New di-n-butyltin(iv)-bis-(1-alkoxy-isoquinoline-4-nitrile thiolate): crystallographic and computational studies†
Abstract
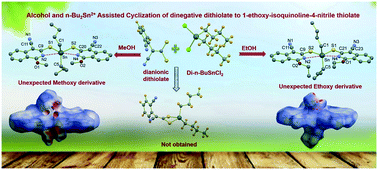
The reaction between di-n-butyltin(IV) chloride with the dinegative dithiolate ligand 2-(cyanobenzo)nitrile-dithiolate in two different alcoholic media viz. methyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol fortuitously yielded di-n-butyltin(IV)-bis-(1-methoxy-isoquinoline-4-nitrile thiolate) (Sn-Me) and di-n-butyltin(IV)-bis-(1-ethoxy-isoquinoline-4-nitrile thiolate) (Sn-Et). Similarly the reaction of di-n-butyltin(IV) chloride with 2-methoxy phenyl acetonitrile dithiolate yielded di-n-butyltin(IV)-2-methoxy phenyl acetonitrile dithiolate (2-MeCN-Sn). These compounds have been characterized by micro analyses, IR, UV-vis, 1H, 13C and 119Sn NMR spectroscopy as well as by single crystal X-ray diffraction technique in case of Sn-Et, Sn-Me. The X-ray analyses revealed that in both Sn-Me and Sn-Et, the Sn(IV) center adopts a skew trapezoidal bipyramidal geometry with Sn at the centre and two sulfur and two ring nitrogen atoms of 1-alkoxy-isoquinoline-4-nitrile thiolates are at the corners of a trapezoid with two n-butyl groups adopting axial positions resembling the cis–trans pathway. Both Sn-Me and Sn-Et display varied types of non-covalent interactions. The nature of these interactions has been addressed with the aid of Hirshfeld surface analysis, density functional theory and quantum theory of atoms-in-molecules (QTAIM) analyses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...