Formation of CaUO2(CO3)32− and Ca2UO2(CO3)3(aq) complexes at variable temperatures (10–70 °C)†
Abstract
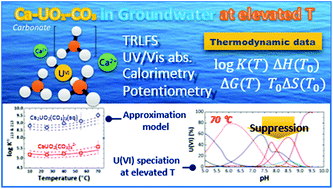
The ternary complexation of calcium uranyl tricarbonate species, CaUO2(CO3)32− and Ca2UO2(CO3)3(aq), which are the predominant U(VI) complexes in groundwater and seawater, was investigated at variable temperatures from 10 to 70 °C. Time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS), calcium ion-selective electrode potentiometry, and ultraviolet/visible (UV/Vis) absorption spectroscopy were complementarily employed to determine the formation constants (log Kx13, x = 1 and 2 for mono- and dicalcium complexes, respectively). 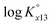 at infinite dilution (zero ionic strength) was determined by correction using specific ion interaction theory (SIT), and an increasing tendency of
at infinite dilution (zero ionic strength) was determined by correction using specific ion interaction theory (SIT), and an increasing tendency of 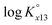 with temperature was observed. In addition, the molar enthalpy of complexation (ΔrHm) was measured by calorimetry at 25 °C. Based on thermodynamic data obtained in this work, the approximation models were examined for the prediction of the temperature effect on the complexation, and the constant enthalpy approximation with the chemical complexation reaction modified to an isoelectric reaction showed a satisfactory prediction of
with temperature was observed. In addition, the molar enthalpy of complexation (ΔrHm) was measured by calorimetry at 25 °C. Based on thermodynamic data obtained in this work, the approximation models were examined for the prediction of the temperature effect on the complexation, and the constant enthalpy approximation with the chemical complexation reaction modified to an isoelectric reaction showed a satisfactory prediction of 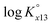 in the temperature range of 10–70 °C. Finally, the results of U(VI) speciation in groundwater indicated that the dominance of calcium uranyl tricarbonate complexes would be weakened at elevated temperatures by the strongly enhanced hydrolysis of U(VI).
in the temperature range of 10–70 °C. Finally, the results of U(VI) speciation in groundwater indicated that the dominance of calcium uranyl tricarbonate complexes would be weakened at elevated temperatures by the strongly enhanced hydrolysis of U(VI).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...