The effect of Rhδ+ dopant in SrTiO3 on the active oxidation state of co-catalytic Pt nanoparticles in overall water splitting†
Abstract
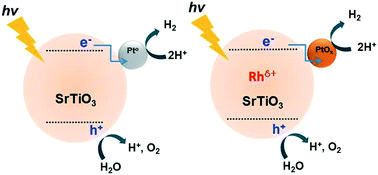
We report on the oxidation state of Pt nanoparticles when deposited on SrTiO3 or Rh-doped SrTiO3 under realistic solar water-splitting conditions. The oxidation state was investigated using state-of-the-art analysis of the reaction in a continuously stirred tank reactor (CSTR) connected to a micro gas chromatograph equipped with a pulsed discharge detector (PDD) detector and ex-situ XPS. We demonstrate an initially large, but transient, peak in the oxygen production rate during the conversion of acidified water using SrTiO3 loaded with Pt nanoparticles prepared by photo-deposition (in the absence of methanol). This was confirmed by XPS analysis to be the result of a change in oxidation state from PtOx to metallic Pt. Remarkably, when PtOx was present on SrTiO3 doped with Rhδ+, the transient peak in the O2 production was of much lower magnitude than when in the absence of Rhδ+. The XPS analysis demonstrates that this can be explained by the incomplete reduction of the Pt nanoparticles in the presence of Rhδ+. The average oxidation state of Pt deposited on SrTiO3 during the water-splitting reaction thus appears very much dependent on the absence or presence of dopants. This effect is often neglected, but is highly relevant for the discussion of composition-activity correlations of (doped) semiconductors functionalized with metal(oxide) nanoparticles in overall water splitting.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...