Design of naturally derived lead phytate as an electrocatalyst for highly efficient CO2 reduction to formic acid†
Abstract
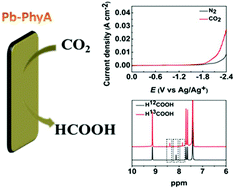
Utilization of naturally occurring resources to design electrocatalysts for CO2 transformation is environmentally and economically compelling. Herein, we describe the first work on the utilization of naturally occurring phytic acid (PhyA) as the building block to prepare lead phytate (Pb-PhyA) as an electrocatalyst for CO2 electro-reduction to HCOOH. The prepared Pb-PhyA exhibited excellent performance in an ionic liquid based catholyte, and the faradaic efficiency of HCOOH could reach 92.7% at a high current density (30.5 mA cm−2) in a ternary electrolyte consisting of [Bzmim]BF4 (12.8 wt%), H2O (9.9 wt%) and acetonitrile.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...