Solvent-dependent chain conformation for ring closure of metal carbonyl oligomers via migration insertion polymerization (MIP) of CpFe(CO)2(CH2)6PPh2†
Abstract
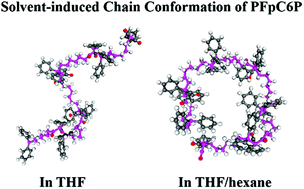
The solution migration insertion polymerization (MIP) of CpFe(CO)2(CH2)6PPh2 (FpC6P) in THF generates linear PFpC6P (l-PFpC6P) oligomers. When THF/hexane mixed solvents are used to replace THF, cyclic PFpC6P (c-PFpC6P) without end groups is produced. In contrast, the MIP of FpC6P in THF/pyrrole, THF/DMSO, and THF/pyridine and the MIP of CpFe(CO)2(CH2)3PPh2 (FpC3P) in THF/hexane generate a mixture of c- and l-oligomers with NMR detectable end groups. Molecular dynamics simulations indicate that both PFpC6P and PFpC3P are extended chains in THF. PFpC6P, regardless of the DP, forms a cyclic structure in THF/hexane with end-to-end distances (Re) less than 10 Å, which facilitates ring closure during the MIP. In other systems, both cyclic and non-cyclic chain conformations are observed. This simulation rationalizes the experimental results and illustrates that PFpP chain conformation is solvent-dependent, and potentially useful as protein-like materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...