Core–sheath structured electrospun nanofibrous membranes for oil–water separation†
Abstract
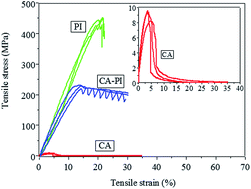
In recent years, both the increasing frequency of oil spill accidents and the urgency to deal seriously with industrial oil-polluted water, encouraged material scientists to design highly efficient, cost effective oil–water separation technologies. We report on electrospun nanofibrous membranes which are composed of core–sheath structured cellulose-acetate (CA)–polyimide (PI) nanofibers. On the surface of the CA–PI fibers a fluorinated polybenzoxazine (F-PBZ) functional layer, in which silica nanoparticles (SNPs) were incorporated, has been applied. Compared with F-PBZ/SNP modified CA fibers reported before for the separation of oil from water, the PI-core of the core–shell F-PBZ/SNP/CA–PI fibers makes the membranes much stronger, being a significant asset in their use. Nanofibrous membranes with a tensile strength higher than 200 MPa, a high water contact angle of 160° and an extremely low oil contact angle of 0° were obtained. F-PBZ/SNP/CA–PI membranes seemed very suitable for gravity-driven oil–water separation as fast and efficient separation (>99%) of oil from water was achieved for various oil–water mixtures. The designed core–sheath structured electrospun nanofibrous membranes may become interesting materials for the treatment of industrial oil-polluted water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...