Sustainable and scalable synthesis of monodisperse carbon nanospheres and their derived superstructures†
Abstract
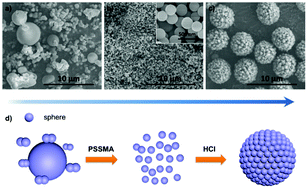
Carbon nanospheres and their derived superstructures have attracted increasing attention due to their widespread applications ranging from electrochemistry to catalysis. However, it remains a great challenge to achieve mass production of biomass-derived monodisperse carbon nanospheres with a diameter <400 nm and their derived superstructures with a controlled size. Here, monodisperse and uniform nanospheres ranging from 120 to 360 nm were synthesized with the introduction of a small amount of poly(4-styrenesulfonic acid-co-maleic acid) sodium salt (PSSMA) to the hydrothermal system. In addition, spherical superstructures constructed of nanospheres with an adjustable size from 1.4 to 5.2 μm were fabricated in the presence of both PSSMA and hydrochloric acid. Moreover, carbonized carbon superstructures showed good performance as supports for catalytic hydrogenation. These findings may open up a new avenue for designing increasingly complex functional biomass-derived materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...