Layer charge robust delamination of organo-clays†
Abstract
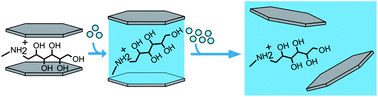
To date delamination of organo-clays is restricted to highly charged, vermiculite-type layered silicates (e.g. n-butylammonium vermiculites) while – counterintuitively – low charged, smectite-type layered silicates do not delaminate although their Coulomb interactions are much weaker. Guided by previous findings, we now identified organo-cations that allowed for extending the delamination of organo clays to charge densities in the regime of low charged smectites as well. Upon intercalation of protonated amino-sugars like N-methyl-D-glucamine (meglumine) robust delamination of 2 : 1 layered silicates via repulsive osmotic swelling in water is achieved. This process is stable over a wide range of charge densities spanning from smectites (layer charge x ∼ 0.3 charges per formula unit Si4O10F2, p.f.u.) to vermiculites (x ∼ 0.7 p.f.u.). It is evidenced that a combination of first, a sufficiently large charge equivalent area (bulkiness) of meglumine with second, a significant hydrophilicity of meglumine leads to swelling above a threshold d-spacing of ≳17.5 Å in moist air (98% r.h.). Hereby, electrostatic attraction is critically weakened, causing the onset of repulsive osmotic swelling which leads to utter delamination. Moreover, meglumine renders delamination tolerant to charge heterogeneities typically found in natural and synthetic clays.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...