Curcumin supplementation improves biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation in conditions of obesity, type 2 diabetes and NAFLD: updating the status of clinical evidence
Abstract
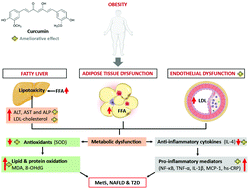
Oxidative stress and inflammation remain the major complications implicated in the development and progression of metabolic complications, including obesity, type 2 diabetes (T2D) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In fact, due to their abundant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, there is a general interest in understanding the therapeutic effects of some major food-derived bioactive compounds like curcumin against diverse metabolic diseases. Hence, a systematic search, through prominent online databases such as MEDLINE, Scopus, and Google Scholar was done focusing on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) reporting on the impact of curcumin supplementation in individuals with diverse metabolic complications, including obesity, T2D and NAFLD. Summarized findings suggest that curcumin supplementation can significantly reduce blood glucose and triglycerides levels, including markers of liver function like alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in patients with T2D and NAFLD. Importantly, this effect was consistent with the reduction of predominant markers of oxidative stress and inflammation, such as the levels of malonaldehyde (MDA), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in these patients. Although RCTs suggest that curcumin is beneficial in ameliorating some metabolic complications, future research is still necessary to enhance its absorption and bioavailability profile, while also optimizing the most effective therapeutic doses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...