Catalytic hydrogenation and one step hydrogenation-esterification to remove acetic acid for bio-oil upgrading: model reaction study
Abstract
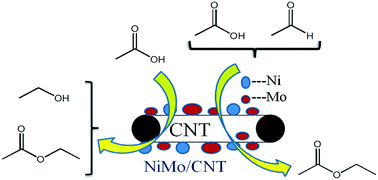
Bio-oil has a complex composition including acids and aldehydes, which lead to undesirable properties, such as high corrosiveness and instability. Upgrading was needed to improve bio-oil quality for its further application as transportation fuels. Hydrogenation and one step hydrogenation-esterification (OHE) were effective methods to convert acids and bio-oil to combustive alcohols and esters. Herein, various CNT-supported (carbon nanotube) non-sulfide catalysts were prepared and catalytic activity was investigated through hydrogenation of acetic acid and OHE of acetic acid and acetaldehyde. Mo-promoted NiMo/CNT catalysts exhibited better catalytic activity in both hydrogenation and OHE reaction for removing acetic acid. The optimal acetic acid conversion rate was up to 17%, with a selectivity of 85% toward ethanol during hydrogenation. OHE showed better efficiency for the conversion of acetic acid compared with hydrogenation. The effect of process parameters on esterification of acetic acid and acetaldehyde together with the selectivity of ethyl acetate were investigated in detail. It was found that addition of extra hydrogen during the OHE reaction was beneficial for improving both acetaldehyde conversion and ethyl acetate selectivity. When extra hydrogen was added twice, the acetaldehyde conversion rose from 66.0% to 81.4%, and the ethyl acetate selectivity improved from 21.8% to 36.8%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...