Inclusion chemistry of a thiazyl radical in zeolite-Y
Abstract
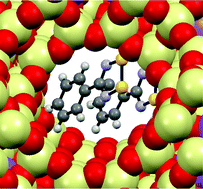
High loading of the radical PhCNSSN˙ (1) into faujasite has been achieved via gas phase diffusion. Whilst the large 12 Å pores can accommodate the enthalpically preferred dimer, the smaller pores dictate inclusion as a paramagnetic monomer. Powder X-ray diffraction studies reveal the host framework is unchanged whilst TGA reveal that the void space has high radical loadings. SQUID magnetometry coupled with EPR spectroscopy indicate that the majority of radicals adopt diamagnetic π*–π* dimers consistent with predominant location of 1 as dimers within the large cavities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...