of 0.86–3.72 μM. In addition, the potential mechanism of cell growth inhibition and apoptotic induction by these compounds was investigated in U87MG cancer cells using cell-based assays, including wound healing assay, flow cytometry, Hoechst staining, acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining, Annexin V-FITC/propidium Iodide dual staining, Rhodamine 123 staining, and carboxy-DCFDA staining. The results indicate that the compounds induce apoptosis in U87MG cells via mitochondrial pathway through up-regulation of pro-apoptotic (Bax) and down-regulation of anti-apoptotic (Bcl-2) genes. Based on these studies, three compounds 17, 23 and 29 have been identified as promising new molecules that have the potential to be developed as leads.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...