Multifunctional Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2/Pr-Imi-NH2·Ag core–shell microspheres as highly efficient catalysts in the aqueous reduction of nitroarenes: improved catalytic activity and facile catalyst recovery
Abstract
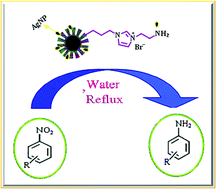
Core@shell nanoparticles with a superparamagnetic iron oxide core, a middle nonporous silica shell, and an outer organo functionalized mesoporous silica shell were synthesized and evaluated for immobilizing Ag nanoparticles. The iron oxide nanoparticles cores were synthesized via improved chemical coprecipitation method and they were silica-coated by surface silylation via a Stober sol–gel process. Afterward, magnetic core–shell structured mesoporous silica microspheres, Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2, were synthesized by silylation of Fe3O4@nSiO2 surface using tetraethyl orthosilicate through surfactant directed self-assembly on the surface, followed by etching of the surfactant molecules. Further modification of the surface by grafting of 3-chloropropyl triethoxysilane, nucleophilic substitution reaction of the chloride with imidazole and then quaternization with 2-bromo ethylamine hydrobromide produced the 2-amino ethyl-3-propyl imidazolium bromide functionalized magnetic core–shell structured mesoporous silica microspheres, Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2/Pr-Im-NH2. Finally, the target nanocomposite, Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2/Pr-Im-NH2·Ag was formed by embedding the silver nanoparticles into the mesoporous nanocomposite. The organic–inorganic nanocomposite was characterized by FT-IR spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), elemental analysis (CHN), vibrating sample magnetometer (VAM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential thermal analysis (DTA), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET). The catalytic activity test with the nitroarene reduction in an aqueous medium by using NaBH4 reveals that this Ag-supported nanocomposite is highly active for a wide range of substrates, suggesting highly promising application potentials of the magnetic core–shell-structured mesoporous organosilica. This method has the advantages of high yields, a cleaner reaction, simple methodology, short reaction times, easy workup, and greener conditions. In addition to the facility of this methodology, it also enhances product purity and promises economic as well as environmental benefits.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...