A direct route from white phosphorus and fluorous alkyl and aryl iodides to the corresponding trialkyl- and triarylphosphines†
Abstract
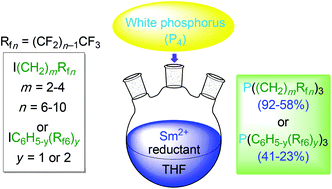
Reactions of white phosphorus (P4), fluorous alkyl iodides I(CH2)mRfn (Rfn = CF3(CF2)n−1; 4.0–5.0 equiv./P), and SmI2 (1.0–1.5 equiv./iodide) in THF afford the corresponding trialkylphosphines P((CH2)mRfn)3 (m,n = 2,8; 2,10; 3,6; 3,8; 4,8; 58–92% after workup). Similar reactions with the fluorous aryl iodides IC6H4(3-Rf6), IC6H4(4-Rf6), and IC6H3(3,5-Rf6)2 require the stronger reductants SmBr2 or SmCl2 and give the triarylphosphines P(C6H4(3-Rf6))3, P(C6H4(4-Rf6))3, and P(C6H3(3,5-Rf6)2)3 (23–41%). These transformations involve non-chain radical additions to P4. Advantages versus existing routes to fluorous phosphines, and general strategic issues in the synthesis of organophosphorus compounds, are discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...