MUFA in metabolic syndrome and associated risk factors: is MUFA the opposite side of the PUFA coin?
Abstract
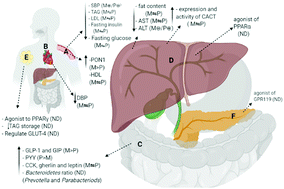
Omega-9 fatty acids represent some of the main mono-unsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) found in plant and animal sources. They can be synthesized endogenously in the human body, but they do not fully provide all the body's requirements. Consequently, they are considered as partially essential fatty acids. MUFA represent a healthier alternative to saturated animal fats and have several health benefits, including the prevention of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and its complications. This review concentrates on the major MUFA pharmacological activities in the context of MetS management, including alleviating cardiovascular disease (CVD) and dyslipidemia, central obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The beneficial effects of MUFA for CVD were found to be consistent with those of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) for the alleviation of systolic and diastolic blood pressure and high low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLc) and triacylglcerol (TAG) levels, albeit MUFA had a more favorable effect on decreasing night systolic blood pressure (SBP). To reduce the obesity profile, the use of MUFA was found to induce a higher oxidation rate with a higher energy expenditure, compared with PUFA. For NAFLD, PUFA was found to be a better potential drug candidate for the improvement of liver steatosis in children than MUFA. Any advantageous outcomes from using MUFA for diabetes and insulin resistance (IR) compared to using PUFA were found to be either non-significant or resulted from a small number of meta-analyses. Such an increase in the number of studies of the mechanisms of action require more clinical and epidemiological studies to confirm the beneficial outcomes, especially over a long-term treatment period.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...