Real-time probing of β-amyloid self-assembly and inhibition using fluorescence self-quenching between neighbouring dyes†
Abstract
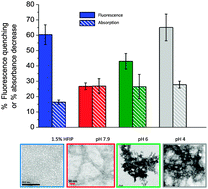
The fluorescence response of the Thioflavin-T (ThT) dye and derivatives has become the standard tool for detecting β-amyloid aggregates (Aβ) in solution. However, it is accepted that ThT-based methods suffer from important drawbacks. Some of these are due to the cationic structure of ThT, which limits its application at slightly acidic conditions; whereas some limitations are related to the general use of an extrinsic-dye sensing strategy and its intrinsic requirement for the formation of a sensor-binding site during the aggregation process. Here, we introduce fluorescence-self-quenching (FSQ) between N-terminally tagged peptides as a strategy to overcome some of these limitations. Using a combination of steady-state, picosecond time-resolved fluorescence and transmission electron microscopy, we characterize the fluorescence response of HiLyte fluor 555-labelled Aβ peptides and demonstrate that Aβ self-assembly organizes the covalently attached probes in close proximity to trigger the self-quenching sensing process over a broad range of conditions. Importantly, we prove that N-terminal tagging of β-amyloid peptides does not alter the self-assembly kinetics or the resulting aggregated structures. We also tested the ability of FSQ-based methods to monitor the inhibition of Aβ1–42 aggregation using the small heat-shock protein Hsp20 as a model system. Overall, FSQ-based strategies for amyloid-sensing fill the gap between current morphology-specific protocols using extrinsic dyes, and highly-specialized single-molecule techniques that are difficult to implement in high-throughput analytical determinations. When performed in Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) format, the method becomes a ratiometric platform to gain insights into amyloid structure and for standardizing in vitro studies of amyloid aggregation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...