BSA-modified poly(pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid) nanoparticles as carriers for combined chemo-photothermal therapy
Abstract
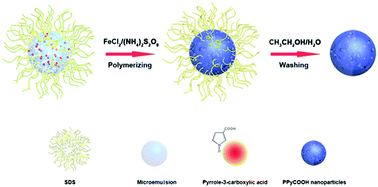
A facile reverse microemulsion method was developed for the synthesis of homogenous poly(pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid) (PPyCOOH) nanoparticles, which used n-heptane as the oil phase, sodium dodecyl sulfate as the surfactant, 1-butanol as the co-surfactant and pyrrole-3-carboxylic solution as the aqueous phase. The obtained PPyCOOH nanoparticles had uniform sizes, high near-infrared absorption and abundant functional groups. To improve their stability and enhance the tumor inhibition rate, the PPyCOOH nanoparticles were modified with bovine serum albumin (BSA) and doxorubicin (DOX). The as-fabricated drug delivery system (DOX@BSA-PPyCOOH) combining photothermal therapy and chemotherapy exhibited pH-sensitive and near infrared laser controlled drug release, which was beneficial for drug enrichment in the tumor and for reducing the toxicity and side effects in normal tissue. Combined chemo-photothermal therapy in vivo revealed that the tumors were completely eliminated and no obvious toxicity was found in the major organs, suggesting that DOX@BSA-PPyCOOH nanoparticles are an efficient nanoagent for cancer treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...