Discovery of coumarin derivatives as fluorescence acceptors for intrinsic fluorescence resonance energy transfer of proteins†
Abstract
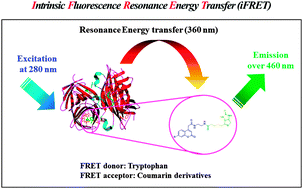
Coumarin analogues were synthezised and evaluated as acceptors for the intrinsic fluorescence resonance energy transfer (iFRET) of tryptophan residues in target proteins. The fluorescence properties such as quantum yields, iFRET efficiencies, and Förster distances of the prepared coumarin analogs were determined in a model system, by their conjugation to biotin, utilizing streptavidin (SAV) as the iFRET donor. The coumarin derivatives reported here represent the most efficient iFRET acceptors for tryptophan, known to date.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...